Related Research Articles

The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.

A wargame is a strategy game in which two or more players command opposing armed forces in a simulation of an armed conflict. Wargaming may be played for recreation, to train military officers in the art of strategic thinking, or to study the nature of potential conflicts. Many wargames re-create specific historic battles, and can cover either whole wars, or any campaigns, battles, or lower-level engagements within them. Many simulate land combat, but there are wargames for naval and air combat, as well.
Operations research, often shortened to the initialism OR, is a discipline that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve decision-making. The term management science is occasionally used as a synonym.

A military exercise, training exercise, maneuver (manoeuvre), or war game is the employment of military resources in training for military operations. Military exercises are conducted to explore the effects of warfare or test tactics and strategies without actual combat. They also ensure the combat readiness of garrisoned or deployable forces prior to deployment from a home base.
Marine Doom is a 1996 modification of the first-person shooter Doom II for the United States Marine Corps, which was later made available for download to the public.

The Office of Naval Research (ONR) is an organization within the United States Department of the Navy responsible for the science and technology programs of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. Established by Congress in 1946, its mission is to plan, foster, and encourage scientific research to maintain future naval power and preserve national security. It carries this out through funding and collaboration with schools, universities, government laboratories, nonprofit organizations, and for-profit organizations, and overseeing the Naval Research Laboratory, the corporate research laboratory for the Navy and Marine Corps. NRL conducts a broad program of scientific research, technology and advanced development.

Future Combat Systems (FCS) was the United States Army's principal modernization program from 2003 to early 2009. Formally launched in 2003, FCS was envisioned to create new brigades equipped with new manned and unmanned vehicles linked by an unprecedented fast and flexible battlefield network. The U.S. Army claimed it was their "most ambitious and far-reaching modernization" program since World War II. Between 1995 and 2009, $32 billion was expended on programs such as this, "with little to show for it".

The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is a not-for-profit university-affiliated research center (UARC) in Howard County, Maryland. It is affiliated with Johns Hopkins University and employs 8,700 people as of 2024. APL is the nation's largest UARC.

The Institute for Creative Technologies (ICT) is a University Affiliated Research Center at the University of Southern California located in Playa Vista, California. ICT was established in 1999 with funding from the US Army.

Noble Resolve is a United States Joint Forces Command (USJFCOM) experimentation campaign plan to enhance homeland defense and improve military support to civil authorities in advance of and following natural and man-made disasters.

Military simulations, also known informally as war games, are simulations in which theories of warfare can be tested and refined without the need for actual hostilities. Military simulations are seen as a useful way to develop tactical, strategical and doctrinal solutions, but critics argue that the conclusions drawn from such models are inherently flawed, due to the approximate nature of the models used. Many professional analysts object to the term wargames as this is generally taken to be referring to the civilian hobby, thus the preference for the term simulation.

Close Combat is a 1996 real-time computer wargame developed by Atomic Games and published by Microsoft. Set during World War II, it simulates the conflict between the United States' 29th Infantry Division and Germany's 352nd Infantry Division after the Invasion of Normandy. The player controls an artificially intelligent army whose behavior is dictated by psychological models: each soldier makes decisions based on the circumstances of the battlefield and can disobey the player's orders.
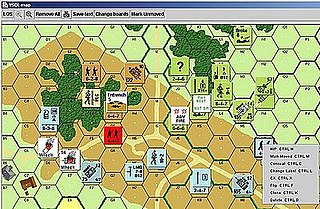
A computer wargame is a wargame played on a digital device. Descended from board wargaming, it simulates military conflict at the tactical, operational or strategic level. Computer wargames are both sold commercially for recreational use and, in some cases, used for military purposes.
Irregular warfare (IW) is defined in United States joint doctrine as "a violent struggle among state and non-state actors for legitimacy and influence over the relevant populations." In practice, control of institutions and infrastructure is also important. Concepts associated with irregular warfare are older than the term itself.

Pat Proctor is a Kansas State Representative, representing the 41st House District. He was first elected in November 2020.
Panzer Campaigns is a series of operational level wargames originally developed by John Tiller Software, and currently by Wargame Design Studio. The games were originally published until 2010 by HPS Simulations, then self published by John Tiller Software until being bought out by Wargame Design Studio in 2021, after Tiller's death. There are currently 29 titles in the series, spanning the various fronts of World War II.
The Joint Theater Level Simulation (JTLS) is used to simulate joint, combined, and coalition civil-military operations at the operational level. Used for civil/military simulations and humanitarian assistance/disaster relief (HA/DR) scenarios, JTLS is an interactive, computer-assisted simulation that models multi-sided air, ground, and naval resources with logistical Special Operation Forces (SOF) and intelligence support. The primary purpose of JTLS is to create a realistic environment in which agency staff can operate as they would within a real-world or operational situation.also information.A training audience conducts a scenario or event to practice their ability to coordinate various staff functions.
Newman & Spurr Consultancy is a training, simulation and consultancy provider headquartered in Camberley, Surrey, England.

A wargame, generally, is a type of strategy game which realistically simulates warfare. A professional wargame, specifically, is a wargame that is used by military organizations to train officers in tactical and strategic decision-making, to test new tactics and strategies, or to predict trends in future conflicts. This is in contrast to recreational wargames, which are designed for fun and competition.

Betty Rose Weber Holz was an American mathematician who worked for the United States Army.
References
- ↑ Richard E. Zimmerman. CARMONETTE: A concept of tactical war games (Staff paper / Johns Hopkins University, Operations Research Office).
- ↑ Ben Connable, Walter L. Perry, Abby Doll, Natasha Lander and Dan Madden (2014). "Introduction". Modeling, Simulation, and Operations Analysis in Afghanistan and Iraq. Rand Corporation. pp. 1–12. ISBN 9780833082114. JSTOR 10.7249/j.ctt5vjwt0.8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)(registration required) - ↑ Shrader, Charles. "OFFICE OF THE DEPUTY UNDER SECRETARY OF THE ARMY FOR OPERATIONS RESEARCH UNITED STATES ARMY WASHINGTON, D.C., 2006 History of Operations Research in the United States Army" (PDF). history.army.mil. Retrieved 2019-09-06.
- ↑ Sharon Ghamari-Tabrizi. "U.S. Wargaming Grows Up: A Short History of the Diffusion of Wargaming in the Armed Forces and Industry in the Postwar Period up to 1964". www.strategypage.com.
- ↑ "A Brief History of Electrical Technology". www.scaruffi.com. Retrieved 2019-09-05.