Sexual assault is an act in which one intentionally sexually touches another person without that person's consent, or coerces or physically forces a person to engage in a sexual act against their will. It is a form of sexual violence, which includes child sexual abuse, groping, rape, or the torture of the person in a sexual manner.
A proportion of victims of rape or other sexual violence incidents are male. Historically, rape was thought to be, and defined as, a crime committed solely against females. This belief is still held in some parts of the world, but rape of males is now commonly criminalized and has been subject to more discussion than in the past.

Sexual penetration is the insertion of a body part or other object into a body orifice, such as the mouth, vagina or anus, as part of human sexual activity or animal sexual behavior.

Zināʾ (زِنَاء) or zinā is an Islamic legal term referring to unlawful sexual intercourse. According to traditional jurisprudence, zina can include adultery, fornication, prostitution, rape, sodomy, incest, and bestiality. Zina must be proved by testimony of four Muslim eyewitnesses to the actual act of penetration, or a confession repeated four times and not retracted later. The offenders must have acted of their own free will. Rapists could be prosecuted under different legal categories which used normal evidentiary rules. Making an accusation of zina without presenting the required eyewitnesses is called qadhf (القذف), which is itself a hudud offense.
The precise definitions of and punishments for aggravated sexual assault and aggravated rape vary from nation to nation and state to state within nations.
The legal age of consent for sexual activity varies by jurisdiction across Asia. The specific activity engaged in or the gender of participants can also be relevant factors. Below is a discussion of the various laws dealing with this subject. The highlighted age refers to an age at or above which an individual can engage in unfettered sexual relations with another who is also at or above that age. Other variables, such as homosexual relations or close in age exceptions, may exist, and are noted when relevant, for example in Indonesia.
The ages of consent for sexual activity vary from age 15 to 18 across Australia, New Zealand and other parts of Oceania. The specific activity and the gender of its participants is also addressed by the law. The minimum age is the age at or above which an individual can engage in unfettered sexual relations with another person of minimum age. Close in age exceptions may exist and are noted where applicable. In Vanuatu the homosexual age of consent is set higher at 18, while the heterosexual age of consent is 15. Same sex sexual activity is illegal at any age for males in Papua New Guinea, Kiribati, the Cook Islands, Samoa, Tonga and Tuvalu; it is outlawed for both men and women in the Solomon Islands. In all other places the age of consent is independent of sexual orientation or gender.
The ages of consent vary by jurisdiction across Europe. The ages of consent are between 14 and 18. The vast majority of countries set their ages in the range of 14 to 16; only four countries, Cyprus (17), Ireland (17), Turkey (18) and Vatican City (18), do not fit into this pattern. The laws can also stipulate which specific activities are permitted or specify the age at which one or other sex can legally participate. The highlighted age is that from which a young person can lawfully engage in a non-commercial sexual act with an older person, regardless of their age difference, provided the older one is not in a position of power, a relative, or is committing another form of exploitation. In some jurisdictions, including Italy and Hungary, there are exemptions if the age difference is within prescribed bounds. All jurisdictions in Europe have equal and gender-neutral age limits.
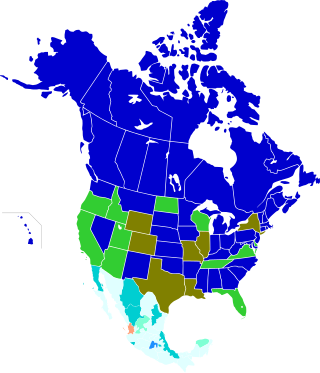
In North America, the legal age of consent relating to sexual activity varies by jurisdiction.

The age of consent in Africa for sexual activity varies by jurisdiction across the continent. The specific activity engaged in or the gender of its participants can also affect this age and the legality of sexual activity. The highlighted age refers to an age at or above which an individual can engage in unfettered sexual relations with another person who is also at or above that age. Other variables, for example homosexual and/or sodomy provision(s) that are illegal or close in age exceptions may exist and are stated when relevant.
Rape is a type of sexual assault initiated by one or more persons against another person without that person's consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, under threat or manipulation, by impersonation, or with a person who is incapable of giving valid consent.
In common law jurisdictions, statutory rape is nonforcible sexual activity in which one of the individuals is below the age of consent. Although it usually refers to adults engaging in sexual contact with minors under the age of consent, it is a generic term, and very few jurisdictions use the actual term statutory rape in the language of statutes.

The Offences Against the Person Act 1828 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It consolidated provisions in the law related to offences against the person from a number of earlier statutes into a single Act. It was part of the criminal law reforms known collectively as "Peel's Acts", passed with the objective of simplifying the law. Among the laws it replaced was clause XXVI of Magna Carta, the first time any part of Magna Carta was repealed, and the Buggery Act 1533. It also abolished the crime of petty treason.

Sodomy, also called buggery in British English, generally refers to either anal sex between people, or any sexual activity between a human and an animal (bestiality). It may also mean any non-procreative sexual activity. Originally, the term sodomy, which is derived from the story of Sodom and Gomorrah in the Book of Genesis, was commonly restricted to anal sex. Sodomy laws in many countries criminalized the behavior. In the Western world, many of these laws have been overturned or are routinely not enforced. A person who practices sodomy is sometimes referred to as a sodomite.

In the United States, each state and territory sets the age of consent either by statute or the common law applies, and there are several federal statutes related to protecting minors from sexual predators. Depending on the jurisdiction, the legal age of consent is between 16 and 18. In some places, civil and criminal laws within the same state conflict with each other.
Rape is a statutory offence in England and Wales. The offence is created by section 1 of the Sexual Offences Act 2003:
(1) A person (A) commits an offence if—
(2) Whether a belief is reasonable is to be determined having regard to all the circumstances, including any steps A has taken to ascertain whether B consents.
(3) Sections 75 and 76 apply to an offence under this section.
(4) A person guilty of an offence under this section is liable, on conviction on indictment, to imprisonment for life.
The expression sexual intercourse has been used as a legal term of art in England and Wales. From its enactment to its repeal on the 1 May 2004, section 44 of the Sexual Offences Act 1956 read:
Where, on the trial of any offence under this Act, it is necessary to prove sexual intercourse, it shall not be necessary to prove the completion of the intercourse by the emission of seed, but the intercourse shall be deemed complete upon proof of penetration only
Rape in Alabama is currently defined across three sections of its Criminal Code: Definitions, Rape in the First Degree, and Rape in the Second Degree. Each section addresses components of the crime such as age, sentencing, the genders of the individuals involved, and the acts involved.
Rape laws vary across the United States jurisdictions. However, rape is federally defined for statistical purposes as:
Penetration, no matter how slight, of the vagina or anus with any body part or object, or oral penetration by a sex organ of another person, without the consent of the victim.
Sexual consent plays an important role in laws regarding rape, sexual assault and other forms of sexual violence. In a court of law, whether or not the alleged victim had freely given consent, and whether or not they were deemed to be capable of giving consent, can determine whether the alleged perpetrator is guilty of rape, sexual assault or some other form of sexual misconduct.






