Related Research Articles

A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.

A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroid, kidney and prostate. There may be a lump, pain, or neurological signs from pressure. A bone tumor might present with a pathologic fracture. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia and nausea. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the tumour is found when investigating another problem.

An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchymal origin and that exhibits osteoblastic differentiation and produces malignant osteoid.
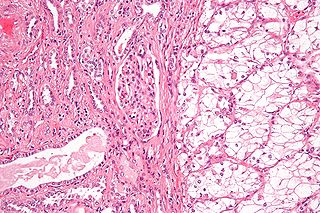
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases. RCC occurrence shows a male predominance over women with a ratio of 1.5:1. RCC most commonly occurs between 6th and 7th decade of life.

Chondrosarcoma is a bone sarcoma, a primary cancer composed of cells derived from transformed cells that produce cartilage. A chondrosarcoma is a member of a category of tumors of bone and soft tissue known as sarcomas. About 30% of bone sarcomas are chondrosarcomas. It is resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Unlike other primary bone sarcomas that mainly affect children and adolescents, a chondrosarcoma can present at any age. It more often affects the axial skeleton than the appendicular skeleton.
The perichondrium is a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage of developing bone. It consists of two separate layers: an outer fibrous layer and inner chondrogenic layer. The fibrous layer contains fibroblasts, which produce collagenous fibres. The chondrogenic layer remains undifferentiated and can form chondroblasts. Perichondrium can be found around the perimeter of elastic cartilage and hyaline cartilage.

Chondrocytes are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word chondroblast is commonly used to describe an immature chondrocyte, the term is imprecise, since the progenitor of chondrocytes can differentiate into various cell types, including osteoblasts.

A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that lacks the ability either to invade neighboring tissue or metastasize. When removed, benign tumors usually do not grow back, whereas malignant tumors are cancerous and sometimes do. Unlike most benign tumors elsewhere in the body, benign brain tumors can be life-threatening. Benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate than malignant tumors and the tumor cells are usually more differentiated. They are typically surrounded by an outer surface or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.
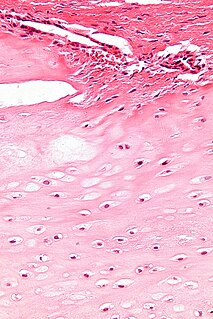
Enchondroma is a type of benign bone tumor belonging to the group of cartilage tumors. There may be no symptoms, or it may present typically in the short tubular bones of the hands with a swelling, pain or pathological fracture.

Giant-cell tumor of the bone (GCTOB), is a relatively uncommon tumor of the bone. It is characterized by the presence of multinucleated giant cells. Malignancy in giant-cell tumor is uncommon and occurs in about 2% of all cases. However, if malignant degeneration does occur, it is likely to metastasize to the lungs. Giant-cell tumors are normally benign, with unpredictable behavior. It is a heterogeneous tumor composed of three different cell populations. The giant-cell tumour stromal cells (GCTSC) constitute the neoplastic cells, which are from an osteoblastic origin and are classified based on expression of osteoblast cell markers such as alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin. In contrast, the mononuclear histiocytic cells (MNHC) and multinucleated giant cell (MNGC) fractions are secondarily recruited and comprise the non-neoplastic cell population. They are derived from an osteoclast-monocyte lineage determined primarily by expression of CD68, a marker for monocytic precursor cells. In most patients, the tumors are slow to develop, but may recur locally in as many as 50% of cases.

Chondroblasts, or perichondrial cells, is the name given to mesenchymal progenitor cells in situ which, from endochondral ossification, will form chondrocytes in the growing cartilage matrix. Another name for them is subchondral cortico-spongious progenitors. They have euchromatic nuclei and stain by basic dyes.

Subungual exostoses are a type of non-cancerous bone tumor of the chondrogenic type, and consists of bone and cartilage. It usually projects from the upper surface of the big toe underlying the nailbed, giving rise to a painful swelling that destroys the nail. Subsequent ulceration and infection may occur.

Synovial chondromatosis is a locally aggressive bone tumor of the cartilaginous type. It consists of several hyaline cartilaginous nodules and has the potential of becoming cancerous.

Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC), is a non-cancerous bone tumor composed of multiple varying sizes of spaces in a bone which are filled with blood. The term is a misnomer, as the lesion is neither an aneurysm nor a cyst. It generally presents with pain and swelling in the affected bone. Pressure on neighbouring tissues may cause compression effects such as neurological symptoms.

A malignant mixed Müllerian tumor, also known as malignant mixed mesodermal tumor (MMMT) is a cancer found in the uterus, the ovaries, the fallopian tubes and other parts of the body that contains both carcinomatous and sarcomatous components. It is divided into two types, homologous and a heterologous type. MMMT account for between two and five percent of all tumors derived from the body of the uterus, and are found predominantly in postmenopausal women with an average age of 66 years. Risk factors are similar to those of adenocarcinomas and include obesity, exogenous estrogen therapies, and nulliparity. Less well-understood but potential risk factors include tamoxifen therapy and pelvic irradiation.

Salivary gland tumours also known as mucous gland adenomas or neoplasms are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800-1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral cavity. Patients with these types of tumours may be asymptomatic.
A mixed tumor is a tumor that derives from multiple tissue types. A biplastic tumor or biphasic tumor has two tissue types.

The following is a simplified (deprecated) version of the 2021 WHO classification of the tumours of the central nervous system. Currently, as of 2021, clinicians are using the WHO grade 5th edition, which incorporates recent advances in molecular pathology.
Bizarre parosteal osteochondromatous proliferation (BPOP), also known as Nora's lesion, is a type of non-cancerous bone tumor belonging to the group of cartilage tumors. It is generally seen in the tubular bones of the hands and feet, where it presents with a rapidly enlarging painless lump in a finger or toe.
The WHO Classification of Tumours, more commonly known as the WHO Blue Books, is a series of books that classify tumours. They are compiled by expert consensus and published by the WHO's International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). They appear in print and online in a series of 15 books, each of which focuses on a major tumour group and defines the cause, mechanism, signs and symptoms, basic structure, diagnosis, epidemiology and outcomes of up to 300 types of tumours.
References
- ↑ Engel, Hannes; Herget, Georg W.; Füllgraf, Hannah; Sutter, Reto; Benndorf, Matthias; Bamberg, Fabian; Jungmann, Pia M. (March 2021). "Chondrogenic Bone Tumors: The Importance of Imaging Characteristics". RöFo: Fortschritte auf dem Gebiete der Röntgenstrahlen und der Nuklearmedizin. 193 (3): 262–275. doi: 10.1055/a-1288-1209 . ISSN 1438-9010. PMID 33152784.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours. International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2020. p. 338. ISBN 978-92-832-4502-5.
- ↑ Choi, Joon Hyuk; Ro, Jae Y. (1 May 2021). "The 2020 WHO Classification of Tumors of Bone: An Updated Review" . Advances in Anatomic Pathology. 28 (3): 119–138. doi:10.1097/PAP.0000000000000293. ISSN 1533-4031. PMID 33480599. S2CID 231679037.