
Structural engineering is a sub-discipline of civil engineering in which structural engineers are trained to design the 'bones and joints' that create the form and shape of human-made structures. Structural engineers also must understand and calculate the stability, strength, rigidity and earthquake-susceptibility of built structures for buildings and nonbuilding structures. The structural designs are integrated with those of other designers such as architects and building services engineer and often supervise the construction of projects by contractors on site. They can also be involved in the design of machinery, medical equipment, and vehicles where structural integrity affects functioning and safety. See glossary of structural engineering.

Forensic engineering has been defined as "the investigation of failures—ranging from serviceability to catastrophic—which may lead to legal activity, including both civil and criminal". The forensic engineering field is very broad in terms of the many disciplines that it covers, investigations that use forensic engineering are case of environmental damages to structures, system failures of machines, explosions, electrical, fire point of origin, vehicle failures and many more.

The Tay Bridge carries rail traffic across the Firth of Tay in Scotland between Dundee and the suburb of Wormit in Fife. Its span is 2.75 miles. It is the second bridge to occupy the site.

The Great Sheffield Flood was a flood that devastated parts of Sheffield, England, on 11 March 1864, when the Dale Dyke Dam broke as its reservoir was being filled for the first time. At least 240 people died and more than 600 houses were damaged or destroyed by the flood. The immediate cause was a crack in the embankment, the cause of which was never determined. The dam's failure led to reforms in engineering practice, setting standards on specifics that needed to be met when constructing such large-scale structures. The dam was rebuilt in 1875.

An environmental disaster or ecological disaster is defined as a catastrophic event regarding the natural environment that is due to human activity. This point distinguishes environmental disasters from other disturbances such as natural disasters and intentional acts of war such as nuclear bombings.

Two overhead walkways in the Hyatt Regency Hotel in Kansas City, Missouri, collapsed on July 17, 1981, killing 114 people and injuring 216. Loaded with partygoers, the concrete and glass platforms crashed onto a tea dance in the lobby. Kansas City society was affected for years, with the collapse resulting in billions of dollars of insurance claims, legal investigations, and city government reforms.
The Banqiao Reservoir Dam is a dam on the River Ru (汝河), a tributary of the Hong River in Zhumadian City, Henan province, China. The Banqiao dam and Shimantan Reservoir Dam are among 62 dams in Zhumadian that failed catastrophically in 1975 during Typhoon Nina. The dam was subsequently rebuilt.

In aviation, a tailstrike or tail strike occurs when the tail or empennage of an aircraft strikes the ground or other stationary object. This can happen with a fixed-wing aircraft with tricycle undercarriage, in both takeoff where the pilot rotates the nose up too rapidly, or in landing where the pilot raises the nose too sharply during final approach, often in attempting to land too near the runway threshold. It can also happen during helicopter operations close to the ground, when the tail inadvertently strikes an obstacle.
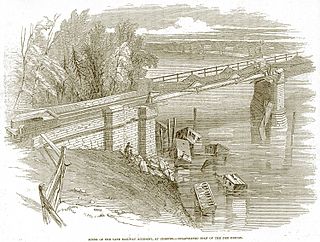
The Dee Bridge disaster was a rail accident that occurred on 24 May 1847 in Chester, England, that resulted in five fatalities. It revealed the weakness of cast iron beam bridges reinforced by wrought iron tie bars, and brought criticism of its designer, Robert Stephenson, the son of George Stephenson.

Typhoon Nina, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Bebeng, was a deadly tropical cyclone that triggered the Banqiao Dam collapse in China's Henan Province, in August 1975. It formed on July 30, and gradually intensified as it moved generally to the west. On August 2, Nina reached peak intensity, and a day later the typhoon struck Taiwan. It weakened before moving ashore southeastern China, and later moved slowly through Central China. There, it dropped heavy rainfall, causing several dam failures, including the Banqiao Dam. It is the deadliest typhoon in the Pacific, killing 229,000 people. The floods killed 26,000 people, 100,000 people died from subsequent famine and diseases, and 230,000 people died from the consequences of the 1975 Banqiao Dam failure.

The Tay Bridge disaster occurred during a violent storm on Sunday 28 December 1879, when the first Tay Rail Bridge collapsed as a North British Railway (NBR) passenger train on the Edinburgh to Aberdeen Line from Burntisland bound for its final destination of Dundee passed over it, killing everybody on board. The bridge—designed by Sir Thomas Bouch—used lattice girders supported by iron piers, with cast iron columns and wrought iron cross-bracing. The piers were narrower and their cross-bracing was less extensive and robust than on previous similar designs by Bouch.

At 22:43 on 24 May 2001, a large portion of the third floor of the Versailles Wedding Hall collapsed in Talpiot, Jerusalem, Israel. Twenty-three people fell to their deaths through two stories, while another 356 were injured to varying degrees.

A dam failure or dam burst is a catastrophic type of structural failure characterized by the sudden, rapid, and uncontrolled release of impounded water or the likelihood of such an uncontrolled release. Between the years 2000 and 2009 more than 200 notable dam failures happened worldwide.
The Mianus River Bridge is a span that carries Interstate 95 over the Mianus River, between Cos Cob and Riverside, Connecticut. It is the second bridge on the site. The original bridge collapsed in 1983, killing three motorists. The replacement span is officially named the Michael L. Morano Bridge, after a state senator Michael L. Morano who represented Greenwich.
Silver Lake Dam is a dam located on the Dead River 30 miles (48.3 km) upstream of Marquette, Michigan. It is the farthest upstream of five dams on the river and had no electricity generating facilities. The dam failed on May 14, 2003, and forced the evacuation of 1800 people. The dam was rebuilt in 2008.

Structural integrity and failure is an aspect of engineering that deals with the ability of a structure to support a designed structural load without breaking and includes the study of past structural failures in order to prevent failures in future designs.

Engineering disasters often arise from shortcuts in the design process. Engineering is the science and technology used to meet the needs and demands of society. These demands include buildings, aircraft, vessels, and computer software. In order to meet society’s demands, the creation of newer technology and infrastructure must be met efficiently and cost-effectively. To accomplish this, managers and engineers need a mutual approach to the specified demand at hand. This can lead to shortcuts in engineering design to reduce costs of construction and fabrication. Occasionally, these shortcuts can lead to unexpected design failures.

In August 1975, the Banqiao Dam and 61 others throughout Henan collapsed following the landfall of Typhoon Nina. The dam collapse created the third-deadliest flood in history which affected 12,000 km2 with a total population of 10.15 million, including around 30 cities and counties, with estimates of the death toll ranging from 26,000 to 240,000. The flood also caused the collapse of 5 million to 6.8 million houses. The dam failure took place in the context of the Cultural Revolution.















