
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is governed in a framework of a representative democratic republic under a five-power system first envisioned by Sun Yat-sen in 1906, whereby under the constitutional amendments, the President is head of state and the Premier is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Executive Yuan. Legislative power is vested primarily in the Legislative Yuan. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. In addition, the Examination Yuan is in charge of validating the qualification of civil servants, and the Control Yuan inspects, reviews, and audits the policies and operations of the government.

Chen Shui-bian is a Taiwanese former politician and lawyer who served as the 5th president of the Republic of China (Taiwan) from 2000 to 2008. Chen was the first president from the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) which ended the Kuomintang's (KMT) 55 years of continuous rule in Taiwan. He is sometimes referred to by the nickname A-Bian (阿扁).
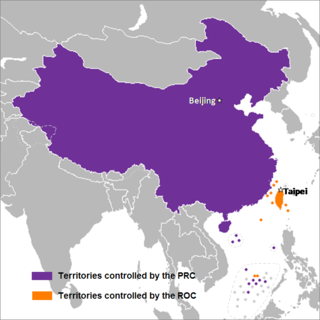
Chinese unification, also known as Cross-Strait unification or Chinese reunification, is the potential unification of territories currently controlled, or claimed, by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China ("Taiwan") under one political entity, possibly the formation of a political union between the two republics. Together with full Taiwan independence, unification is one of the main proposals to address questions on the political status of Taiwan, which is a central focus of Cross-Strait relations.
The term One China may refer, in alphabetical order, to one of the following:

The Constitution of the Republic of China is the fifth and current constitution of the Republic of China (ROC), ratified by the Kuomintang during the Constituent National Assembly session on 25 December 1946, in Nanjing, and adopted on 25 December 1947. The constitution, along with its Additional Articles, remains effective in ROC-controlled territories.

The Kaohsiung Incident, also known as the Formosa Incident, the Meilidao Incident, or the Formosa Magazine incident, was a crackdown on pro-democracy demonstrations that occurred in Kaohsiung, Taiwan, on 10 December 1979 during Taiwan's martial law period.
The history of the Republic of China began in 1912 with the end of the Qing dynasty, when the Xinhai Revolution and the formation of the Republic of China put an end to 2,000 years of imperial rule. The Republic experienced many trials and tribulations after its founding which included being dominated by elements as disparate as warlord generals and foreign powers.

The Presbyterian Church in Taiwan is the largest Protestant Christian denomination based in Taiwan.

The 2004 Taiwanese legislative election was held on 11 December 2004. All 225 seats of the Legislative Yuan were up for election: 168 elected by single non-transferable vote, 41 elected through party-list Proportional representation, eight elected from overseas Chinese constituencies on the basis of the proportion of nationwide votes received by participating political parties, eight elected by popular vote among the aboriginal populations. Members served three-year terms beginning on 1 February 2005, and ending 31 January 2008. The next term served four years.

This is a timeline of the Republic of China.
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP)-led People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Kuomintang (KMT)-led Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are often credited as creating a diplomatic basis for semi-official cross-strait exchanges which began in the early 1990s and is a precondition set by the PRC for engaging in cross-strait dialogue.
Taiwan is a multi-party democracy. The 2000 presidential victory of Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) candidate Chen Shui-bian followed more than 50 years of rule by the Kuomintang (KMT) and marked the first transition from one political party to another in the Taiwanese history, reported by a Government Information Office (GIO) website as the "first ever in Chinese history". This followed gradual democratic reforms since the 1980s and 1990s; most notably, martial law was lifted in 1987, and the Temporary Provisions Effective During the Period of Communist Rebellion were repealed in 1991 for Republic of China Constitution to be effective in Taiwan. The human rights record in Taiwan is generally held to have experienced significant transformation since the 1990s.
The mass media in Taiwan is considered to be one of the freest and most competitive in Asia. Cable TV usage is high and there is also a wide selection of newspapers available covering most political viewpoints.

The Nationalist government, officially the National Government of the Republic of China, refers to the government of the Republic of China from 1 July 1925 to 20 May 1948, led by the nationalist Kuomintang (KMT) party.

The Broadcasting Corporation of China (BCC) is a broadcasting company in the Republic of China. It was founded as the Central Broadcasting System in Nanjing in 1928.

Martial law in Taiwan refers to the periods in the history of Taiwan after World War II, during control by the Republic of China Armed Forces of the Kuomintang-led regime. The term is specifically used to refer to the over 38-year-long consecutive martial law period between 20 May 1949 and 14 July 1987, which was qualified as "the longest imposition of martial law by a regime anywhere in the world" at that time.

Dang Guo was the one-party system adopted by the Republic of China under the Kuomintang, lasting from 1924 to 1987. It was adopted after Sun Yat-sen acknowledged the efficacy of the nascent Soviet Union's political system, including its system of dictatorship. Chiang Kai-shek later used the Kuomintang to control and operate the National Government of the Republic of China (ROC) and the National Revolutionary Army. All major national policies of the government bureaucracy were formulated by the Kuomintang, giving the party supreme power over the whole nation. Following the beliefs of Sun Yat-sen, political power should have been returned to the people after the National Revolutionary Army militarily ended the Warlord Era. However, martial law in the ROC continued from 1949 until 1987, during which other political parties were banned. Martial law was lifted in 1987 by President Chiang Ching-kuo, a move that legalized other political parties such as the Democratic Progressive Party and ended the Dang Guo.

The Republic of China (ROC), or simply China, was a sovereign state based on mainland China from 1912 to 1949 prior to the government's relocation to Taiwan, where it continues to be based today. The ROC was established on 1 January 1912 during the Xinhai Revolution against the Qing dynasty, ending the imperial history of China. The Republican government was ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT) as a one-party state based in Nanjing from 1927, until its flight to Taipei on 7 December 1949 following the KMT's de facto defeat by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in the Chinese Civil War. The CCP proclaimed the People's Republic of China on 1 October 1949, while the ROC retains control over the "Free Area", with the political status of Taiwan remaining in dispute to this day.
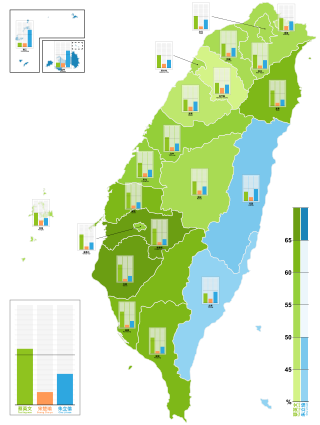
Presidential elections were held in Taiwan on 16 January 2016. Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) candidate Tsai Ing-wen with her independent running mate Chen Chien-jen won over Eric Chu of the Kuomintang (KMT) and James Soong of the People First Party (PFP). Tsai became the first female president in Taiwan, as well as in the Chinese-speaking world.
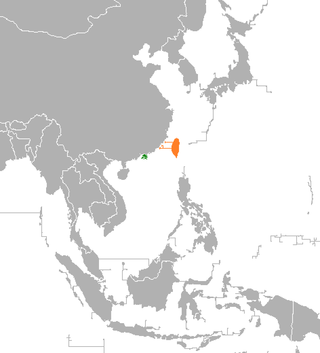
Relations between the government of Hong Kong and the Republic of China (Taiwan) encompass both when the Republic of China controlled mainland China, and afterwards, when the Republic of China fled to Taiwan.















