In mathematics, a square number or perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it equals 32 and can be written as 3 × 3.
In mathematics, a polygonal number is a number represented as dots or pebbles arranged in the shape of a regular polygon. The dots are thought of as alphas (units). These are one type of 2-dimensional figurate numbers.
25 (twenty-five) is the natural number following 24 and preceding 26.
81 (eighty-one) is the natural number following 80 and preceding 82.
1000 or one thousand is the natural number following 999 and preceding 1001. In most English-speaking countries, it can be written with or without a comma or sometimes a period separating the thousands digit: 1,000.
300 is the natural number following 299 and preceding 301.
400 is the natural number following 399 and preceding 401.
500 is the natural number following 499 and preceding 501.
700 is the natural number following 699 and preceding 701.
600 is the natural number following 599 and preceding 601.
800 is the natural number following 799 and preceding 801.
2000 is a natural number following 1999 and preceding 2001.
4000 is the natural number following 3999 and preceding 4001. It is a decagonal number.
5000 is the natural number following 4999 and preceding 5001. Five thousand is the largest isogrammic number in the English language.

In elementary number theory, a centered square number is a centered figurate number that gives the number of dots in a square with a dot in the center and all other dots surrounding the center dot in successive square layers. That is, each centered square number equals the number of dots within a given city block distance of the center dot on a regular square lattice. While centered square numbers, like figurate numbers in general, have few if any direct practical applications, they are sometimes studied in recreational mathematics for their elegant geometric and arithmetic properties.
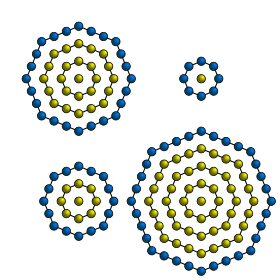
The centered polygonal numbers are a class of series of figurate numbers, each formed by a central dot, surrounded by polygonal layers of dots with a constant number of sides. Each side of a polygonal layer contains one more dot than each side in the previous layer; so starting from the second polygonal layer, each layer of a centered k-gonal number contains k more dots than the previous layer.

A centered nonagonal number is a centered figurate number that represents a nonagon with a dot in the center and all other dots surrounding the center dot in successive nonagonal layers. The centered nonagonal number for n layers is given by the formula
225 is the natural number following 224 and preceding 226.
252 is the natural number following 251 and preceding 253.
288 is the natural number following 287 and preceding 289. Because 288 = 2 · 12 · 12, it may also be called "two gross" or "two dozen dozen".