Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, whether organized as a corporation, partnership or sole proprietorship, and to individuals, although it is most prominently used by corporate entities. In contrast, Chapter 7 governs the process of a liquidation bankruptcy, though liquidation may also occur under Chapter 11; while Chapter 13 provides a reorganization process for the majority of private individuals.
Chapter 7 of Title 11 of the United States Code governs the process of liquidation under the bankruptcy laws of the United States, in contrast to Chapters 11 and 13, which govern the process of reorganization of a debtor. Chapter 7 is the most common form of bankruptcy in the United States.
Personal bankruptcy law allows, in certain jurisdictions, an individual to be declared bankrupt. Virtually every country with a modern legal system features some form of debt relief for individuals. Personal bankruptcy is distinguished from corporate bankruptcy.
Debt restructuring is a process that allows a private or public company or a sovereign entity facing cash flow problems and financial distress to reduce and renegotiate its delinquent debts to improve or restore liquidity so that it can continue its operations.
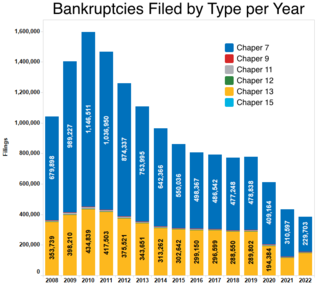
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).

In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company (debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be insolvent. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet insolvency.

The Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA) is a legislative act that made several significant changes to the United States Bankruptcy Code.
Chapter 12 of Title 11 of the United States Code, or simply chapter 12, is a chapter of the Bankruptcy Code. It is similar to Chapter 13 in structure, but it offers additional benefits to farmers and fishermen in certain circumstances, beyond those available to ordinary wage earners. Chapter 12 is applicable only to family farmers and fishermen.
A discharge in United States bankruptcy law, when referring to a debtor's discharge, is a statutory injunction against the commencement or continuation of an action to collect, recover or offset a debt as a personal liability of the debtor. The discharge is one of the primary benefits afforded by relief under the Bankruptcy Code and is essential to the "fresh start" of debtors following bankruptcy that is a central principle under federal bankruptcy law. Discharge is also believed to play an important role in credit markets by encouraging lenders, who may be more sophisticated and have better information than debtors, to monitor debtors and limit risk-taking.
An individual voluntary arrangement (IVA) is a formal alternative in England and Wales for individuals wishing to avoid bankruptcy. In Scotland, the equivalent statutory debt solution is known as a protected trust deed.
Debt settlement is a settlement negotiated with a debtor's unsecured creditor. Commonly, creditors agree to forgive a large part of the debt: perhaps around half, though results can vary widely. When settlements are finalized, the terms are put in writing. It is common that the debtor makes one lump-sum payment in exchange for the creditor agreeing that the debt is now cancelled and the matter closed. Some settlements are paid out over a number of months. In either case, as long as the debtor does what is agreed in the negotiation, no outstanding debt will appear on the former debtor's credit report.
An unfair preference is a legal term arising in bankruptcy law where a person or company transfers assets or pays a debt to a creditor shortly before going into bankruptcy, that payment or transfer can be set aside on the application of the liquidator or trustee in bankruptcy as an unfair preference or simply a preference.
In finance, a secured transaction is a loan or a credit transaction in which the lender acquires a security interest in collateral owned by the borrower and is entitled to foreclose on or repossess the collateral in the event of the borrower's default. The terms of the relationship are governed by a contract, or security agreement. A common example would be a consumer who purchases a car on credit. If the consumer fails to make the payments on time, the lender will take the car and resell it, applying the proceeds of the sale toward the loan. Mortgages and deeds of trust are another example. In the United States, secured transactions in personal property are governed by Article 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code (U.C.C.).
A general assignment or assignment is a concept in bankruptcy law in which an insolvent entity's assets are assigned to someone as an alternative to a bankruptcy. One form is an "assignment for the benefit of creditors", abbreviated ABC or AFBC.
Toibb v. Radloff, 501 U.S. 157 (1991), was a case in which the United States Supreme Court held that individuals are eligible to file for relief under the reorganization provisions of chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code, even if they are not engaged in a business. The case overturned the lower courts ruling which restricted individuals to chapter 7.
The insolvency law of Switzerland is the law governing insolvency, foreclosure, bankruptcy and debt restructuring proceedings in Switzerland. It is principally codified in the Federal Statute on Debt Enforcement and Bankruptcy of 11 April 1889 as well as in ancillary federal and cantonal laws.
A cram down or cramdown is the involuntary imposition by a court of a reorganization plan over the objection of some classes of creditors.
Bankruptcy in Florida is made under title 11 of the United States Code, which is referred to as the Bankruptcy Code. Although bankruptcy is a federal procedure, in certain regards, it looks to state law, such as to exemptions and to define property rights. The Bankruptcy Code provides that each state has the choice whether to "opt in" and use the federal exemptions or to "opt out" and to apply the state law exemptions. Florida is an "opt out" state in regard to exemptions. Bankruptcy in the United States is provided for under federal law as provided in the United States Constitution. Under the federal constitution, there are no state bankruptcy courts. The bankruptcy laws are primarily contained in 11 U.S.C. 101, et seq. The Bankruptcy Code underwent a substantial amendment in 2005 with the "Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005", often referred to as "BAPCPA". The Bankruptcy Code provides for a set of federal bankruptcy exemptions, but each states is allowed is choose whether it will "opt in" or "opt out" of the federal exemptions. In the event that a state opts out of the federal exemptions, the exemptions are provided for the particular exemption laws of the state with the application with certain federal exemptions.
Bank of America, N. A. v. Caulkett, 575 U.S. 790, 135 S. Ct. 1995 (2015), is a bankruptcy law case decided by the Supreme Court of the United States on June 1, 2015. In Caulkett, the Court held that 11 U.S.C. § 506(d) does not permit a Chapter 7 debtor to void a junior mortgage on the debtor's property when the amount of the debt secured by the senior mortgage on that property exceeds the property's current market value.



