
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The term metal–insulator–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another near-synonym is insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET).
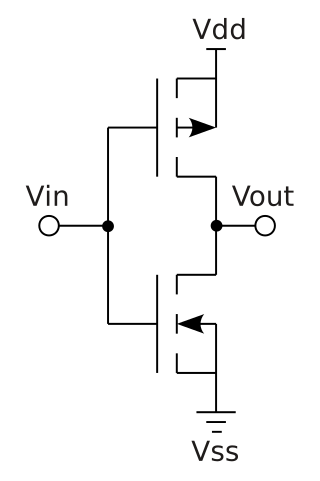
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.

Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both use the same cell design, consisting of floating gate MOSFETs. They differ at the circuit level depending on whether the state of the bit line or word lines is pulled high or low: in NAND flash, the relationship between the bit line and the word lines resembles a NAND gate; in NOR flash, it resembles a NOR gate.

EEPROM or E2PROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) is a type of non-volatile memory. It is used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip device, to store relatively small amounts of data by allowing individual bytes to be erased and reprogrammed.

An EPROM, or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power supply has been turned off and back on is called non-volatile. It is an array of floating-gate transistors individually programmed by an electronic device that supplies higher voltages than those normally used in digital circuits. Once programmed, an EPROM can be erased by exposing it to strong ultraviolet (UV) light source. EPROMs are easily recognizable by the transparent fused quartz window on the top of the package, through which the silicon chip is visible, and which permits exposure to ultraviolet light during erasing.
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data.
Reading is an action performed by computers, to acquire data from a source and place it into their volatile memory for processing. Computers may read information from a variety of sources, such as magnetic storage, the Internet, or audio and video input ports. Reading is one of the core functions of a Turing machine.

A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a multigate device, a MOSFET built on a substrate where the gate is placed on two, three, or four sides of the channel or wrapped around the channel, forming a double or even multi gate structure. These devices have been given the generic name "FinFETs" because the source/drain region forms fins on the silicon surface. The FinFET devices have significantly faster switching times and higher current density than planar CMOS technology.
In the semiconductor industry, the term high-κ dielectric refers to a material with a high dielectric constant, as compared to silicon dioxide. High-κ dielectrics are used in semiconductor manufacturing processes where they are usually used to replace a silicon dioxide gate dielectric or another dielectric layer of a device. The implementation of high-κ gate dielectrics is one of several strategies developed to allow further miniaturization of microelectronic components, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's Law.
The floating-gate MOSFET (FGMOS), also known as a floating-gate MOS transistor or floating-gate transistor, is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) where the gate is electrically isolated, creating a floating node in direct current, and a number of secondary gates or inputs are deposited above the floating gate (FG) and are electrically isolated from it. These inputs are only capacitively connected to the FG. Since the FG is surrounded by highly resistive material, the charge contained in it remains unchanged for long periods of time, nowadays typically longer than 10 years. Usually Fowler-Nordheim tunneling and hot-carrier injection mechanisms are used to modify the amount of charge stored in the FG.
Hot carrier injection (HCI) is a phenomenon in solid-state electronic devices where an electron or a “hole” gains sufficient kinetic energy to overcome a potential barrier necessary to break an interface state. The term "hot" refers to the effective temperature used to model carrier density, not to the overall temperature of the device. Since the charge carriers can become trapped in the gate dielectric of a MOS transistor, the switching characteristics of the transistor can be permanently changed. Hot-carrier injection is one of the mechanisms that adversely affects the reliability of semiconductors of solid-state devices.
SONOS, short for "silicon–oxide–nitride–oxide–silicon", more precisely, "polycrystalline silicon"—"silicon dioxide"—"silicon nitride"—"silicon dioxide"—"silicon", is a cross sectional structure of MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor), realized by P.C.Y. Chen of Fairchild Camera and Instrument in 1977. This structure is often used for non-volatile memories, such as EEPROM and flash memories. It is sometimes used for TFT LCD displays. It is one of CTF (charge trap flash) variants. It is distinguished from traditional non-volatile memory structures by the use of silicon nitride (Si3N4 or Si9N10) instead of "polysilicon-based FG (floating-gate)" for the charge storage material. A further variant is "SHINOS" ("silicon"—"hi-k"—"nitride"—"oxide"—"silicon"), which is substituted top oxide layer with high-κ material. Another advanced variant is "MONOS" ("metal–oxide–nitride–oxide–silicon"). Companies offering SONOS-based products include Cypress Semiconductor, Macronix, Toshiba, United Microelectronics Corporation and Floadia.
nvSRAM is a type of non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM). nvSRAM extends the functionality of basic SRAM by adding non-volatile storage such as an EEPROM to the SRAM chip. In operation, data is written to and read from the SRAM portion with high-speed access; the data in SRAM can then be stored into or retrieved from the non-volatile storage at lower speeds when needed.
The programmable metallization cell, or PMC, is a non-volatile computer memory developed at Arizona State University. PMC, a technology developed to replace the widely used flash memory, providing a combination of longer lifetimes, lower power, and better memory density. Infineon Technologies, who licensed the technology in 2004, refers to it as conductive-bridging RAM, or CBRAM. CBRAM became a registered trademark of Adesto Technologies in 2011. NEC has a variant called "Nanobridge" and Sony calls their version "electrolytic memory".

Read-only memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be electronically modified after the manufacture of the memory device. Read-only memory is useful for storing software that is rarely changed during the life of the system, also known as firmware. Software applications for programmable devices can be distributed as plug-in cartridges containing ROM.
Dawon Kahng was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET, along with his colleague Mohamed Atalla, in 1959. Kahng and Atalla developed both the PMOS and NMOS processes for MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. The MOSFET is the most widely used type of transistor, and the basic element in most modern electronic equipment.

The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three terminals: source, gate, and drain. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source.

The memory cell is the fundamental building block of computer memory. The memory cell is an electronic circuit that stores one bit of binary information and it must be set to store a logic 1 and reset to store a logic 0. Its value is maintained/stored until it is changed by the set/reset process. The value in the memory cell can be accessed by reading it.
The metal–nitride–oxide–semiconductor or metal–nitride–oxide–silicon (MNOS) transistor is a type of MOSFET in which the oxide layer is replaced by a double layer of nitride and oxide. It is an alternative and supplement to the existing standard MOS technology, wherein the insulation employed is a nitride-oxide layer. It is used in non-volatile computer memory.

UltraRAM is a brand name and a storage device technology that is under development. The Physics and Engineering department of Lancaster University in collaboration with Department of Physics at Warwick published a paper in the journal of advanced electronic materials suggesting an improvement in non volatile memory technology. It has been described as a memory storage technology that "combines the non-volatility of a data storage memory, like flash, with the speed, energy-efficiency, and endurance of a working memory, like DRAM" which means it could retain data like a hard drive. While the Lancaster team performed some basic experiments to demonstrate the principles in action, UltraRAM remains mostly theoretical at the moment. The Lancaster University researchers say that further work is ongoing to improve quality, fine-tune the fabrication process, and implement and scale UltraRAM devices.















