
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.

The Four Corners is a region of the Southwestern United States consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, southeastern corner of Utah, northeastern corner of Arizona, and northwestern corner of New Mexico. Most of the Four Corners region belongs to semi-autonomous Native American nations, the largest of which is the Navajo Nation, followed by Hopi, Ute, and Zuni tribal reserves and nations. The Four Corners region is part of a larger region known as the Colorado Plateau and is mostly rural, rugged, and arid.

The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries.

Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important pre-Columbian cultural and historical areas in the United States.

The Argentine Northwest is a geographic and historical region of Argentina composed of the provinces of Catamarca, Jujuy, La Rioja, Salta, Santiago del Estero and Tucumán.

The Chuska Mountains are an elongate range on the southwest Colorado Plateau and within the Navajo Nation whose highest elevations approach 10,000 feet. The range is about 80 by 15 km. It trends north-northwest and is crossed by the state line between Arizona and New Mexico. The highlands are a dissected plateau, with an average elevation of about 2,740 m (8,990 ft), and subdued topography. The highest point is Roof Butte at 2,994 m (9,823 ft), near the northern end of the range in Arizona. Other high points include the satellite Beautiful Mountain at 2,861 m (9,386 ft) and Lukachukai Mountains at 2,885 m (9,465 ft), both also near the northern end, and Matthews Peak at 2,911 m (9,551 ft). The San Juan Basin borders the Chuskas on the east, and typical elevations in nearby parts of that basin are near 1,800 m (5,900 ft). The eastern escarpment of the mountains is marked by slumps and landslides that extend out onto the western margin of the San Juan Basin. To the north, the Chuskas are separated from the Carrizo Mountains by Red Rock Valley, which is today commonly referred to as Red Valley.

The Chaco Wash is an arroyo cutting through Chaco Canyon, which is located in northwestern New Mexico on the Colorado Plateau. Another arroyo known as Escavada Wash is a tributary that feeds in from the northeast, near the western end of Chaco Canyon. Chaco Wash flows northwest to become the intermittent Chaco River. It is a tributary of the San Juan River.

Wijiji is an Ancestral Puebloan great house and archaeological site located in Chaco Canyon, in New Mexico, United States.

Chetro Ketl is an Ancestral Puebloan great house and archeological site located in Chaco Culture National Historical Park, New Mexico, United States. Construction on Chetro Ketl began c. 990 and was largely complete by 1075, with significant remodeling occurring in the early and mid-1110s. Following the onset of a severe drought, most Chacoans emigrated from the canyon by 1140; by 1250 Chetro Ketl's last inhabitants had vacated the structure.

Pueblo del Arroyo is an Ancestral Puebloan great house and archaeological site located in Chaco Culture National Historical Park, in New Mexico, United States.
The Chaco Slope is a geographical region located in the northwestern portion of the U.S. state of New Mexico. It borders the Chaco Core, which contains both Chacra Mesa and Chaco Canyon. The canyon itself is noted for its Chacoan Anasazi ruins. The Chaco Slope is differentiated from the neighboring Chuska Valley, Chaco Core, and Chaco Plateau by distinct surface water drainage patterns and geological formations. These regions were first labelled by archaeologist Gwinn Vivian.
The Gobernador Slope is a geographical region located in the northwestern portion of the U.S. state of New Mexico. It is near both Chacra Mesa and Chaco Canyon, which are noted for their Chacoan Anasazi ruins. The Chaco Slope is differentiated from the neighboring Chuska Valley, Chaco Core and Chaco Plateau by distinct surface water drainage patterns and geological formations. These regions were first labelled by archaeologist Gwinn Vivian.

Hungo Pavi is an Ancestral Puebloan great house and archaeological site located in Chaco Canyon, northwestern New Mexico, United States. A set of ruins located just 1 mile (2 km) from the ruins of Una Vida, Hungo Pavi measured 872 feet (266 m) in circumference. Initial explorations revealed 72 ground-level rooms, with structures reaching four stories in height. One large circular kiva has been identified. Its ruins now lie within Chaco Culture National Historical Park.

Pueblo Alto is an Ancestral Puebloan great house and archaeological site located in Chaco Culture National Historical Park, northwestern New Mexico, United States. The complex, comprising 89 rooms in a single-story layout, is located on a mesa top near the middle of Chaco Canyon; 0.6 miles (1 km) from Pueblo Bonito, it was begun between AD 1020 and 1050. Its location made the community visible to most of the inhabitants of the San Juan Basin; indeed, it was only 2.3 miles (3.7 km) north of Tsin Kletsin, on the opposite side of the canyon. The community was the center of a bead- and turquoise-processing industry that influenced the development of all villages in the canyon; chert tool production was also common. It shares its mesa with another great house, Nuevo Alto, both of which are now protected within the borders of Chaco Culture National Historical Park. Storerooms at Pueblo Alto opened to the outside rather than into the interior rooms and there was a huge midden of pottery. This and chert found in the midden came mostly from the Chuska area 70 km (43 mi) to the west.
Kin Nahasbas is a Chacoan Anasazi great house and archaeological site located in Chaco Canyon, 25 miles southwest of Nageezi, New Mexico, United States. Built in either the 9th or 10th centuries, it was major pueblo located slightly north of the Una Vida complex, which is positioned at the foot of the north mesa. Limited excavation has been conducted in this area. The ruins are now protected within the borders of Chaco Culture National Historical Park.
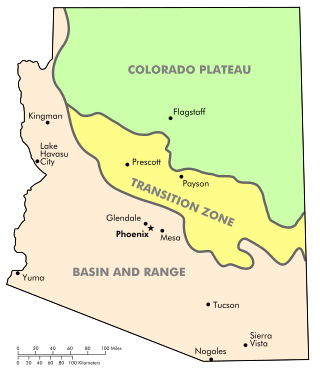
The Arizona transition zone is a diagonal northwest-by-southeast region across central Arizona. The region is a transition from the higher-elevation Colorado Plateau in Northeast Arizona and the Basin and Range region of lower-elevation deserts in the southwest and south.

The Arizona/New Mexico Mountains ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Arizona and New Mexico.
The Defiance Plateau, part of the geologic Defiance Uplift, is an approximately 75-mile (121 km) long, mostly north-trending plateau of Apache County, Arizona, with its east and southeast perimeter, as parts of San Juan and McKinley Counties, New Mexico.

Narbona Pass is a pass through the natural break between the Tunicha and Chuska Mountains, an elongated range on the Colorado Plateau on the Navajo Nation. A paved road, New Mexico Highway 134, crosses the range through Narbona Pass, connecting Sheep Springs to Crystal. Contrary to Navajo tradition of not naming monuments after people, the pass was given the name Narbona to celebrate his victory over an invading Mexican army that was sent to destroy the Navajo in 1835. Known in the Navajo Language as So Sila, the pass was lately named in English for Colonel John M. Washington in 1859. He was a New Mexico military governor who led an expedition into Navajo country in 1849 in which he was accused of walling up a Navajo Spring, and whose troops later shot Navajo leader Narbona.

The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition, which developed from the Picosa culture. The people and their archaeological culture are often referred to as Anasazi, meaning "ancient enemies", as they were called by Navajo. Contemporary Puebloans object to the use of this term, with some viewing it as derogatory.

















