
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

A furnace, referred to as a heater or boiler in British English, is an appliance used to generate heat for all or part of a building. Furnaces are mostly used as a major component of a central heating system. Furnaces are permanently installed to provide heat to an interior space through intermediary fluid movement, which may be air, steam, or hot water. Heating appliances that use steam or hot water as the fluid are normally referred to as a residential steam boilers or residential hot water boilers. The most common fuel source for modern furnaces in North America and much of Europe is natural gas; other common fuel sources include LPG, fuel oil, wood and in rare cases coal. In some areas electrical resistance heating is used, especially where the cost of electricity is low or the primary purpose is for air conditioning. Modern high-efficiency furnaces can be up to 98% efficient and operate without a chimney, with a typical gas furnace being about 80% efficient. Waste gas and heat are mechanically ventilated through either metal flue pipes or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes that can be vented through the side or roof of the structure. Fuel efficiency in a gas furnace is measured in AFUE.

A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint.
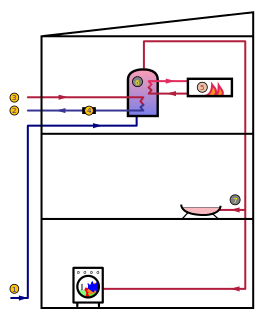
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.

Solar water heating (SWH) is heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations is available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications.

A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building and optionally also able to heat domestic hot water from one main source of heat. It is a component of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, which can both cool and warm interior spaces.
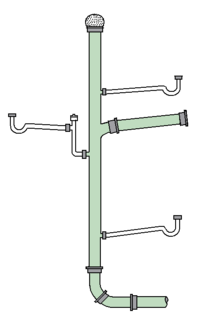
In modern plumbing, a drain-waste-vent is a system that allows air to enter the plumbing system to maintain proper air pressure to enable the removal of sewage and greywater from a dwelling. Drain refers to water produced at fixtures such as sinks, and showers; waste refers to water from toilets. As the water runs down, proper venting is required to allow water to flow freely, and avoid a vacuum from being created. As the water runs down air must be allowed into the waste pipe either through a roof vent (external), or an internal vent.

Hydronics is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution as heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and steam systems. Historically, in large-scale commercial buildings such as high-rise and campus facilities, a hydronic system may include both a chilled and a heated water loop, to provide for both heating and air conditioning. Chillers and cooling towers are used either separately or together as means to provide water cooling, while boilers heat water. A recent innovation is the chiller boiler system, which provides an efficient form of HVAC for homes and smaller commercial spaces.

Electric heat tracing, heat tape or surface heating, is a system used to maintain or raise the temperature of pipes and vessels using heat tracing cables. Trace heating takes the form of an electrical heating element run in physical contact along the length of a pipe. The pipe is usually covered with thermal insulation to retain heat losses from the pipe. Heat generated by the element then maintains the temperature of the pipe. Trace heating may be used to protect pipes from freezing, to maintain a constant flow temperature in hot water systems, or to maintain process temperatures for piping that must transport substances that solidify at ambient temperatures. Electric trace heating cables are an alternative to steam trace heating where steam is unavailable or unwanted.

Thermosiphon is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney.

Electric heating is a process in which electrical energy is converted directly to heat energy at around 100% efficiency, using rather cheap devices. Common applications include space heating, cooking, water heating and industrial processes. An electric heater is an electrical device that converts an electric current into heat. The heating element inside every electric heater is an electrical resistor, and works on the principle of Joule heating: an electric current passing through a resistor will convert that electrical energy into heat energy. Most modern electric heating devices use nichrome wire as the active element; the heating element, depicted on the right, uses nichrome wire supported by ceramic insulators.
Economizers, or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.

A fan coil unit (FCU), also known as a Vertical Fan Coil-Unit (VFC), is a device consisting of a heat exchanger (coil) and a fan. As part of an HVAC system found in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings using ducted split air conditioning or with central plant cooling, a fan coil unit is often connected to ductwork and a thermostat to regulate the temperature of one or more spaces as well as assisting the main air handling unit for each space if used with chillers. The thermostat controls the fan speed and/or the throughput of water to the heat exchanger using a control valve.

Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plant or any similar use of such an engine.

Radiators and convectors are heat exchangers designed to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of space heating.
HVAC is a major sub discipline of mechanical engineering. The goal of HVAC design is to balance indoor environmental comfort with other factors such as installation cost, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. The discipline of HVAC includes a large number of specialized terms and acronyms, many of which are summarized in this glossary.

Hydronic balancing, also called hydraulic balancing, is the process of optimising the distribution of water in a building's hydronic heating or cooling system by equalizing the system pressure so it provides the intended indoor climate at optimum energy efficiency and minimal operating cost.

Tankless water heaters — also called instantaneous, continuous flow, inline, flash, on-demand, or instant-on water heaters — are water heaters that instantly heat water as it flows through the device, and do not retain any water internally except for what is in the heat exchanger coil. Copper heat exchangers are preferred in these units because of their high thermal conductivity and ease of fabrication.
The Glossary of Geothermal Heating and Cooling provides definitions of many terms used within the Geothermal heat pump industry. The terms in this glossary may be used by industry professionals, for education materials, and by the general public.



















