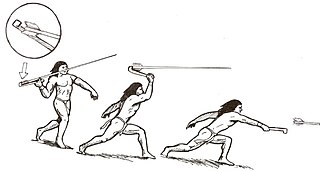
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or atlatl is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface that allows the user to store energy during the throw.

Creswell Crags is an enclosed limestone gorge on the border between Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire, England, near the villages of Creswell and Whitwell. The cliffs in the ravine contain several caves that were occupied during the last ice age, between around 43,000 and 10,000 years ago. Its caves contain the northernmost cave art in Europe. The evidence of occupation found in the rich series of sediments that accumulated over many thousands of years is regarded as internationally unique in demonstrating how prehistoric people managed to live at the extreme northernmost limits of their territory during the Late Pleistocene period.

Homo heidelbergensis is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of H. erectus in 1950 as H. e. heidelbergensis, but towards the end of the century, it was more widely classified as its own species. It is debated whether or not to constrain H. heidelbergensis to only Europe or to also include African and Asian specimens, and this is further confounded by the type specimen being a jawbone, because jawbones feature few diagnostic traits and are generally missing among Middle Pleistocene specimens. Thus, it is debated if some of these specimens could be split off into their own species or a subspecies of H. erectus. Because the classification is so disputed, the Middle Pleistocene is often called the "muddle in the middle".

Acheulean, from the French acheuléen after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped "hand axes" associated with Homo erectus and derived species such as Homo heidelbergensis.

Bilzingsleben is a former stone quarry in Thuringia, Germany, notable for its wealth of palaeolithic human fossils and artifacts.

The woolly rhinoceros is an extinct species of rhinoceros that inhabited northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene epoch. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia. The species range contracted towards Siberia beginning around 17,000 years ago, with the youngest known records being around 14,000 years old in northeast Siberia, coinciding with the Bølling–Allerød warming, which likely disrupted its habitat, with environmental DNA records possibly extending the range of the species around 9,800 years ago. Its closest living relative in the Sumatran rhinoceros.

Schöningen is a town of about 11,000 inhabitants in the district of Helmstedt, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Clactonian is the name given by archaeologists to an industry of European flint tool manufacture that dates to the early part of the Hoxnian Interglacial around 424-415,000 years ago. Clactonian tools were made by Homo heidelbergensis. The Clactonian is primarly distinguished from the (globally) contemporaneous Acheulean industry by its lack of use of handaxe tools.

The throwing stick or throwing club is a wooden rod with either a pointed tip or a spearhead attached to one end, intended for use as a weapon. A throwing stick can be either straight or roughly boomerang-shaped, and is much shorter than the javelin. It became obsolete as slings and bows became more prevalent, except on the Australian continent, where the native people continued refining the basic design. Throwing sticks shaped like returning boomerangs are designed to fly straight to a target at long ranges, their surfaces acting as airfoils. When tuned correctly they do not exhibit curved flight, but rather they fly on an extended straight flight path. Straight flight ranges greater than 100 m (330 ft) have been reported by historical sources as well as in recent research.

The straight-tusked elephant is an extinct species of elephant that inhabited Europe and Western Asia during the Middle and Late Pleistocene. One of the largest known elephant species, mature bulls on average had a shoulder height of 3.81–4.2 metres (12.5–13.8 ft) and a weight of 10.8–15 tonnes (24,000–33,000 lb). Like modern elephants, the straight-tusked elephant lived in herds, flourishing during interglacial periods, when its range would extend as far north as Great Britain. Skeletons found in association with stone tools and wooden spears suggest they were scavenged and hunted by early humans, including Neanderthals. It is the ancestral species of most dwarf elephants that inhabited islands in the Mediterranean.
The prehistory of the County of Norfolk, England is broken into specific time periods, these being Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic.

The Boxgrove Palaeolithic site is an internationally important archaeological site north-east of Boxgrove in West Sussex with findings that date to the Lower Palaeolithic. The oldest human remains in Britain have been discovered on the site, fossils of Homo heidelbergensis dating to 500,000 years ago. Boxgrove is also one of the oldest sites in Europe with direct evidence of hunting and butchering by early humans. Only part of the site is protected through designation, one area being a 9.8-hectare (24-acre) geological Site of Special Scientific Interest, as well as a Geological Conservation Review site.

Swanscombe Skull Site or Swanscombe Heritage Park is a 3.9-hectare (9.6-acre) geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Swanscombe, north-west Kent, England. It contains two Geological Conservation Review sites and a National Nature Reserve. The park lies in a former gravel quarry, Barnfield Pit, which is the most important site in the Swanscombe complex, alongside several other nearby pits.

The Schöningen spears are a set of ten wooden weapons from the Palaeolithic Age that were excavated between 1994 and 1999 from the 'Spear Horizon' in the open-cast lignite mine in Schöningen, Helmstedt district, Germany. The spears are the oldest hunting weapons discovered and were found together with animal bones and stone and bone tools. Being used by the oldest known group of hunters, they provided never before uncovered proof that early human ancestors were much closer to modern humans in both complex social structure and technical ability than thought before. The excavations took place under the management of Hartmut Thieme of the Lower Saxony State Service for Cultural Heritage (NLD).

Samu is the nickname given to a fragmentary Middle Pleistocene human occipital, also known as Vertesszolos Man or Vertesszolos occipital, discovered in Vértesszőlős, Central Transdanubia, Hungary.

Qesem cave is a Lower Paleolithic archaeological site near the town of Kafr Qasim in Israel. Early humans were occupying the site by 400,000 until c. 200,000 years ago.

Tautavel Man refers to the archaic humans which—from approximately 550,000 to 400,000 years ago—inhabited the Caune de l’Arago, a limestone cave in Tautavel, France. They are generally grouped as part of a long and highly variable lineage of transitional morphs which inhabited the Middle Pleistocene of Europe, and would eventually evolve into the Neanderthals. They have been variably assigned to either H. (s.?) heidelbergensis, or as a European subspecies of H. erectus as H. e. tautavelensis. The skull is reconstructed based on the specimens Arago 21 and 47, and it is, to a degree, more characteristic of what might be considered a typical H. erectus morphology than a typical H. heidelbergensis morphology. The brain capacity is 1,166 cc. They seem to have had an overall robust skeleton. Average height may have been 166 cm.

The narrow-nosed rhinoceros, also known as the steppe rhinoceros is an extinct species of rhinoceros belonging to the genus Stephanorhinus that lived in western Eurasia, including Europe, as well as North Africa during the Pleistocene. It first appeared in Europe around 500,000 years ago during the Middle Pleistocene and survived there until at least 34,000 years Before Present.

Stephanorhinus kirchbergensis, also known as Merck's rhinoceros is an extinct species of rhinoceros belonging to the genus Stephanorhinus from the Middle to Late Pleistocene of Eurasia. Its range spanned from Western Europe to Eastern Asia. Among the last members of the genus, it co-existed alongside Stephanorhinus hemitoechus in the western part of its range.
The Schöningen site is a Paleolithic archaeological site in Germany, dating to around 300,000 years ago. It is best known for the Schöningen spears, some of the oldest known wooden spears, found in the "spear horizon", though the site as a whole covers a broader span of time.


















