
Cloacina was a goddess who presided over the Cloaca Maxima ('Greatest Drain'), the main interceptor discharge outfall of the system of sewers in Rome.

Cloacina was a goddess who presided over the Cloaca Maxima ('Greatest Drain'), the main interceptor discharge outfall of the system of sewers in Rome.
The theonym Cloācīna is a derivative of the noun cloāca ('sewer, underground drainage'; cf. cluere 'to purify'), itself from Proto-Italic *klowā-, ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *ḱleuH-o- ('clean'). A cult-title of Venus, Cloācīna may be interpreted as meaning 'The Purifier'. [1]
The Cloaca Maxima was said to have been begun by Tarquinius Priscus, one of Rome's Etruscan kings, and finished by another, Tarquinius Superbus: Cloacina might have originally been an Etruscan deity. According to one of Rome's foundation myths, Titus Tatius, king of the Sabines, erected a statue to Cloacina at the place where Romans and Sabines met to confirm the end of their conflict, following the rape of the Sabine women. Tatius instituted lawful marriage between Sabines and Romans, uniting them as one people, ruled by himself and by Rome's founder, Romulus. The peace between Sabines and Romans was marked by a cleansing ritual using myrtle, at or very near an ancient Etruscan shrine to Cloacina, above a small stream that would later be enlarged as the main outlet for Rome's main sewer, the Cloaca Maxima. As myrtle was one of Venus' signs, and Venus was a goddess of union, peace and reconciliation, Cloacina was recognised as Venus Cloacina (Venus the Cleanser). She was also credited with the purification of sexual intercourse within marriage. [2] [3] [4]

The small, circular shrine of Venus Cloacina was situated before the Basilica Aemilia on the Roman Forum and directly above the Cloaca Maxima. Some Roman coins had images of Cloacina's shrine. The clearest show two females, presumed to be deities, each with a bird perched on a pillar. One holds a small object, possibly a flower; birds and flowers are signs of Venus, among other deities. The figures may have represented the two aspects of the divinity, Cloacina-Venus. [5]

Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, or Tarquin the Elder, was the legendary fifth king of Rome and first of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned for thirty-eight years. Tarquinius expanded Roman power through military conquest and grand architectural constructions. His wife was the prophetess Tanaquil.

Lucius Tarquinius Superbus was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic. He is commonly known as Tarquin the Proud, from his cognomen Superbus.
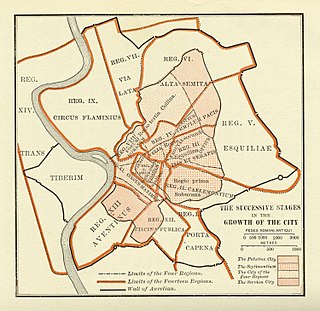
The Roman Kingdom, also referred to as the Roman monarchy or the regal period of ancient Rome, was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to tradition, the Roman Kingdom began with the city's founding c. 753 BC, with settlements around the Palatine Hill along the river Tiber in central Italy, and ended with the overthrow of the kings and the establishment of the Republic c. 509 BC.

The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire. It measured 621 m (2,037 ft) in length and 118 m (387 ft) in width and could accommodate over 150,000 spectators. In its fully developed form, it became the model for circuses throughout the Roman Empire. The site is now a public park.

Venus is a Roman goddess, whose functions encompass love, beauty, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity, and victory. In Roman mythology, she was the ancestor of the Roman people through her son, Aeneas, who survived the fall of Troy and fled to Italy. Julius Caesar claimed her as his ancestor. Venus was central to many religious festivals, and was revered in Roman religion under numerous cult titles.

In ancient Roman religion, Ceres was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships. She was originally the central deity in Rome's so-called plebeian or Aventine Triad, then was paired with her daughter Proserpina in what Romans described as "the Greek rites of Ceres". Her seven-day April festival of Cerealia included the popular Ludi Ceriales. She was also honoured in the May lustration (lustratio) of the fields at the Ambarvalia festival: at harvest-time: and during Roman marriages and funeral rites. She is usually depicted as a mature woman.

In ancient Roman religion and mythology, Liber, also known as Liber Pater, was a god of viticulture and wine, male fertility and freedom. He was a patron deity of Rome's plebeians and was part of their Aventine Triad. His festival of Liberalia became associated with free speech and the rights attached to coming of age. His cult and functions were increasingly associated with Romanised forms of the Greek Dionysus/Bacchus, whose mythology he came to share.

In Roman mythology and religion, Quirinus is an early god of the Roman state. In Augustan Rome, Quirinus was also an epithet of Janus, as Janus Quirinus.
In ancient Roman religion, Sancus was a god of trust, honesty, and oaths. His cult, one of the most ancient amongst the Romans, probably derived from Umbrian influences. Cato and Silius Italicus wrote that Sancus was a Sabine god and father of the eponymous Sabine hero Sabus. He is thus sometimes considered a founder-deity.

The Sabines were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.

Fauna is a Roman rustic goddess said in differing ancient sources to be the wife, sister, or daughter of Faunus. Varro regarded her as the female counterpart of Faunus, and said that the fauni all had prophetic powers. She is also called Fatua or Fenta Fauna.

In Etruscan and Sabine religion, Feronia was a goddess associated with wildlife, fertility, health, and abundance, also venerated by the Faliscans and later adopted into ancient Roman religion. As the goddess who granted freedom to slaves or civil rights to the most humble part of society, she was especially honored among plebeians and freedmen. Her festival, the Feroniae, was November 13 during the Ludi Plebeii, in conjunction with Fortuna Primigenia; both were goddesses of Praeneste.

Flora is a Roman goddess of flowers and spring – a symbol for nature and flowers. While she was otherwise a relatively minor figure in Roman mythology, being one among several fertility goddesses, her association with the spring gave her particular importance at the coming of springtime, as did her role as goddess of youth. She was one of the fifteen deities who had their own flamen, the Floralis, one of the flamines minores. Her Greek counterpart is Chloris.
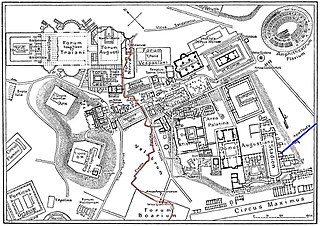
The Cloaca Maxima was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name is related to that of Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove waste from the city. It carried effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city. The sewer started at the Forum Augustum and ended at the Ponte Rotto and Ponte Palatino. It began as an open air canal, but it developed into a much larger sewer over the course of time. Agrippa renovated and reconstructed much of the sewer. This would not be the only development in the sewers. By the first century CE all eleven Roman aqueducts were connected to the sewer. After the Roman Empire fell the sewer still was used. By the 19th century, it became a tourist attraction. Some parts of the sewer are still used today. Whilst still being used, it was highly valued as a sacred symbol of Roman culture, and Roman engineering.
Sanitation in ancient Rome, acquired from the Etruscans, was very advanced compared to other ancient cities and provided water supply and sanitation services to residents of Rome. Although there were many sewers, public latrines, baths and other sanitation infrastructure, disease was still rampant. The baths are known to symbolise the "great hygiene of Rome".

The Shrine of Venus Cloacina — the "Shrine of Venus of the Sewer" — was a small sanctuary on the Roman Forum, honoring the divinity of the Cloaca Maxima, the spirit of the "Great Drain" or Sewer of Rome. Cloacina, the Etruscan goddess associated with the entrance to the sewer system, was later identified with the Roman goddess Venus for unknown reasons, according to Pliny the Elder.

Vulcan is the god of fire including the fire of volcanoes, deserts, metalworking and the forge in ancient Roman religion and myth. He is often depicted with a blacksmith's hammer. The Vulcanalia was the annual festival held August 23 in his honor. His Greek counterpart is Hephaestus, the god of fire and smithery. In Etruscan religion, he is identified with Sethlans.

The Vinalia were Roman festivals of the wine harvest, wine vintage and gardens, held in honour of Jupiter and Venus. The Vinalia prima, also known as the Vinalia urbana was held on 23 April to bless and sample last year's wine and ask for good weather until the next harvest. The Vinalia rustica was on 19 August, before the harvest and grape-pressing.
A toilet god is a deity associated with latrines and toilets. Belief in toilet gods – a type of household deity – has been known from both modern and ancient cultures, ranging from Japan to ancient Rome. Such deities have been associated with health, well-being and fertility and have been propitiated in a wide variety of ways, including making offerings, invoking and appeasing them through prayers, meditating and carrying out ritual actions such as clearing one's throat before entering or even biting the latrine to transfer spiritual forces back to the god.