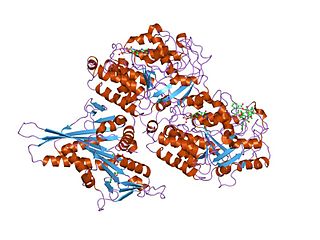
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.

(+)-Discodermolide is a polyketide natural product found to stabilize microtubules. (+)-discodermolide was isolated by Gunasekera and his co-workers at the Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute from the deep-sea sponge Discodermia dissoluta in 1990. (+)-Discodermolide was found to be a potent inhibitor of tumor cell growth in several MDR cancer cell lines. (+)-discodermolide also shows some unique characters, including a linear backbone structure, immunosuppressive properties both in vitro and in vivo, potent induction of an accelerated senescence phenotype, and synergistic antiproliferative activity in combination with paclitaxel. Discodermolide was recognized as one of the most potent natural promoters of tubulin assembly. A large number of efforts toward the total synthesis of (+)-discodermolide were directed by its interesting biological activities and extreme scarcity of natural sources. The compound supply necessary for complete clinical trials cannot be met by harvesting, isolation, and purification. As of 2005, attempts at synthesis or semi-synthesis by fermentation have proven unsuccessful. As a result, all discodermolide used in preclinical studies and clinical trials has come from large-scale total synthesis.

Epothilones are a class of potential cancer drugs. Like taxanes, they prevent cancer cells from dividing by interfering with tubulin, but in early trials, epothilones have better efficacy and milder adverse effects than taxanes.
Combretum caffrum, commonly known as Cape bushwillow, is a species of tree native to South Africa. It is endemic to the Cape Provinces.

Cryptophycins are a family of macrolide molecules that are potent cytotoxins and have been studied for potential antiproliferative properties useful in developing chemotherapy. They are members of the depsipeptide family.

Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of Camptotheca acuminata, a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically more recently in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today: topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also been found in other plants including Chonemorpha fragrans.

Eribulin, sold under the brand name Halaven, is an anticancer medication used to treat breast cancer and liposarcoma.

Combretastatin A-4 is a combretastatin and a stilbenoid. It can be isolated from Combretum caffrum, the Eastern Cape South African bushwillow tree or in Combretum leprosum, the mofumbo, a species found in Brazil.

Combretastatin A-1 is a combretastatin and a stilbenoid. It can be found in Combretum caffrum, the Eastern Cape South African Bushwillow tree.

Fosbretabulin is a microtubule destabilizing experimental drug, a type of vascular-targeting agent, a drug designed to damage the vasculature of cancer tumours causing central necrosis. It is a derivative of combretastatin. It is formulated as the salts fosbretabulin disodium and fosbretabulin tromethamine.

Postpericardiotomy syndrome (PPS) is a medical syndrome referring to an immune phenomenon that occurs days to months after surgical incision of the pericardium. PPS can also be caused after a trauma, a puncture of the cardiac or pleural structures, after percutaneous coronary intervention, or due to pacemaker or pacemaker wire placement.
Tubulin inhibitors are chemotherapy drugs that interfere directly with the tubulin system, which is in contrast to those chemotherapy drugs acting on DNA. Microtubules play an important role in eukaryotic cells. Alpha- and beta-tubulin, the main components of microtubules, have gained considerable interest because of their function and biophysical properties and has become the subject of intense study.

Withaferin A is a steroidal lactone, derived from Acnistus arborescens, Withania somnifera and other members of family Solanaceae. It is the first member of the withanolide class of ergostane type product to be discovered.

Taccalonolides are a class of microtubule-stabilizing agents isolated from Tacca chantrieri that has been shown to have selective cancer-fighting properties. Other examples of microtubule-stabilizing agents include taxanes and epothilones, both of which prevent cancer cells from dividing by interfering with tubulin. While taxanes like Paclitaxel and docetaxel have been used successfully against breast, ovarian, prostate, and non–small-cell lung cancers, intrinsic and acquired drug resistance limit their anticancer properties. Unlike taxanes, taccalonolides appear to work through a different mechanism of action that does not involve tubulin, although recently isolated taccalonolides AF and AJ have shown tubulin-interaction activity. The discovery of taccalonolides opens up new possibilities to treat cancer cells, especially ones that are taxane or epithilone resistant.

Combretastatin B-1 is a combretastatin and a dihydrostilbenoid. It can be found in Combretum caffrum, the Eastern Cape South African bushwillow tree or in Combretum kraussii, the forest bushwillow.
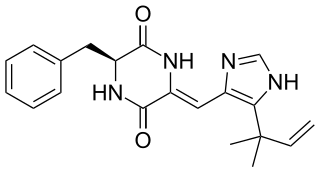
Phenylahistin is a metabolite produced by the fungus Aspergillus ustus that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines featuring a dehydrohistidine residue that exhibit important biological activities, such as anti-cancer or neurotoxic effects.
Curacin A is a hybrid polyketide synthase (PKS)/nonribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS) derived natural product produced isolated from the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Curacin A belongs to a family of natural products including jamaicamide, mupirocin, and pederin that have an unusual terminal alkene. Additionally, Curacin A contains a notable thiazoline ring and a unique cyclopropyl moiety, which is essential to the compound's biological activity. Curacin A has been characterized as potent antiproliferative cytotoxic compound with notable anticancer activity for several cancer lines including renal, colon, and breast cancer. Curacin A has been shown to interact with colchicine binding sites on tubulin, which inhibits microtubule polymerization, an essential process for cell division and proliferation.
Kalkitoxin, a toxin derived from the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula, induces NMDA receptor mediated neuronal necrosis, blocks voltage-dependent sodium channels, and induces cellular hypoxia by inhibiting the electron transport chain (ETC) complex 1.
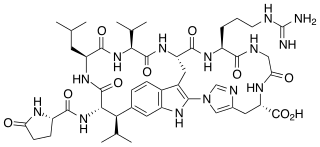
Moroidin is a biologically active compound found in the plants Dendrocnide moroides and Celosia argentea. It is a peptide composed of eight amino acids, with unusual leucine-tryptophan and tryptophan-histidine cross-links that form its two rings. Moroidin has been shown to be at least one of several bioactive compounds responsible for the painful sting of the Dendrocnide moroides plant. It also has demonstrated anti-mitotic properties, specifically by inhibition of tubulin polymerization. Anti-mitotic activity gives moroidin potential as a chemotherapy drug, and this property combined with its unusual chemical structure has made it a target for organic synthesis.
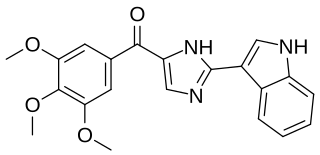
Sabizabulin is a chemical compound from the group of indole and imidazole derivatives that was first reported in 2012 by Dalton, Li, and Miller. It is being studied as a mitotic inhibitor and chemotherapeutic agent in castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer and in SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infections.

















