
The Open Systems Interconnection model is a conceptual model, originally conceived as the 7 layer onion skin architecture by Jack Houldsworth of ICL that 'provides a common basis for the coordination of [ISO] standards development for the purpose of systems interconnection'. In the OSI reference model, the communications between a computing system are split into seven different abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behaviour. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more.

X.25 is an ITU-T standard protocol suite for packet-switched data communication in wide area networks (WAN). It was originally defined by the International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee in a series of drafts and finalized in a publication known as The Orange Book in 1976.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the session layer is layer 5.

In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing.
An application layer is an abstraction layer that specifies the shared communications protocols and interface methods used by hosts in a communications network. An application layer abstraction is specified in both the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) and the OSI model. Although both models use the same term for their respective highest-level layer, the detailed definitions and purposes are different.
FCAPS is the ISO Telecommunications Management Network model and framework for network management. FCAPS is an acronym for fault, configuration, accounting, performance, security, the management categories into which the ISO model defines network management tasks. In non-billing organizations accounting is sometimes replaced with administration.
Connectionless-mode Network Service (CLNS) or simply Connectionless Network Service is an OSI network layer datagram service that does not require a circuit to be established before data is transmitted, and routes messages to their destinations independently of any other messages. As such it is a "best-effort" rather than a "reliable" delivery service. CLNS is not an Internet service, but provides capabilities in an OSI network environment similar to those provided by the Internet protocol suite. The service is specified in ISO/IEC 8348, the OSI Network Service Definition
The Common Management Information Protocol (CMIP) is the OSI specified network management protocol.
Element management is concerned with managing network elements on the network element management layer (NEL) of the TMN . An element management system (EMS) manages one or more of a specific type of telecommunications network elements (NE).
A management information base (MIB) is a database used for managing the entities in a communication network. Most often associated with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), the term is also used more generically in contexts such as in OSI/ISO Network management model. While intended to refer to the complete collection of management information available on an entity, it is often used to refer to a particular subset, more correctly referred to as MIB-module.
The Telecommunications Management Network is a protocol model defined by ITU-T for managing open systems in a communications network. It is part of the ITU-T Recommendation series M.3000 and is based on the OSI management specifications in ITU-T Recommendation series X.700.
The Guidelines for the Definition of Managed Objects (GDMO) is a specification for defining managed objects of interest to the Telecommunications Management Network for use in CMIP.
The Open Systems Interconnection protocols are a family of information exchange standards developed jointly by the ISO and the ITU-T. The standardization process began in 1977.
IEC 62056 is a set of standards for electricity metering data exchange by International Electrotechnical Commission.
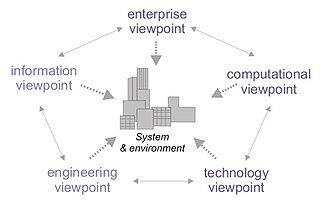
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
CEN ISO/IEEE 11073 Health informatics - Medical / health device communication standards enable communication between medical, health care and wellness devices and external computer systems. They provide automatic and detailed electronic data capture of client-related and vital signs information, and of device operational data.
IEC 60870 part 6 in electrical engineering and power system automation, is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed part 6 to provide a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems which is compatible with ISO standards and ITU-T recommendations.
Security service is a service, provided by a layer of communicating open systems, which ensures adequate security of the systems or of data transfers as defined by ITU-T X.800 Recommendation.
X.800 and ISO 7498-2 are technically aligned. This model is widely recognized



