Related Research Articles

Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms.

A compressed-air car is a compressed-air vehicle powered by pressure vessels filled with compressed air. It is propelled by the release and expansion of the air within a motor adapted to compressed air. The car might be powered solely by air, or combined with other fuels such as gasoline, diesel, or an electric plant with regenerative braking.
A propellant is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the engine that expels the propellant is called a reaction engine. Although technically a propellant is the reaction mass used to create thrust, the term "propellant" is often used to describe a substance which contains both the reaction mass and the fuel that holds the energy used to accelerate the reaction mass. For example, the term "propellant" is often used in chemical rocket design to describe a combined fuel/propellant, although the propellants should not be confused with the fuel that is used by an engine to produce the energy that expels the propellant. Even though the byproducts of substances used as fuel are also often used as a reaction mass to create the thrust, such as with a chemical rocket engine, propellant and fuel are two distinct concepts.

Compressed-air energy storage (CAES) is a way to store energy for later use using compressed air. At a utility scale, energy generated during periods of low demand can be released during peak load periods.

Alternative fuels, also known as non-conventional and advanced fuels, are fuels derived from sources other than petroleum. Alternative fuels include gaseous fossil fuels like propane, natural gas, methane, and ammonia; biofuels like biodiesel, bioalcohol, and refuse-derived fuel; and other renewable fuels like hydrogen and electricity.

A compressed-air vehicle (CAV) is a transport mechanism fueled by tanks of pressurized atmospheric gas and propelled by the release and expansion of the gas within a pneumatic motor.

Bottled gas is a term used for substances which are gaseous at standard temperature and pressure (STP) and have been compressed and stored in carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or composite containers known as gas cylinders.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inexpensive or when demand is low, and later returned to the grid when demand is high, and electricity prices tend to be higher.

Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) is a technique used to separate some gas species from a mixture of gases under pressure according to the species' molecular characteristics and affinity for an adsorbent material. It operates at near-ambient temperature and significantly differs from the cryogenic distillation commonly used to separate gases. Selective adsorbent materials are used as trapping material, preferentially adsorbing the target gas species at high pressure. The process then swings to low pressure to desorb the adsorbed gas.
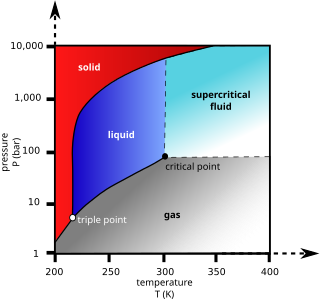
Supercritical carbon dioxide is a fluid state of carbon dioxide where it is held at or above its critical temperature and critical pressure.
An integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) is a technology using a high pressure gasifier to turn coal and other carbon based fuels into pressurized gas—synthesis gas (syngas). It can then remove impurities from the syngas prior to the electricity generation cycle. Some of these pollutants, such as sulfur, can be turned into re-usable byproducts through the Claus process. This results in lower emissions of sulfur dioxide, particulates, mercury, and in some cases carbon dioxide. With additional process equipment, a water-gas shift reaction can increase gasification efficiency and reduce carbon monoxide emissions by converting it to carbon dioxide. The resulting carbon dioxide from the shift reaction can be separated, compressed, and stored through sequestration. Excess heat from the primary combustion and syngas fired generation is then passed to a steam cycle, similar to a combined cycle gas turbine. This process results in improved thermodynamic efficiency, compared to conventional pulverized coal combustion.
A zinc–bromine battery is a rechargeable battery system that uses the reaction between zinc metal and bromine to produce electric current, with an electrolyte composed of an aqueous solution of zinc bromide. Zinc has long been used as the negative electrode of primary cells. It is a widely available, relatively inexpensive metal. It is rather stable in contact with neutral and alkaline aqueous solutions. For this reason it is used today in zinc–carbon and alkaline primaries.

A primarylife support system (PLSS), is a device connected to an astronaut or cosmonaut's spacesuit, which allows extra-vehicular activity with maximum freedom, independent of a spacecraft's life support system. A PLSS is generally worn like a backpack. The functions performed by the PLSS include:

A carbon dioxide scrubber is a piece of equipment that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). It is used to treat exhaust gases from industrial plants or from exhaled air in life support systems such as rebreathers or in spacecraft, submersible craft or airtight chambers. Carbon dioxide scrubbers are also used in controlled atmosphere (CA) storage. They have also been researched for carbon capture and storage as a means of combating climate change.
The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few.
A liquid nitrogen vehicle is powered by liquid nitrogen, which is stored in a tank. Traditional nitrogen engine designs work by heating the liquid nitrogen in a heat exchanger, extracting heat from the ambient air and using the resulting pressurized gas to operate a piston or rotary motor. Vehicles propelled by liquid nitrogen have been demonstrated, but are not used commercially. One such vehicle, Liquid Air, was demonstrated in 1902.

A cryogenic gas plant is an industrial facility that creates molecular oxygen, molecular nitrogen, argon, krypton, helium, and xenon at relatively high purity. As air is made up of nitrogen, the most common gas in the atmosphere, at 78%, with oxygen at 19%, and argon at 1%, with trace gasses making up the rest, cryogenic gas plants separate air inside a distillation column at cryogenic temperatures to produce high purity gasses such as argon, nitrogen, oxygen, and many more with 1 ppm or less impurities. The process is based on the general theory of the Hampson-Linde cycle of air separation, which was invented by Carl von Linde in 1895.
Cryogenic energy storage (CES) is the use of low temperature (cryogenic) liquids such as liquid air or liquid nitrogen to store energy. The technology is primarily used for the large-scale storage of electricity. Following grid-scale demonstrator plants, a 250 MWh commercial plant is now under construction in the UK, and a 400 MWh store is planned in the USA.
Power-to-gas is a technology that uses electric power to produce a gaseous fuel. When using surplus power from wind generation, the concept is sometimes called windgas.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Andy Colthorpe (12 April 2023). "Energy Dome: Turning a greenhouse gas into a cheaper form of energy storage than lithium-ion batteries". Editors blog. Energy Storage News. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ↑ Justine Calma (12 Oct 2022). "Meet the CO2 battery cozying up with a wind energy giant". The Verge. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
t faces stiff competition, but the CO2 battery has some unique strengths that could accelerate the transition to clean energy
- ↑ Mr. Simone Maccarini (2021). "The Carbon Dioxide for energy storage applications" (PDF). DoE. Thermochemical Power Group, University of Genoa (italy). Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ↑ "Our Technology". Corporate website. Energy Dome. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ↑ "CO2 battery licensed by Energy Dome". Power generation: news and insights. Ansaldo Energia. Retrieved 16 April 2023.