Related Research Articles

A phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. Approximately 80–100% of individuals with an amputation experience sensations in their amputated limb. However, only a small percentage will experience painful phantom limb sensation. These sensations are relatively common in amputees and usually resolve within two to three years without treatment. Research continues to explore the underlying mechanisms of phantom limb pain (PLP) and effective treatment options.
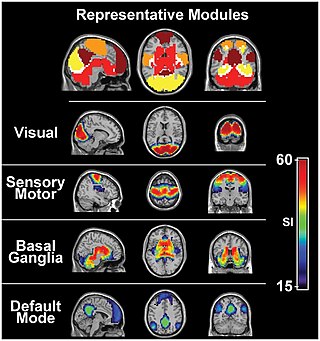
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons, neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception and interoception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, balance and visceral sensation. Sense organs are transducers that convert data from the outer physical world to the realm of the mind where people interpret the information, creating their perception of the world around them.
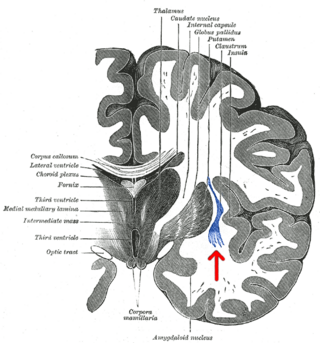
The claustrum is a thin sheet of neurons and supporting glial cells, that connects to the cerebral cortex and subcortical regions including the amygdala, hippocampus and thalamus of the brain. It is located between the insular cortex laterally and the putamen medially, encased by the extreme and external capsules respectively. Blood to the claustrum is supplied by the middle cerebral artery. It is considered to be the most densely connected structure in the brain, and thus hypothesized to allow for the integration of various cortical inputs such as vision, sound and touch, into one experience. Other hypotheses suggest that the claustrum plays a role in salience processing, to direct attention towards the most behaviorally relevant stimuli amongst the background noise. The claustrum is difficult to study given the limited number of individuals with claustral lesions and the poor resolution of neuroimaging.
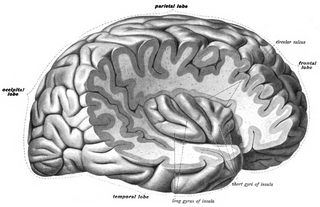
The insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain.
Affective neuroscience is the study of how the brain processes emotions. This field combines neuroscience with the psychological study of personality, emotion, and mood. The basis of emotions and what emotions are remains an issue of debate within the field of affective neuroscience.
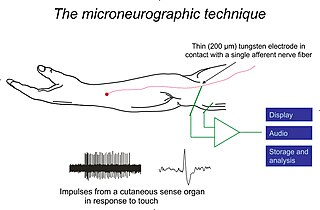
Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed to visualize and record the traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. It can also be used in animal recordings. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified nerve, a fine tungsten needle microelectrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high input impedance differential amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates nerve impulses of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.
The simulation theory of empathy holds that humans anticipate and make sense of the behavior of others by activating mental processes that, if they culminated in action, would produce similar behavior. This includes intentional behavior as well as the expression of emotions. The theory says that children use their own emotions to predict what others will do; we project our own mental states onto others.
Tactile discrimination is the ability to differentiate information through the sense of touch. The somatosensory system is the nervous system pathway that is responsible for this essential survival ability used in adaptation. There are various types of tactile discrimination. One of the most well known and most researched is two-point discrimination, the ability to differentiate between two different tactile stimuli which are relatively close together. Other types of discrimination like graphesthesia and spatial discrimination also exist but are not as extensively researched. Tactile discrimination is something that can be stronger or weaker in different people and two major conditions, chronic pain and blindness, can affect it greatly. Blindness increases tactile discrimination abilities which is extremely helpful for tasks like reading braille. In contrast, chronic pain conditions, like arthritis, decrease a person's tactile discrimination. One other major application of tactile discrimination is in new prosthetics and robotics which attempt to mimic the abilities of the human hand. In this case tactile sensors function similarly to mechanoreceptors in a human hand to differentiate tactile stimuli.

Touch is perceiving the environment using skin. Specialized receptors in the skin send signals to the brain indicating light and soft pressure, hot and cold, body position and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also includes the visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory and vestibular senses.
Haptic memory is the form of sensory memory specific to touch stimuli. Haptic memory is used regularly when assessing the necessary forces for gripping and interacting with familiar objects. It may also influence one's interactions with novel objects of an apparently similar size and density. Similar to visual iconic memory, traces of haptically acquired information are short lived and prone to decay after approximately two seconds. Haptic memory is best for stimuli applied to areas of the skin that are more sensitive to touch. Haptics involves at least two subsystems; cutaneous, or everything skin related, and kinesthetic, or joint angle and the relative location of body. Haptics generally involves active, manual examination and is quite capable of processing physical traits of objects and surfaces.

Christian Keysers is a French and German neuroscientist.
Pain empathy is a specific variety of empathy that involves recognizing and understanding another person's pain.
Mirror-touch synesthesia is a rare condition which causes individuals to experience a similar sensation in the same part or opposite part of the body that another person feels. For example, if someone with this condition were to observe someone touching their cheek, they would feel the same sensation on their own cheek. Synesthesia, in general, is described as a condition in which a concept or sensation causes an individual to experience an additional sensation or concept. Synesthesia is usually a developmental condition; however, recent research has shown that mirror touch synesthesia can be acquired after sensory loss following amputation.

Mindfulness has been defined in modern psychological terms as "paying attention to relevant aspects of experience in a nonjudgmental manner", and maintaining attention on present moment experience with an attitude of openness and acceptance. Meditation is a platform used to achieve mindfulness. Both practices, mindfulness and meditation, have been "directly inspired from the Buddhist tradition" and have been widely promoted by Jon Kabat-Zinn. Mindfulness meditation has been shown to have a positive impact on several psychiatric problems such as depression and therefore has formed the basis of mindfulness programs such as mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, mindfulness-based stress reduction and mindfulness-based pain management. The applications of mindfulness meditation are well established, however the mechanisms that underlie this practice are yet to be fully understood. Many tests and studies on soldiers with PTSD have shown tremendous positive results in decreasing stress levels and being able to cope with problems of the past, paving the way for more tests and studies to normalize and accept mindful based meditation and research, not only for soldiers with PTSD, but numerous mental inabilities or disabilities.

Tactile hallucination is the false perception of tactile sensory input that creates a hallucinatory sensation of physical contact with an imaginary object. It is caused by the faulty integration of the tactile sensory neural signals generated in the spinal cord and the thalamus and sent to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI) and secondary somatosensory cortex (SII). Tactile hallucinations are recurrent symptoms of neurological diseases such as schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Ekbom's syndrome and delirium tremens. Patients who experience phantom limb pains also experience a type of tactile hallucination. Tactile hallucinations are also caused by drugs such as cocaine and alcohol.
C tactile afferents are nerve receptors in mammalian skin that generally respond to nonpainful stimulation such as light touch. For this reason they are classified as ‘low-threshold mechanoreceptors’. As group C nerve fibers, they are unmyelinated and have slow conduction velocities. They are mostly associated with the sensation of pleasant touch, though they may also mediate some forms of pain. CT afferents were discovered by Åke Vallbo using the technique of microneurography.

Interoception is the collection of senses providing information to the organism about the internal state of the body. This can be both conscious and subconscious. It encompasses the brain's process of integrating signals relayed from the body into specific subregions—like the brainstem, thalamus, insula, somatosensory, and anterior cingulate cortex—allowing for a nuanced representation of the physiological state of the body. This is important for maintaining homeostatic conditions in the body and, potentially, facilitating self-awareness.
Meditation and pain is the study of the physiological mechanisms underlying meditation—specifically its neural components—that implicate it in the reduction of pain perception.
Social cognitive neuroscience is the scientific study of the biological processes underpinning social cognition. Specifically, it uses the tools of neuroscience to study "the mental mechanisms that create, frame, regulate, and respond to our experience of the social world". Social cognitive neuroscience uses the epistemological foundations of cognitive neuroscience, and is closely related to social neuroscience. Social cognitive neuroscience employs human neuroimaging, typically using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Human brain stimulation techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct-current stimulation are also used. In nonhuman animals, direct electrophysiological recordings and electrical stimulation of single cells and neuronal populations are utilized for investigating lower-level social cognitive processes.
Valeria Gazzola is an Italian neuroscientist, associate professor at the Faculty of Social and Behavioral Sciences at the University of Amsterdam (UvA) and member of the Young Academy of Europe. She is also a tenured department head at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience (NIN) in Amsterdam, where she leads her own research group and the Social Brain Lab together with neuroscientist Christian Keysers. She is a specialist in the neural basis of empathy and embodied cognition: Her research focusses on how the brain makes individuals sensitive to the actions and emotions of others and how this affects decision-making.
References
- ↑ Sahi, Razia S.; Dieffenbach, Macrina C.; Gan, Siyan; Lee, Maya; Hazlett, Laura I.; Burns, Shannon M.; Lieberman, Matthew D.; Shamay-Tsoory, Simone G.; Eisenberger, Naomi I. (2021-02-09). "The comfort in touch: Immediate and lasting effects of handholding on emotional pain". PLOS ONE. 16 (2): e0246753. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1646753S. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246753 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 7872251 . PMID 33561164.
- 1 2 Call, Josep; Aureli, Filippo; de Waal, Frans B.M. (July 1999). "Reconciliation patterns among stumptailed macaques: a multivariate approach". Animal Behaviour. 58 (1): 165–172. doi:10.1006/anbe.1999.1116. ISSN 0003-3472. PMID 10413553. S2CID 28385684.
- ↑ Suvilehto, Juulia T.; Glerean, Enrico; Dunbar, Robin I. M.; Hari, Riitta; Nummenmaa, Lauri (2015-11-10). "Topography of social touching depends on emotional bonds between humans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (45): 13811–13816. Bibcode:2015PNAS..11213811S. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519231112 . ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4653180 . PMID 26504228.
- ↑ Suvilehto, Juulia T.; Nummenmaa, Lauri; Harada, Tokiko; Dunbar, Robin I. M.; Hari, Riitta; Turner, Robert; Sadato, Norihiro; Kitada, Ryo (2019-04-24). "Cross-cultural similarity in relationship-specific social touching". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 286 (1901): 20190467. doi:10.1098/rspb.2019.0467. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 6501924 . PMID 31014213.
- ↑ Clay, Zanna; de Waal, Frans B. M. (2013-01-30). Noë, Ronald (ed.). "Bonobos Respond to Distress in Others: Consolation across the Age Spectrum". PLOS ONE. 8 (1): e55206. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...855206C. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055206 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3559394 . PMID 23383110.
- ↑ Eckstein, Monika; Mamaev, Ilshat; Ditzen, Beate; Sailer, Uta (2020). "Calming Effects of Touch in Human, Animal, and Robotic Interaction—Scientific State-of-the-Art and Technical Advances". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 11: 1153. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.555058 . ISSN 1664-0640. PMC 7672023 . PMID 33329093.
- ↑ Uvnäs-Moberg, Kerstin; Handlin, Linda; Petersson, Maria (2015-01-12). "Self-soothing behaviors with particular reference to oxytocin release induced by non-noxious sensory stimulation". Frontiers in Psychology. 5: 1529. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01529 . ISSN 1664-1078. PMC 4290532 . PMID 25628581.
- ↑ Khodabakhsh, Sonia (2021-07-07). "Factors Affecting Life Satisfaction of Older Adults in Asia: A Systematic Review". Journal of Happiness Studies. 23 (3): 1289–1304. doi:10.1007/s10902-021-00433-x. ISSN 1389-4978. S2CID 237829194.
- ↑ Björklund, Anders; Dunnett, Stephen B. (May 2007). "Fifty years of dopamine research". Trends in Neurosciences. 30 (5): 185–187. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2007.03.004. ISSN 0166-2236. PMID 17397938. S2CID 15069210.
- ↑ Morrison, India (December 2016). "Keep Calm and Cuddle on: Social Touch as a Stress Buffer". Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology. 2 (4): 344–362. doi: 10.1007/s40750-016-0052-x . ISSN 2198-7335. S2CID 151590286.
- 1 2 Coan, James A.; Schaefer, Hillary S.; Davidson, Richard J. (December 2006). "Lending a Hand". Psychological Science. 17 (12): 1032–1039. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01832.x. ISSN 0956-7976. PMID 17201784. S2CID 3446344.
- ↑ Harlow, H. F.; Dodsworth, R. O.; Harlow, M. K. (1965-07-01). "Total social isolation in monkeys". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 54 (1): 90–97. Bibcode:1965PNAS...54...90H. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.90 . ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 285801 . PMID 4955132.
- ↑ Suomi, Stephen J.; Leroy, Helen A. (1982). "In memoriam: Harry F. Harlow (1905-1981)". American Journal of Primatology. 2 (4): 319–342. doi:10.1002/ajp.1350020402. ISSN 0275-2565. PMID 32188173.
- ↑ Tavris, Carol A. (2014-09-30). "Teaching Contentious Classics". APS Observer. 27 (8).
- ↑ Barnett, Lynn (August 2005). "Keep in touch: The importance of touch in infant development". Infant Observation. 8 (2): 115–123. doi:10.1080/13698030500171530. ISSN 1369-8036. S2CID 144169988.
- ↑ Feldman, Ruth; Singer, Magi; Zagoory, Orna (March 2010). "Touch attenuates infants' physiological reactivity to stress". Developmental Science. 13 (2): 271–278. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2009.00890.x. ISSN 1363-755X. PMID 20136923.
- ↑ Field, Tiffany (April 2001). "Massage Therapy Facilitates Weight Gain in Preterm Infants". Current Directions in Psychological Science. 10 (2): 51–54. doi:10.1111/1467-8721.00113. ISSN 0963-7214. S2CID 145369350.
- ↑ Schore, Allan N. (January 2001). "Effects of a secure attachment relationship on right brain development, affect regulation, and infant mental health". Infant Mental Health Journal. 22 (1–2): 7–66. doi:10.1002/1097-0355(200101/04)22:1<7::aid-imhj2>3.0.co;2-n. ISSN 0163-9641.
- ↑ The developing mind: how relationships and the brain interact to shape who we are. 2012-10-01.
- ↑ Cekaite, Asta; Kvist Holm, Malva (2017-04-03). "The Comforting Touch: Tactile Intimacy and Talk in Managing Children's Distress". Research on Language and Social Interaction. 50 (2): 109–127. doi: 10.1080/08351813.2017.1301293 . ISSN 0835-1813. S2CID 41680345.
- ↑ Dawson, Geraldine; Frey, Karin; Panagiotides, Heracles; Osterling, Julie; HessI, David (February 1997). "Infants of Depressed Mothers Exhibit Atypical Frontal Brain Activity A Replication and Extension of Previous Findings". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 38 (2): 179–186. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01852.x. ISSN 0021-9630. PMID 9232464.
- ↑ Nelson, Charles A.; Zeanah, Charles H.; Fox, Nathan A. (2019-01-15). "How Early Experience Shapes Human Development: The Case of Psychosocial Deprivation". Neural Plasticity. 2019: 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2019/1676285 . ISSN 2090-5904. PMC 6350537 . PMID 30774652.
- ↑ Meehan, Therese C. (July 1998). "Therapeutic touch as a nursing intervention: Integrative literature reviews and meta-analyses". Journal of Advanced Nursing. 28 (1): 117–125. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2648.1998.00771.x. PMID 9687138. S2CID 32762335.
- ↑ Whelan, Kathleen M.; Wishnia, Gracie S. (July 2003). "Reiki Therapy". Holistic Nursing Practice. 17 (4): 209–217. doi:10.1097/00004650-200307000-00008. ISSN 0887-9311. PMID 12889549. S2CID 34464263.
- ↑ So, Pui Shan; Jiang, Johnny Y; Qin, Ying (2008-10-08), So, Pui Shan (ed.), "Touch therapies for pain relief in adults", Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4), Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: CD006535, doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006535.pub2, PMID 18843720 , retrieved 2021-11-13
- ↑ Weekes, DeLois P.; Kagan, Sarah H.; James, Kelly; Seboni, Naomi (January 1993). "The Phenomenon of Hand Holding as a Coping Strategy in Adolescents Experiencing Treatment-Related Pain". Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing. 10 (1): 19–25. doi:10.1177/104345429301000105. ISSN 1043-4542. PMID 8435155. S2CID 24938732.
- ↑ "Touching During and After Childbirth", Touch in Early Development, Psychology Press, pp. 33–48, 2014-02-25, doi:10.4324/9781315806112-8, ISBN 9781315806112 , retrieved 2021-11-24
- ↑ Goldstein, Pavel; Weissman-Fogel, Irit; Dumas, Guillaume; Shamay-Tsoory, Simone G. (2018-02-26). "Brain-to-brain coupling during handholding is associated with pain reduction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115 (11): E2528–E2537. Bibcode:2018PNAS..115E2528G. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703643115 . ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 5856497 . PMID 29483250.
- 1 2 Kinreich, Sivan; Djalovski, Amir; Kraus, Lior; Louzoun, Yoram; Feldman, Ruth (December 2017). "Brain-to-Brain Synchrony during Naturalistic Social Interactions". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 17060. Bibcode:2017NatSR...717060K. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-17339-5. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 5719019 . PMID 29213107. S2CID 19774735.
- ↑ López-Solà, Marina; Koban, Leonie; Wager, Tor D. (November 2018). "Transforming Pain With Prosocial Meaning: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study". Psychosomatic Medicine. 80 (9): 814–825. doi:10.1097/psy.0000000000000609. ISSN 1534-7796. PMC 6218300 . PMID 29846310.
- 1 2 Fairhurst, Merle T; McGlone, Francis; Croy, Ilona (February 2022). "Affective touch: a communication channel for social exchange". Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences. 43: 54–61. doi:10.1016/j.cobeha.2021.07.007. ISSN 2352-1546. S2CID 237579186.
- ↑ Kraus, Jakub; Frick, Andreas; Roman, Robert; Jurkovičová, Lenka; Mareček, Radek; Mikl, Michal; Brázdil, Milan; Fredrikson, Mats (2019-11-01). "Soothing the emotional brain: modulation of neural activity to personal emotional stimulation by social touch". Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. 14 (11): 1179–1185. doi:10.1093/scan/nsz090. ISSN 1749-5016. PMC 7057286 . PMID 31820813.
- ↑ Fred., Levin (2009). Emotion and the psychodynamics of the cerebellum : a neuro-psychoanalytical analysis and synthesis. Karnac. ISBN 978-1-84940-850-9. OCLC 729246854.
- ↑ Strata, Piergiorgio (2015-01-28). "The Emotional Cerebellum". The Cerebellum. 14 (5): 570–577. doi:10.1007/s12311-015-0649-9. ISSN 1473-4222. PMID 25626523. S2CID 12776671.
- ↑ Small, Dana M. (2010-05-29). "Taste representation in the human insula". Brain Structure and Function. 214 (5–6): 551–561. doi:10.1007/s00429-010-0266-9. ISSN 1863-2653. PMID 20512366. S2CID 25481014.
- ↑ Wright, P.; He, G.; Shapira, N. A.; Goodman, W. K.; Liu, Y. (October 2004). "Disgust and the insula: fMRI responses to pictures of mutilation and contamination". NeuroReport. 15 (15): 2347–2351. doi:10.1097/00001756-200410250-00009. ISSN 0959-4965. PMID 15640753. S2CID 6864309.
- ↑ Wicker, Bruno; Keysers, Christian; Plailly, Jane; Royet, Jean-Pierre; Gallese, Vittorio; Rizzolatti, Giacomo (October 2003). "Both of Us Disgusted in My Insula". Neuron. 40 (3): 655–664. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00679-2 . ISSN 0896-6273. PMID 14642287. S2CID 766157.
- ↑ McGlone, Francis; Wessberg, Johan; Olausson, Håkan (May 2014). "Discriminative and Affective Touch: Sensing and Feeling". Neuron. 82 (4): 737–755. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.001 . ISSN 0896-6273. PMID 24853935. S2CID 17883511.
- 1 2 3 Löken, Line S.; Wessberg, Johan; Morrison, India; McGlone, Francis; Olausson, Håkan (2009). "Coding of pleasant touch by unmyelinated afferents in humans". Nature Neuroscience. 12 (5): 547–548. doi:10.1038/nn.2312. PMID 19363489. S2CID 4311541.
- ↑ Håkan, Perini, Irene Morrison, India Olausson (2015). Seeking pleasant touch: neural correlates of behavioral preferences for skin stroking. Linköpings universitet, Avdelningen för neuro-och inflammationsvetenskap. OCLC 1234124087.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Hughes, Richard A. C. (1990), "Clinical Features of Guillain-Barré Syndrome", Guillain-Barré Syndrome, Clinical Medicine and the Nervous System, London: Springer London, pp. 121–140, doi:10.1007/978-1-4471-3175-5_6, ISBN 978-1-4471-3177-9 , retrieved 2021-11-18
- ↑ Peled-Avron, Leehe; Shamay-Tsoory, Simone G. (2017-03-24). "Don't touch me! autistic traits modulate early and late ERP components during visual perception of social touch". Autism Research. 10 (6): 1141–1154. doi:10.1002/aur.1762. ISSN 1939-3792. PMID 28339141. S2CID 23554343.
- 1 2 Olausson, H.; Lamarre, Y.; Backlund, H.; Morin, C.; Wallin, B.G.; Starck, G.; Ekholm, S.; Strigo, I.; Worsley, K.; Vallbo, Å.B.; Bushnell, M.C. (2002). "Unmyelinated tactile afferents signal touch and project to insular cortex". Nature Neuroscience. 5 (9): 900–904. doi:10.1038/nn896. PMID 12145636. S2CID 14648389.
- ↑ Namkung, Ho; Kim, Sun-Hong; Sawa, Akira (August 2018). "The Insula: An Underestimated Brain Area in Clinical Neuroscience, Psychiatry, and Neurology". Trends in Neurosciences. 41 (8): 551–554. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.05.004 . ISSN 0166-2236. PMID 29895478. S2CID 48360408.
- ↑ Håkan, McGlone, Francis Wessberg, Johan Olausson (2014). Discriminative and Affective Touch: Sensing and Feeling. Linköpings universitet, Avdelningen för neuro-och inflammationsvetenskap. OCLC 1234123163.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Håkan, Liljencrantz, Jaquette Olausson (2014-03-06). Tactile C fibers and their contributions to pleasant sensations and to tactile allodynia. Frontiers Media S.A. OCLC 908676124.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Pawling, Ralph; Cannon, Peter R.; McGlone, Francis P.; Walker, Susannah C. (2017-03-10). "C-tactile afferent stimulating touch carries a positive affective value". PLOS ONE. 12 (3): e0173457. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1273457P. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173457 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5345811 . PMID 28282451.
- 1 2 Saarinen, Aino; Harjunen, Ville; Jasinskaja-Lahti, Inga; Jääskeläinen, Iiro P.; Ravaja, Niklas (December 2021). "Social touch experience in different contexts: A review". Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 131: 360–372. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.027 . ISSN 0149-7634. PMID 34537266. S2CID 237524220.
- 1 2 Crane, Laura; Goddard, Lorna; Pring, Linda (May 2009). "Sensory processing in adults with autism spectrum disorders". Autism. 13 (3): 215–228. doi:10.1177/1362361309103794. ISSN 1362-3613. PMID 19369385. S2CID 30227503.
- ↑ Failla, Michelle D.; Gerdes, Madison B.; Williams, Zachary J.; Moore, David J.; Cascio, Carissa J. (November 2020). "Increased pain sensitivity and pain-related anxiety in individuals with autism". PAIN Reports. 5 (6): e861. doi:10.1097/pr9.0000000000000861. ISSN 2471-2531. PMC 7676593 . PMID 33235944.