
In economics, inflation refers to a general progressive increase in prices of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualised percentage change in a general price index.
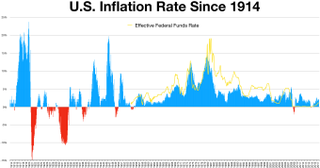
A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.
In economics, the GDP deflator is a measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy in a year. GDP stands for gross domestic product, the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within the territory of a country over a particular period of time.
The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves. It analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures, by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint.
The terms of trade (TOT) is the relative price of exports in terms of imports and is defined as the ratio of export prices to import prices. It can be interpreted as the amount of import goods an economy can purchase per unit of export goods.

Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living. Changes in the cost of living over time are often operationalized in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living in different geographic areas. Differences in cost of living between locations can also be measured in terms of purchasing power parity rates.
In economics, nominal value is measured in terms of money, whereas real value is measured against goods or services. A real value is one which has been adjusted for inflation, enabling comparison of quantities as if the prices of goods had not changed on average. Changes in value in real terms therefore exclude the effect of inflation. In contrast with a real value, a nominal value has not been adjusted for inflation, and so changes in nominal value reflect at least in part the effect of inflation.
The PCE price index (PCEPI), also referred to as the PCE deflator, PCE price deflator, or the Implicit Price Deflator for Personal Consumption Expenditures by the BEA, and as the Chain-type Price Index for Personal Consumption Expenditures (CTPIPCE) by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), is a United States-wide indicator of the average increase in prices for all domestic personal consumption. It is benchmarked to a base of 2012 = 100. Using a variety of data including U.S. Consumer Price Index and Producer Price Index prices, it is derived from the largest component of the GDP in the BEA's National Income and Product Accounts, personal consumption expenditures.
A price index is a normalized average of price relatives for a given class of goods or services in a given region, during a given interval of time. It is a statistic designed to help to compare how these price relatives, taken as a whole, differ between time periods or geographical locations.

The Producer Price Index (PPI) is the official measure of producer prices in the economy of the United States. It measures average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output. The PPI was known as the Wholesale Price Index, or WPI, up to 1978. It is published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics and is one of the oldest economic time series compiled by the Federal government of the United States.

The general price level is a hypothetical measure of overall prices for some set of goods and services, in an economy or monetary union during a given interval, normalized relative to some base set. Typically, the general price level is approximated with a daily price index, normally the Daily CPI. The general price level can change more than once per day during hyperinflation.
In Statistics, Economics and Finance, an index is a statistical measure of change in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from different perspectives.
The Consumer Expenditure Survey is a Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) household survey that collects information on the buying habits of U.S. consumers. The program consists of two components — the Interview Survey and the Diary Survey — each with its own sample. The surveys collect data on expenditures, income, and consumer unit characteristics. In May 2020, the American Association for Public Opinion Research recognized the CE program with its 2020 Policy Impact Award, for joint work by the BLS -- including CE and the Division of Price and Index Number Research -- and the Census Bureau on the Supplemental Poverty thresholds and measure, and the essential contributions these data products have made to the understanding, discussion, and advancement of public policy related to the alleviation of poverty in the United States.
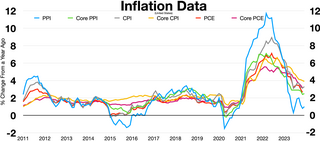
The United States Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a set of consumer price indices calculated by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). To be precise, the BLS routinely computes many different CPIs that are used for different purposes. Each is a time series measure of the price of consumer goods and services. The BLS publishes the CPI monthly.
The Gerschenkron effect, developed by Alexander Gerschenkron, claims that changing the base year for an index determines the growth rate of the index. This effect is applicable only to aggregation method using reference price structure or reference volume structure. However, if production is measured by "real" tearms, this effect does not exist.
In economics, the Törnqvist index is a price or quantity index. In practice, Törnqvist index values are calculated for consecutive periods, then these are strung together, or "chained". Thus, the core calculation does not refer to a single base year.
This page lists details of the consumer price index by country
A hedonic index is any price index which uses information from hedonic regression, which describes how product price could be explained by the product's characteristics. Hedonic price indexes have proved to be very useful when applied to calculate price indices for information and communication products and housing, because they can successfully mitigate problems such as those that arise from there being new goods to consider and from rapid changes of quality.
The United States Chained Consumer Price Index (C-CPI-U), also known as chain-weighted CPI or chain-linked CPI is a time series measure of price levels of consumer goods and services created by the Bureau of Labor Statistics as an alternative to the US Consumer Price Index. It is based on the idea that when prices of different goods change at different rates, consumers will adjust their purchasing patterns by purchasing more of products whose relative prices have declined and fewer of those whose relative price has increased. This reduces the cost of living reported, but has no change on the cost of living; it is simply a way of accounting for a microeconomic "substitution effect." The "fixed weight" CPI also takes such substitutions into account, but does so through a periodic adjustment of the "basket of goods" that it represents, rather than through a continuous adjustment in that basket. Application of the chained CPI to federal benefits has been controversially proposed to reduce the federal deficit.






