
Pseudotsuga macrocarpa, commonly called the bigcone spruce or bigcone Douglas-fir, is an evergreen conifer native to the mountains of southern California. It is notable for having the largest cones in the genus Pseudotsuga, hence the name.

Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the coolest month, and feature hot temperatures all year-round. Annual precipitation is often abundant in tropical climates, and shows a seasonal rhythm but may have seasonal dryness to varying degrees. There are normally only two seasons in tropical climates, a wet season and a dry season. The annual temperature range in tropical climates is normally very small. Sunlight is intense in these climates.

Ficus benjamina, commonly known as weeping fig, benjamin fig or ficus tree, and often sold in stores as just ficus, is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae, native to Asia and Australia. It is the official tree of Bangkok. The species is also naturalized in the West Indies and in the states of Florida and Arizona in the United States. In its native range, its small fruit are favored by some birds.

Ipomoea alba, sometimes called the tropical white morning-glory or moonflower or moon vine, is a species of night-blooming morning glory, native to tropical and subtropical regions of North and South America, from Argentina to northern Mexico, Arizona, Florida and the West Indies. Though formerly classified as genus Calonyction, species aculeatum, it is now properly assigned to genus Ipomoea, subgenus Quamoclit, section Calonyction.

Lawsonia inermis, also known as hina, the henna tree, the mignonette tree, and the Egyptian privet, is a flowering plant and one of the only two species of the genus Lawsonia, with the other being Lawsonia odorata. The species is named after the Scottish physician Isaac Lawson, a good friend of Linnaeus.

Mount Danxia is a noted scenic mountainous area in Renhua County, in the northern part of Guangdong province. It is described on the local signage as a "world famous UNESCO geopark of China". It was inscribed as part of the China Danxia World Heritage Site in 2010 because of its unique geographical in formations and spectacular scenery.

Ulmus macrocarpaHance, the large-fruited elm, is a deciduous tree or large shrub endemic to the Far East excluding Japan. It is notable for its tolerance of drought and extreme cold and is the predominant vegetation on the dunes of the Khorchin sandy lands in the Jilin province of north-eastern China, making a small tree at the base of the dunes, and a shrub at the top.

Climate of Peru describes the diverse climates of this large South American country with an area of 1,285,216 km2 (496,225 sq mi). Peru is located entirely in the tropics but features desert and mountain climates as well as tropical rainforests. Elevations above sea level in the country range from −37 to 6,778 m and precipitation ranges from less than 20 mm (0.79 in) annually to more than 8,000 mm (310 in). There are three main climatic regions: the Pacific Ocean coast is one of the driest deserts in the world but with some unique features; the high Andes mountains have a variety of microclimates depending on elevation and exposure and with temperatures and precipitation from temperate to polar and wet to dry; and the Amazon basin has tropical climates, mostly with abundant precipitation, along with sub-tropical climates in elevations above 1,550 m (5,090 ft).
Gum base is the non-nutritive, non-digestible, water-insoluble masticatory delivery system used to carry sweeteners, flavors, and any other substances in chewing gum and bubble gum. It provides all the basic textural and masticatory properties of gum.

Carissa macrocarpa is a shrub native to tropical and southern Africa. It is commonly known as the Natal plum and, in South Africa, the large num-num. In Zulu, as well as in the Bantu tribes of Uganda, it is called Amathungulu or umThungulu oBomvu. In Afrikaans the fruit is called noem-noem.

Rasbora tawarensis, locally known as depik, is a critically endangered species of cyprinid fish. It is endemic to Lake Laut Tawar in Indonesia, where its population is rapidly decreasing due to ecological disturbances, global warming, introduced species, unlawful fishing practices, and pollution.

Sapium glandulosum is a species of tree in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is native to the Neotropics from Mexico and the Caribbean south to Argentina, and it has been cultivated elsewhere. It is the most common Sapium species. Its common names include gumtree, milktree, leche de olivo, and olivo macho.

Vateria indica, the white dammar, is a species of tree in the family Dipterocarpaceae. It is endemic to the Western Ghats mountains in India. It is threatened by habitat loss. It is a large canopy or emergent tree frequent in tropical wet evergreen forests of the low and mid-elevations.

The Southern Andean Yungas is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Yungas of southwestern Bolivia and northwestern Argentina.

Mammillaria magnimamma, common name Mexican pincushion, is a species of flowering plant in the cactus family Cactaceae.
Ozimops petersi, the inland free-tailed bat is a species of bat found in Australia.

Couma utilis, called the milk tree, sorvinha, sorveira, sorva, and sorva-pequena, is a species of flowering plant in the subfamily Rauvolfioideae, native to the Orinoco and Amazon basins of South America. It is thought that C. utilis was on the verge of being domesticated by indigenous Amazonian peoples prior to the arrival of Europeans in the New World.

Polyscias fulva is a species of flowering plant. It is an evergreen or deciduous tree, native to the mountains of tropical Africa and the southwestern Arabian Peninsula.
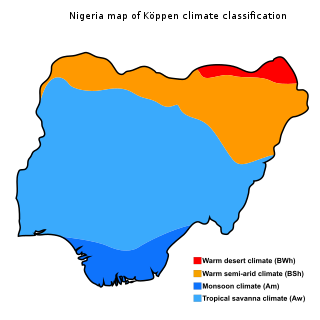
The Climate of Nigeria is mostly tropical. Nigeria has three distinct climatic zones, two seasons and an average temperature, ranging between 21 °C and 35 °C. Two major elements determines the temperature in Nigeria - the altitude of the Sun and the atmosphere's transparency determined by the duo interplay of rainfall and humidity, while the rainfall is mediated by three distinct conditions including convectional, frontal and orographical determinants. In a recent data showing Nigeria's annual temperature and rainfall variations by the World Bank Group, Nigeria's highest average annual mean-temperature is 28.1 °C in 1938, which indicates that 1938 is the driest year, while the wettest year is 1957 with an annual mean rainfall of 1,441.45mm.


















