Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence). A person who commits espionage is called an espionage agent or spy. Any individual or spy ring, in the service of a government, company, criminal organization, or independent operation, can commit espionage. The practice is clandestine, as it is by definition unwelcome. In some circumstances, it may be a legal tool of law enforcement and in others, it may be illegal and punishable by law.

Counterintelligence (counter-intelligence) or counterespionage (counter-espionage) is any activity aimed at protecting an agency's intelligence program from an opposition's intelligence service. It includes gathering information and conducting activities to prevent espionage, sabotage, assassinations or other intelligence activities conducted by, for, or on behalf of foreign powers, organizations or persons.
In espionage jargon, a mole is a long-term spy who is recruited before having access to secret intelligence, subsequently managing to get into the target organization. However, it is popularly used to mean any long-term clandestine spy or informant within an organization. In police work, a mole is an undercover law-enforcement agent who joins an organization in order to collect incriminating evidence about its operations and to eventually charge its members.
A covert operation or undercover operation is a military or police operation involving a covert agent or troops acting under an assumed cover to conceal the identity of the party responsible. Some of the covert operations are also clandestine operations which are performed in secret and meant to stay secret, though many are not.

James Jesus Angleton was an American intelligence operative who served as chief of counterintelligence for the Central Intelligence Agency from 1954 to 1975. According to Director of Central Intelligence Richard Helms, Angleton "was recognized as the dominant counterintelligence figure in the non-communist world."

Reinhard Gehlen was a German lieutenant-general and intelligence officer. He was chief of the Wehrmacht Foreign Armies East military intelligence service on the eastern front during World War II. During the early Cold War, Gehlen sided with the Western Allies as the spymaster of the CIA-funded anti-Soviet Gehlen Organization (1946–56) and the founding president of the Federal Intelligence Service of West Germany (1956–68).

The Bureau of Diplomatic Security, commonly known as Diplomatic Security (DS), is the security branch of the United States Department of State. It conducts international investigations, threat analysis, cyber security, counterterrorism, and protection of people, property, and information. Its mission is to provide a safe and secure environment for officials to execute the foreign policy of the United States.

Tradecraft, within the intelligence community, refers to the techniques, methods, and technologies used in modern espionage (spying) and generally as part of the activity of intelligence assessment. This includes general topics or techniques, or the specific techniques of a nation or organization.

The Directorate of Operations (DO), less formally called the Clandestine Service, is a component of the US Central Intelligence Agency. It was known as the Directorate of Plans from 1951 to 1973; as the Directorate of Operations from 1973 to 2005; and as the National Clandestine Service (NCS) from 2005 to 2015.

Meir Amit was an Israeli politician and cabinet minister. He served as the Chief Director and the head of global operations for Mossad from 1963 to 1968, before entering into politics and holding two ministerial positions. He was also widely regarded as the most successful intelligence officer and a leading political figure for Israel.
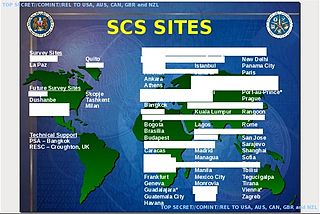
The Special Collection Service (SCS), codenamed F6, is a highly classified joint U.S. Central Intelligence Agency–National Security Agency program charged with inserting eavesdropping equipment in difficult-to-reach places, such as foreign embassies, communications centers, and foreign government installations. Established in the late 1970s and headquartered in Beltsville, Maryland, the SCS has been involved in operations ranging from the Cold War to the Global War on Terrorism.
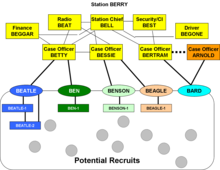
Clandestine human intelligence is intelligence collected from human sources using clandestine espionage methods. These sources consist of people working in a variety of roles within the intelligence community. Examples include the quintessential spy, who collects intelligence; couriers and related personnel, who handle an intelligence organization's (ideally) secure communications; and support personnel, such as access agents, who may arrange the contact between the potential spy and the case officer who recruits them. The recruiter and supervising agent may not necessarily be the same individual. Large espionage networks may be composed of multiple levels of spies, support personnel, and supervisors. Espionage networks are typically organized as a cell system, in which each clandestine operator knows only the people in his own cell, perhaps the external case officer, and an emergency method to contact higher levels if the case officer or cell leader is captured, but has no knowledge of people in other cells. This cellular organization is a form of compartmentalisation, which is an important tactic for controlling access to information, used in order to diminish the risk of discovery of the network or the release of sensitive information.
The Clandestine HUMINT page adheres to the functions within the discipline, including espionage and active counterintelligence.

John Chris Kiriakou is an American author, journalist and former intelligence officer. Kiriakou is a columnist with Reader Supported News and co-host of Political Misfits on Sputnik Radio.
Clandestine HUMINT asset recruiting refers to the recruitment of human agents, commonly known as spies, who work for a foreign government, or within a host country's government or other target of intelligence interest for the gathering of human intelligence. The work of detecting and "doubling" spies who betray their oaths to work on behalf of a foreign intelligence agency is an important part of counterintelligence.
While the CIA cooperates with its French counterpart, the DGSE, the countries do collect information on one another, especially in the economic and scientific areas.

The Spy Museum is the world's first public museum of international espionage, located in Tampere, Finland. The museum was founded in 1998. The idea of the museum was invented by Teppo Turja, who founded the museum. The museum is the only one of its kind in Europe, besides Spy Museum Berlin.
Michael Ross is a Canadian-Israeli expert on intelligence gathering and a former Mossad officer, or "combatant" with a focus upon human source intelligence collection (Humint). Ross speaks upon intelligence issues and publishes articles, and he is the author of the book The Volunteer: The Incredible True Story of an Israeli Spy on the Trail of International Terrorists. Ross advocates vigilance and the continual improvement of intelligence collection systems in order to protect free societies. In August 2007, Ross authored an article in the Canadian daily, National Post entitled, "Obama got it right" wherein he wrote that Osama bin Laden was hiding in Pakistan having been provided sanctuary by Pakistan's Directorate for Inter-Service Intelligence (ISI). Ross urged then presidential nominee, Barack Obama, to engage in unilateral intelligence and military action in Pakistan to hunt and kill al-Qaeda leaders including Osama bin Laden.

The Institute for Intelligence and Special Operations, popularly known as Mossad, is the national intelligence agency of Israel. It is one of the main entities in the Israeli Intelligence Community, along with Aman and Shin Bet.

Spying, as well as other intelligence assessment, has existed since ancient history. In the 1980s scholars characterized foreign intelligence as "the missing dimension" of historical scholarship." Since then a largely popular and scholarly literature has emerged. Special attention has been paid to World War II, as well as the Cold War era (1947–1989) that was a favorite for novelists and filmmakers.