
The European Environment Agency (EEA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) which provides independent information on the environment.
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border region.
The European Union has a number of relationships with nations that are not formally part of the Union. According to the European Union's official site, and a statement by Commissioner Günter Verheugen, the aim is to have a ring of countries, sharing EU's democratic ideals and joining them in further integration without necessarily becoming full member states.

The regional policy of the European Union (EU), also referred as Cohesion Policy, is a policy with the stated aim of improving the economic well-being of regions in the European Union and also to avoid regional disparities. More than one third of the EU's budget is devoted to this policy, which aims to remove economic, social and territorial disparities across the EU, restructure declining industrial areas and diversify rural areas which have declining agriculture. In doing so, EU regional policy is geared towards making regions more competitive, fostering economic growth and creating new jobs. The policy also has a role to play in wider challenges for the future, including climate change, energy supply and globalisation.
The Structural Funds and the Cohesion Fund are financial tools set up to implement the regional policy of the European Union. They aim to reduce regional disparities in income, wealth and opportunities. Europe's poorer regions receive most of the support, but all European regions are eligible for funding under the policy's various funds and programmes. The current Regional Policy framework is set for a period of seven years, from 2014 to 2020.
The Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF) of the European Union, also called the financial perspective, is a seven-year framework regulating its annual budget. It is laid down in a unanimously adopted Council Regulation with the consent of the European Parliament. The financial framework sets the maximum amount of spendings in the EU budget each year for broad policy areas ("headings") and fixes an overall annual ceiling on payment and commitment appropriations.

The European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) is a fund allocated by the European Union. Its purpose is to transfer money from richer regions, and invest it in the infrastructure and services of underdeveloped regions. This will allow those regions to start attracting private sector investments, and create jobs on their own.
The CARDS programme, of Community Assistance for Reconstruction, Development and Stabilisation, is the EU's main instrument of financial assistance to the Western Balkans, covering specifically the countries of Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Kosovo and Albania. It was created in 2000 by Council Regulation 2666/2000. However it was only in 2001 that the programme became operative under its own regulations, as in the first period it supported projects previously funded by the PHARE and OBNOVA programmes. The programme is the main financial instrument of EU's Stabilisation and Association process (SAp). A total of €5.13 billion is secured for all CARDS actions during 2000-2006, as after that day it will be replaced by the Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance (IPA), which will cover both candidate and potential candidate countries.
Interreg is a series of programmes to stimulate cooperation between regions in and out of the European Union (EU), funded by the European Regional Development Fund. The first Interreg started in 1989. Interreg IV covered the period 2007–2013. Interreg V (2014–2020) covers all 27 EU member states, the EFTA countries, six accession countries and 18 neighbouring countries. It has a budget of EUR 10.1 billion, which represents 2.8% of the total of the European Cohesion Policy budget. Since the non EU countries don't pay EU membership fee, they contribute directly to Interreg, not through ERDF.
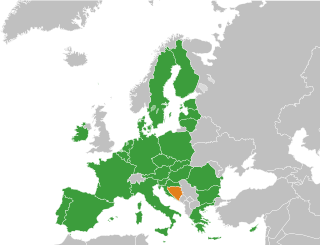
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union is the stated aim of the present relations between the two entities. Bosnia and Herzegovina has been recognised by the EU as a "potential candidate country" for accession since the decision of the European Council in Thessaloniki in 2003 and is on the current agenda for future enlargement of the EU. Bosnia and Herzegovina takes part in the Stabilisation and Association Process and trade relations are regulated by an Interim Agreement.
The Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance, or simply IPA, is a funding mechanism of the European Union. As of 2007, it replaced previous programmes such as the PHARE, ISPA, SAPARD and CARDS. Unlike the previous assistance programs, IPA offers funds to both EU candidate countries and potential candidates.
A cross-border region is a territorial entity that is made of several local or regional authorities that are co-located yet belong to different nation states. Cross-border regions exist to take advantage of geographical conditions to strengthen their competitiveness.
The European Grouping for Territorial Cooperation (EGTC) is a European Union level form of transnational cooperation between countries and local authorities with legal personality. EU Council Regulation 1082/2006 of 5 July 2006 forms its legal basis. As of April 2016, 62 EGTCs are in existence.

Region Sønderjylland–Schleswig is the regional centre for cross-border cooperation between the municipalities of Tønder, Aabenraa, Haderslev and Sønderborg, and regional council of southern Denmark, the districts Schleswig-Flensburg and Nordfriesland, plus the city of Flensburg.

The LIFE Programme is the European Union’s funding instrument for the environment and climate action. The general objective of LIFE is to contribute to the implementation, updating and development of EU environmental and climate policy and legislation by co-financing projects with European added value.
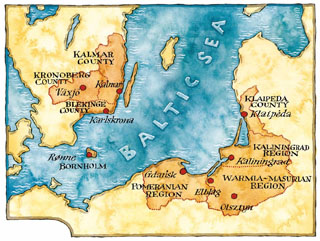
Euroregion Baltic(ERB) is an institutionalised form of cross-border cooperation in the south-east of the Baltic Sea Region, consisting of eight regions of Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden.

The Greater Region of Luxembourg, or simply Greater Region, is a geopolitical region within Europe, created to promote economic, cultural, touristic and social development and cooperation. It occupies an area of 65,401 square kilometres (25,251 sq mi) with Luxembourg at its center and including adjacent regions of Belgium, Germany and France.

The Pyrenees–Mediterranean Euroregion is a Euroregion founded on 29 October 2004. It is a political cooperation project between Catalonia, the Balearic Islands, and Occitanie. The Autonomous Community of Aragon suspended participation in 2006 due to an ongoing conflict with Catalonia about some religious art.

Andreas Kiefer is Secretary General of the Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of the Council of Europe, an institution representing local and regional authorities of the 47 member states of the Council of Europe.
The European Neighbourhood Instrument (ENI) came into force in 2014. It is the financial arm of the European Neighbourhood Policy, the EU’s foreign policy towards its neighbours to the East and to the South. It has a budget of €15.4 billion and provides the bulk of funding through a number of programmes.










