In mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.

In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called coordinate lines, coordinate axes or just axes of the system. The point where they meet is called the origin and has (0, 0) as coordinates.

A sphere is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. Formally, a sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance r from a given point in three-dimensional space. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and r is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. A sphere is a degenerate case of a torus.

In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if their intersection forms right angles at the point of intersection called a foot. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the perpendicular symbol, ⟂. Perpendicular intersections can happen between two lines, between a line and a plane, and between two planes.
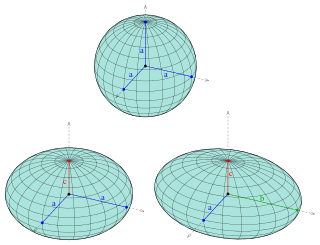
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.

In geometry, a normal is an object such as a line, ray, or vector that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the (infinite) line perpendicular to the tangent line to the curve at the point. A normal vector may have length one or its length may represent the curvature of the object ; its algebraic sign may indicate sides.

A 3D projection is a design technique used to display a three-dimensional (3D) object on a two-dimensional (2D) surface. These projections rely on visual perspective and aspect analysis to project a complex object for viewing capability on a simpler plane.

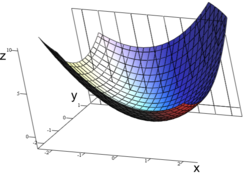
A surface of revolution is a surface in Euclidean space created by rotating a curve around an axis of rotation.

In mathematical physics, scalar potential, simply stated, describes the situation where the difference in the potential energies of an object in two different positions depends only on the positions, not upon the path taken by the object in traveling from one position to the other. It is a scalar field in three-space: a directionless value (scalar) that depends only on its location. A familiar example is potential energy due to gravity.

In mathematics, a parametric equation defines a group of quantities as functions of one or more independent variables called parameters. Parametric equations are commonly used to express the coordinates of the points that make up a geometric object such as a curve or surface, called parametric curve and parametric surface, respectively. In such cases, the equations are collectively called a parametric representation, or parametric system, or parameterization of the object.
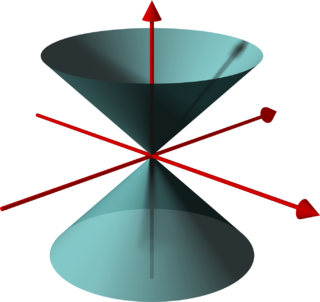
In geometry, a (general) conical surface is the unbounded surface formed by the union of all the straight lines that pass through a fixed point — the apex or vertex — and any point of some fixed space curve — the directrix — that does not contain the apex. Each of those lines is called a generatrix of the surface.

A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base to a point called the apex or vertex.

A cylinder has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.

In three-dimensional geometry, skew lines are two lines that do not intersect and are not parallel. A simple example of a pair of skew lines is the pair of lines through opposite edges of a regular tetrahedron. Two lines that both lie in the same plane must either cross each other or be parallel, so skew lines can exist only in three or more dimensions. Two lines are skew if and only if they are not coplanar.

In geometry, a three-dimensional space is a mathematical space in which three values (coordinates) are required to determine the position of a point. Most commonly, it is the three-dimensional Euclidean space, the Euclidean n-space of dimension n=3 that models physical space. More general three-dimensional spaces are called 3-manifolds.
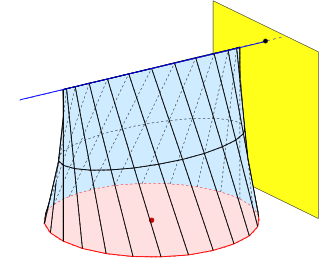
In geometry a conoid is a ruled surface, whose rulings (lines) fulfill the additional conditions:

In mathematics, a Euclidean plane is a Euclidean space of dimension two, denoted E2. It is a geometric space in which two real numbers are required to determine the position of each point. It is an affine space, which includes in particular the concept of parallel lines. It has also metrical properties induced by a distance, which allows to define circles, and angle measurement.
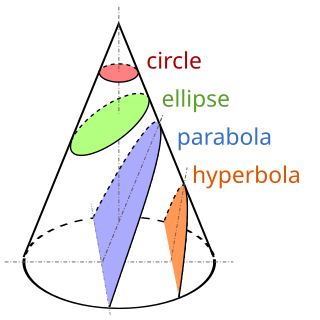
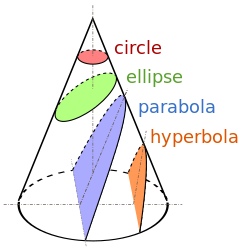
A conic section, conic or a quadratic curve is a curve obtained from a cone's surface intersecting a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though it was sometimes called as a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties.

In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line that is between its endpoints. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between its endpoints. A closed line segment includes both endpoints, while an open line segment excludes both endpoints; a half-open line segment includes exactly one of the endpoints. In geometry, a line segment is often denoted using a line above the symbols for the two endpoints.
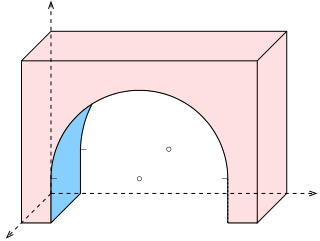
Axonometry is a graphical procedure belonging to descriptive geometry that generates a planar image of a three-dimensional object. The term "axonometry" means "to measure along axes", and indicates that the dimensions and scaling of the coordinate axes play a crucial role. The result of an axonometric procedure is a uniformly-scaled parallel projection of the object. In general, the resulting parallel projection is oblique ; but in special cases the result is orthographic, which in this context is called an orthogonal axonometry.