
Envisat is a large Earth-observing satellite which has been inactive since 2012. It is still in orbit and considered space debris. Operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), it was the world's largest civilian Earth observation satellite.

Mars Express is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The Mars Express mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally referred to the speed and efficiency with which the spacecraft was designed and built. However, "Express" also describes the spacecraft's relatively short interplanetary voyage, a result of being launched when the orbits of Earth and Mars brought them closer than they had been in about 60,000 years.

The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy. The agency cooperates with numerous national and international entities who are active in aerospace research and technology.

European Remote Sensing satellite (ERS) was the European Space Agency's first Earth-observing satellite programme using a polar orbit. It consisted of two satellites, ERS-1 and ERS-2, with ERS-1 being launched in 1991.

Space-based radar or spaceborne radar is a radar operating in outer space; orbiting radar is a radar in orbit and Earth orbiting radar is a radar in geocentric orbit. A number of Earth-observing satellites, such as RADARSAT, have employed synthetic aperture radar (SAR) to obtain terrain and land-cover information about the Earth.

Rokot, also transliterated Rockot, was a Soviet Union space launch vehicle that was capable of launching a payload of 1,950 kilograms (4,300 lb) into a 200-kilometre (120 mi) Earth orbit with 63° inclination. It was based on the UR-100N intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), supplied and operated by Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center. The first launches started in the 1990s from Baikonur Cosmodrome out of a silo. Later commercial launches commenced from Plesetsk Cosmodrome using a launch ramp specially rebuilt from one for the Kosmos-3M launch vehicle. The cost of the launcher itself was about US$15 million in 1999; The contract with European Space Agency (ESA) for launching Swarm in September 2013 was worth €27.1 million.

The GEOSAT was a U.S. Navy Earth observation satellite, launched on March 12, 1985 into an 800 km, 108° inclination orbit, with a nodal period of about 6040 seconds. The satellite carried a radar altimeter capable of measuring the distance from the satellite to sea surface with a relative precision of about 5 cm. The initial phase was an 18-month classified Geodetic Mission (GM) have a ground-track with a near-23-day repeat with closure to within 50 kilometers. The effect of atmospheric drag was such that by fall 1986 GEOSAT was in an almost exact 23-day repeat orbit.

Copernicus is the Earth observation component of the European Union Space Programme, managed by the European Commission and implemented in partnership with the EU Member States, the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), the Joint Research Centre (JRC), the European Environment Agency (EEA), the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA), Frontex, SatCen and Mercator Océan.
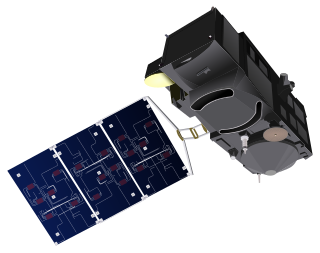
Sentinel-3 is an Earth observation heavy satellite series developed by the European Space Agency as part of the Copernicus Programme. It currently consists of 2 satellites: Sentinel-3A and Sentinel-3B. After initial commissioning, each satellite was handed over to EUMETSAT for the routine operations phase of the mission. Two recurrent satellites— Sentinel-3C and Sentinel-3D— will follow in approximately 2025 and 2028 respectively to ensure continuity of the Sentinel-3 mission.

Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) is a satellite which forms part of ESA's Living Planet Programme. It is intended to provide new insights into Earth's water cycle and climate. In addition, it is intended to provide improved weather forecasting and monitoring of snow and ice accumulation.
The Living Planet Programme (LPP) is a programme within the European Space Agency which is managed by the Earth Observation Programmes Directorate. LPP consists of two classes of Earth observation missions including research missions known as Earth Explorers, and the Earth Watch class of missions whose objective is to develop support operational applications such as numerical weather forecasting or resource management.

CryoSat-2 is a European Space Agency (ESA) Earth Explorer Mission that launched on April 8, 2010. CryoSat-2 is dedicated to measuring polar sea ice thickness and monitoring changes in ice sheets. Its primary objective is to measure the thinning of Arctic sea ice, but has applications to other regions and scientific purposes, such as Antarctica and oceanography.

SARAL is a cooperative altimetry technology mission of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES). SARAL performs altimetric measurements designed to study ocean circulation and sea surface elevation.

EarthCARE is a planned joint European/Japanese satellite, the sixth of ESA's Earth Explorer Programme. The main goal of the mission is the observation and characterization of clouds and aerosols as well as measuring the reflected solar radiation and the infrared radiation emitted from Earth's surface and atmosphere.

CryoSat-1, also known as just CryoSat, was a European Space Agency satellite which was lost in a launch failure in 2005. The satellite was launched as part of the European Space Agency's CryoSat mission, which aims to monitor ice in the high latitudes. The second mission satellite, CryoSat-2, was successfully launched in April 2010.
ICESat-2, part of NASA's Earth Observing System, is a satellite mission for measuring ice sheet elevation and sea ice thickness, as well as land topography, vegetation characteristics, and clouds. ICESat-2, a follow-on to the ICESat mission, was launched on 15 September 2018 onboard Delta II as the final flight from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, into a near-circular, near-polar orbit with an altitude of approximately 496 km (308 mi). It was designed to operate for three years and carry enough propellant for seven years. The satellite orbits Earth at a speed of 6.9 kilometers per second (4.3 mi/s).
SEOSat-Ingenio, was a Spanish project to produce a satellite capable of providing wide-field imagery ensuring a repeat cycle of 38 days at 2.5 metre panchromatic resolution and 10 metre colour resolution, from a Sun-synchronous polar orbit; it was Spain's first optical imaging satellite. The satellite was part of the Spanish Earth Observation Satellite program. The mission was funded by Spain's Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI). SEOSat-Ingenio information was to be used by various Spanish civil, institutional or government users. However, under the Copernicus Programme of the European Union, it was also accessible to other European users, as well as to the Group on Earth observation of the Global Observing System of Earth.

ArgoMoon is a CubeSat that was launched into a heliocentric orbit on Artemis 1, the maiden flight of the Space Launch System, on 16 November 2022 at 06:47:44 UTC. The objective of the ArgoMoon spacecraft is to take detailed images of the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage following Orion separation, an operation that will demonstrate the ability of a cubesat to conduct precise proximity maneuvers in deep space. ASI has not confirmed nor denied whether this took place, but several images of the Earth and the Moon were taken.
Biomass is an Earth observing satellite planned for launch by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2024 on a Vega launch vehicle.














