
A centimetre or centimeter is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one hundredth of a metre, centi being the SI prefix for a factor of 1/100. Equivalently, there are 100 centimetres in 1 metre. The centimetre was the base unit of length in the now deprecated centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system of units.
Density is a substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ, although the Latin letter D can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume:
Kilo is a decimal unit prefix in the metric system denoting multiplication by one thousand (103). It is used in the International System of Units, where it has the symbol k, in lowercase.
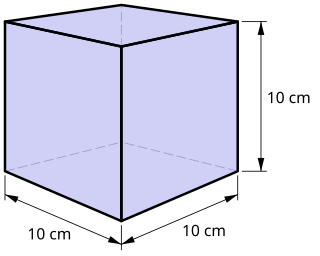
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The prefix kilo-, for example, may be added to gram to indicate multiplication by one thousand: one kilogram is equal to one thousand grams. The prefix milli-, likewise, may be added to metre to indicate division by one thousand; one millimetre is equal to one thousandth of a metre.

Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units or by various imperial or US customary units. The definition of length (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region.

The kilogram per cubic metre is the unit of density in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined by dividing the SI unit of mass, the kilogram, by the SI unit of volume, the cubic metre.
In chemistry and related fields, the molar volume, symbol Vm, or of a substance is the ratio of the volume occupied by a substance to the amount of substance, usually given at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass (M) divided by the mass density (ρ):
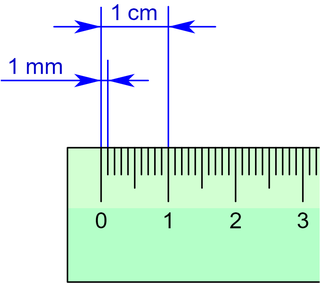
The millimetre or millimeter is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one thousandth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length. Therefore, there are one thousand millimetres in a metre. There are ten millimetres in a centimetre.

A cubic centimetre is a commonly used unit of volume that corresponds to the volume of a cube that measures 1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm. One cubic centimetre corresponds to a volume of one millilitre. The mass of one cubic centimetre of water at 3.98 °C is almost equal to one gram.
The square metre or square meter is the unit of area in the International System of Units (SI) with symbol m2. It is the area of a square with sides one metre in length.
The cubic foot is an imperial and US customary (non-metric) unit of volume, used in the United States and the United Kingdom. It is defined as the volume of a cube with sides of one foot in length. Its volume is 28.3168 L.
The decimetre, is a unit of length in the International System of Units, equal to one tenth of a metre, ten centimetres, one hundred millimetres, and 3.937 inches.
In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance is a mass-specific intrinsic property of the substance, defined as the quotient of the substance's volume to its mass. It is the reciprocal of density ρ (rho) and it is also related to the molar volume and molar mass:
In analytical chemistry, a standard solution is a solution containing a precisely known concentration of an element or a substance. A known mass of solute is dissolved to make a specific volume. It is prepared using a standard substance, such as a primary standard. Standard solutions are used to determine the concentrations of other substances, such as solutions in titration. The concentrations of standard solutions are normally expressed in units of moles per litre, moles per cubic decimetre (mol/dm3), kilomoles per cubic metre (kmol/m3) or in terms related to those used in particular titrations. A simple standard is obtained by the dilution of a single element or a substance in a soluble solvent with which it reacts. A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has high molecular weight. Some primary standards of titration of acids include sodium carbonate.

The grave, abbreviated gv, is the unit of mass used in the first metric system which was implemented in France in 1793. In 1795, the grave was renamed as the kilogram.

The gram per cubic centimetre is a unit of density in the CGS system, and is commonly used in chemistry. It is defined by dividing the CGS unit of mass, the gram, by the CGS unit of volume, the cubic centimetre. The official SI symbols are g/cm3, g·cm−3, or g cm−3. It is equivalent to the units gram per millilitre (g/mL) and kilogram per litre (kg/L). The density of water is about 1 g/cm3, since the gram was originally defined as the mass of one cubic centimetre of water at its maximum density at 4 °C.

The hectare is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), that is, 10,000 square meters, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about 0.405 hectares and one hectare contains about 2.47 acres.











