Related Research Articles
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.
Tumid lupus erythematosus is a rare, but distinctive entity in which patients present with edematous erythematous plaques, usually on the trunk.
Erythema gyratum repens is a figurate erythema that is rapidly moving and usually a marker of underlying cancer, usually from the lung.
Primary inoculation tuberculosis is a skin condition that develops at the site of inoculation of tubercle bacilli into a tuberculosis-free individual.
Tuberculosis cutis orificialis is a form of cutaneous tuberculosis that occurs at the mucocutaneous borders of the nose, mouth, anus, urinary meatus, and vagina, and on the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue.
Papulonecrotic tuberculid is usually an asymptomatic, chronic skin disorder, presenting in successive crops, skin lesions symmetrically distributed on the extensor extremities.
Aquarium granuloma is a skin condition caused by Mycobacterium marinum, characterized by a skin lesion that presents roughly three weeks after exposure.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis, is inflammation of small blood vessels, characterized by palpable purpura. It is the most common vasculitis seen in clinical practice.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.
Subcutaneous granuloma annulare is a skin condition of unknown cause, most commonly affecting children, with girls affected twice as commonly as boys, characterized by skin lesions most often on the lower legs.
Cutaneous actinomycosis is a chronic disease that affects the deep subcutaneous tissue of the skin. Caused by an anaerobic, Gram-positive, filamentous type of bacteria in the genus Actinomyces, invasion of the soft tissue leads to the formation of abnormal channels leading to the skin surface that discharge pale yellow sulfur granules.
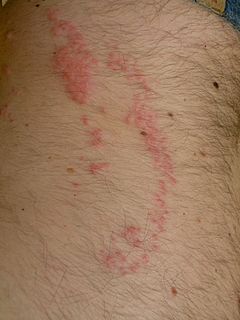
Jellyfish dermatitis is a cutaneous condition caused by stings from a jellyfish.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:
A diabetic bulla is a cutaneous condition characterized by a noninflammatory, spontaneous, painless blister, often in acral locations, seen in diabetic patients.
Diabetic dermadromes constitute a group of cutaneous conditions commonly seen in people with diabetes with longstanding disease. Conditions included in this group are:
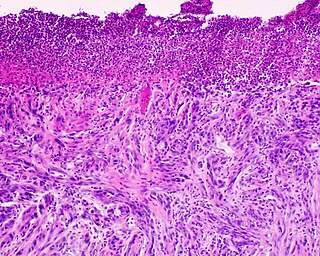
Desmoplastic melanoma is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by a deeply infiltrating type of melanoma with an abundance of fibrous matrix. It usually occurs in the head and neck region of older people with sun-damaged skin. Diagnosis can be difficult as it has a similar appearance to sclerosing melanocytic nevi as well as some nonmelanocytic skin lesions such as scars, fibromas, or cysts.
Median raphe cysts are a cutaneous condition of the penis due to developmental defects near the glans.
Cutaneous lymphoma, also known as lymphoma cutis, is when lymphoma involves the skin. It is characterized by a proliferation of lymphoid tissue.
Poikiloderma of Civatte is a cutaneous condition and refers to reticulated red to red-brown skin patches with telangiectasias. It is identifiable as a reddish-brown discoloration on the side of the neck, usually on both sides. It is more common in lighter-skinned individuals, in females rather than in males and more often affects middle-aged to elderly women. This disease is basically a change of the skin due to dilation of the blood vessels in the neck. "Civatte" was the French dermatologist who first identified it in the 1920s.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
| This cutaneous condition article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |