
A sugar substitute is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie or low-calorie sweetener. Artificial sweeteners may be derived through manufacturing of plant extracts or processed by chemical synthesis. Sugar substitute products are commercially available in various forms, such as small pills, powders, and packets.

Cyclamate is an artificial sweetener. It is 30–50 times sweeter than sucrose, making it the least potent of the commercially used artificial sweeteners. It is often used with other artificial sweeteners, especially saccharin; the mixture of 10 parts cyclamate to 1 part saccharin is common and masks the off-tastes of both sweeteners. It is less expensive than most sweeteners, including sucralose, and is stable under heating. Safety concerns led to it being banned in a few countries, though the European Union considers it safe.

Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, sometimes abbreviated to neohesperidin DC or simply NHDC, is an artificial sweetener derived from citrus.

Saccharin, also called saccharine or benzosulfimide, or used in saccharin sodium or saccharin calcium forms, is a non-nutritive artificial sweetener. Saccharin is a benzoic sulfimide that is about 500 times sweeter than sucrose, but has a bitter or metallic aftertaste, especially at high concentrations. It is used to sweeten products, such as drinks, candies, baked goods, tobacco products, excipients, and for masking the bitter taste of some medicines. It appears as white crystals and is odorless.

Acesulfame potassium, also known as acesulfame K or Ace K, is a synthetic calorie-free sugar substitute often marketed under the trade names Sunett and Sweet One. In the European Union, it is known under the E number E950. It was discovered accidentally in 1967 by German chemist Karl Clauss at Hoechst AG. In chemical structure, acesulfame potassium is the potassium salt of 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide. It is a white crystalline powder with molecular formula C
4H
4KNO
4S and a molecular weight of 201.24 g/mol.

Diet or light beverages are generally sugar-free, artificially sweetened beverages with few or no calories. They are marketed for diabetics and other people who want to reduce their sugar and/or caloric intake.

Sweet'n Low is a brand of artificial sweetener now made primarily from granulated saccharin. When introduced in 1958 in the United States, Sweet'n Low was cyclamate-based, but it was replaced by a saccharin-based formulation in 1969. It is also a brand name applied to a family of sweetener and sweetened products, some containing sweeteners other than saccharin or cyclamate. There have been over 500 billion Sweet'N Low packets produced.

Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketones, and sugar alcohols. Some are sweet at very low concentrations, allowing their use as non-caloric sugar substitutes. Such non-sugar sweeteners include saccharin and aspartame. Other compounds, such as miraculin, may alter perception of sweetness itself.

Sulfamic acid, also known as amidosulfonic acid, amidosulfuric acid, aminosulfonic acid, sulphamic acid and sulfamidic acid, is a molecular compound with the formula H3NSO3. This colourless, water-soluble compound finds many applications. Sulfamic acid melts at 205 °C before decomposing at higher temperatures to water, sulfur trioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen.

Enoxolone is a pentacyclic triterpenoid derivative of the beta-amyrin type obtained from the hydrolysis of glycyrrhizic acid, which was obtained from the herb liquorice.

Sodium ferulate, the sodium salt of ferulic acid, is a compound used in traditional Chinese medicine thought to be useful for treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and to prevent thrombosis, although there is no high-quality clinical evidence for such effects. It is found in the root of Angelica sinensis. As of 2005, it was under preliminary clinical research in China. Ferulic acid can also be extracted from the root of the Chinese herb Ligusticum chuanxiong.
Propel Water is an American brand of flavored bottled water that is advertised for having antioxidants and vitamins. It is a beverage product of Gatorade and is marketed by PepsiCo.
Fruit2O, formerly manufactured by Kraft, is a lightly flavored, non-carbonated water beverage introduced in 1999. Fruit2o was introduced to compete not only with the bottled water market but also with the soft drink market. Sunny Delight Beverages purchased the Veryfine Products line from Kraft in 2007.

Calcium alginate is a water-insoluble, gelatinous, cream-coloured substance that can be created through the addition of aqueous calcium chloride to aqueous sodium alginate. Calcium alginate is also used for entrapment of enzymes and forming artificial seeds in plant tissue culture.

Assugrin is a brand name for a sugar substitute that is a blend of cyclamate and saccharin. Produced in Switzerland by MCM Klosterfrau Vertriebsgesellschaft, Assugrin was the main table sweetener in West Germany.
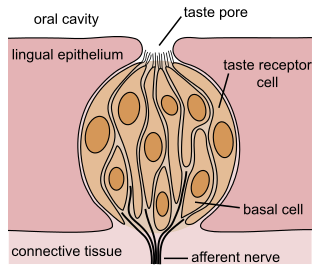
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor cells located on taste buds in the oral cavity, mostly on the tongue. Taste, along with the sense of smell and trigeminal nerve stimulation, determines flavors of food and other substances. Humans have taste receptors on taste buds and other areas, including the upper surface of the tongue and the epiglottis. The gustatory cortex is responsible for the perception of taste.
Suosan is calorie-free artificial sweetener derived from β-alanine, discovered in 1948 by Petersen et Muller.
Calcium stearoyl-2-lactylate or E482 is a versatile, FDA approved food additive. It is one type of a commercially available lactylate. CSL is non-toxic, biodegradable, and typically manufactured using biorenewable feedstocks. Because CSL is a safe and highly effective food additive, it is used in a wide variety of products from baked goods and desserts to packaging.

Funny Face was a brand of powdered drink mix originally made and publicly sold by the Pillsbury Company from 1964 to 1994, and in limited productions from 1994 to 2001. The brand was introduced as competition to the similar Kool-Aid made by Kraft Foods. The product came in assorted flavors sweetened with artificial sweetener, and was mixed with water to make a beverage.
















