Related Research Articles

A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.

A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.

Interlaced video is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This enhances motion perception to the viewer, and reduces flicker by taking advantage of the phi phenomenon.
Progressive scanning is a format of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence. This is in contrast to interlaced video used in traditional analog television systems where only the odd lines, then the even lines of each frame are drawn alternately, so that only half the number of actual image frames are used to produce video. The system was originally known as "sequential scanning" when it was used in the Baird 240 line television transmissions from Alexandra Palace, United Kingdom in 1936. It was also used in Baird's experimental transmissions using 30 lines in the 1920s. Progressive scanning became universally used in computer screens beginning in the early 21st century.

A framebuffer is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor.
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is made by thin film deposition. TFTs are grown on a supporting substrate, such as glass. This differs from the conventional bulk metal oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically is the substrate, such as a silicon wafer. The traditional application of TFTs is in TFT liquid-crystal displays.

A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipment.
A television set or television receiver is an electronic device for the purpose of viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or as a computer monitor. It combines a tuner, display, and loudspeakers. Introduced in the late 1920s in mechanical form, television sets became a popular consumer product after World War II in electronic form, using cathode ray tube (CRT) technology. The addition of color to broadcast television after 1953 further increased the popularity of television sets in the 1960s, and an outdoor antenna became a common feature of suburban homes. The ubiquitous television set became the display device for the first recorded media for consumer use in the 1970s, such as Betamax, VHS; these were later succeeded by DVD. It has been used as a display device since the first generation of home computers and dedicated video game consoles in the 1980s. By the early 2010s, flat-panel television incorporating liquid-crystal display (LCD) technology, especially LED-backlit LCD technology, largely replaced CRT and other display technologies. Modern flat panel TVs are typically capable of high-definition display and can also play content from a USB device. Starting in the late 2010s, most flat panel TVs began to offer 4K and 8K resolutions.
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display is a type of liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.

A super-twisted nematic (STN) display is a type of monochrome passive-matrix liquid crystal display (LCD).

The history of laptops describes the efforts, begun in the 1970s, to build small, portable Personal Computers that combine the components, inputs, outputs and capabilities of a Desktop Computer in a small chassis.
A blue phase mode LCD is a liquid crystal display (LCD) technology that uses highly twisted cholesteric phases in a blue phase. It was first proposed in 2007 to obtain a better display of moving images with, for example, frame rates of 100–120 Hz to improve the temporal response of LCDs. This operational mode for LCDs also does not require anisotropic alignment layers and thus theoretically simplifies the LCD manufacturing process.

AMOLED is a type of OLED display device technology. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels.
Display lag is a phenomenon associated with most types of liquid crystal displays (LCDs) like smartphones and computers and nearly all types of high-definition televisions (HDTVs). It refers to latency, or lag between when the signal is sent to the display and when the display starts to show that signal. This lag time has been measured as high as 68 ms, or the equivalent of 3-4 frames on a 60 Hz display. Display lag is not to be confused with pixel response time, which is the amount of time it takes for a pixel to change from one brightness value to another. Currently the majority of manufacturers quote the pixel response time, but neglect to report display lag.
Electrically operated display devices have developed from electromechanical systems for display of text, up to all-electronic devices capable of full-motion 3D color graphic displays. Electromagnetic devices, using a solenoid coil to control a visible flag or flap, were the earliest type, and were used for text displays such as stock market prices and arrival/departure display times. The cathode ray tube was the workhorse of text and video display technology for several decades until being displaced by plasma, liquid crystal (LCD), and solid-state devices such as thin-film transistors (TFTs), LEDs and OLEDs. With the advent of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), integrated circuit (IC) chips, microprocessors, and microelectronic devices, many more individual picture elements ("pixels") could be incorporated into one display device, allowing graphic displays and video.

IBM ThinkPad 760 was a notebook computer introduced in 1995 by the IBM corporation into the market as part of the ThinkPad 700-series. It was succeeded in 1998 by the ThinkPad 770 series.
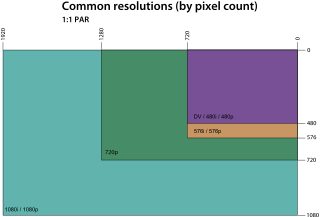
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display.
IPS is a screen technology for liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). In IPS, a layer of liquid crystals is sandwiched between two glass surfaces. The liquid crystal molecules are aligned parallel to those surfaces in predetermined directions (in-plane). The molecules are reoriented by an applied electric field, whilst remaining essentially parallel to the surfaces to produce an image. It was designed to solve the strong viewing angle dependence and low-quality color reproduction of the twisted nematic field effect (TN) matrix LCDs prevalent in the late 1980s.
Low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) is polycrystalline silicon that has been synthesized at relatively low temperatures compared to in traditional methods. LTPS is important for display industries, since the use of large glass panels prohibits exposure to deformative high temperatures. More specifically, the use of polycrystalline silicon in thin-film transistors (LTPS-TFT) has high potential for large-scale production of electronic devices like flat panel LCD displays or image sensors.

The IBM ThinkPad 360 series was a notebook computer series introduced in 1994 by IBM as part of their ThinkPad laptop series. It was succeeded in late 1995 by the IBM ThinkPad 365 series.
References
- ↑ Kim, J.J.H.; Cho, Rae; Kiachian, J. (November 1997). "Interface issues in displaying graphics and video on high resolution flat panel displays". WESCON/97 Conference Proceedings. pp. 307–313. doi:10.1109/WESCON.1997.632353. ISBN 0-7803-4303-4. S2CID 62552477.
- 1 2 "What is DSTN (Double-layer SuperTwisted Nematic)?". www.computerhope.com. 2019-11-16. Retrieved 2022-02-08.
- ↑ Kawamoto, H. (April 2002). "The history of liquid-crystal displays". Proceedings of the IEEE . 90 (4): 460–500. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2002.1002521. ISSN 1558-2256.
- ↑ apoor (2001-06-11). "More Than Meets the Eye". ExtremeTech . Retrieved 2023-02-19.
- ↑ S. Coolidge, Daniel; Jimmerson, J. Michael (1997). A survival guide for road warriors: essentials for the mobile CPA. American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. p. 27. ISBN 0-87051-194-7. OCLC 39913176.
- ↑ "Toshiba's latest color portable PC checks in with a vibrant display". InfoWorld . 2 March 1992.