
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that lasted from 28 February 1998 until 11 June 1999. It was fought between the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which controlled Kosovo before the war, and the Kosovo Albanian separatist militia known as the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA). The conflict ended when the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) intervened by beginning air strikes in March 1999 which resulted in Yugoslav forces withdrawing from Kosovo.

The United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo is the officially mandated mission of the United Nations in Kosovo. The UNMIK describes its mandate as being to "help the United Nations Security Council achieve an overall objective, namely, to ensure conditions for a peaceful and normal life for all inhabitants of Kosovo and advance regional stability in the Western Balkans."

The Kosovo Liberation Army was an ethnic Albanian separatist militia that sought the separation of Kosovo, the vast majority of which is inhabited by Albanians, from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) and Serbia during the 1990s. Albanian nationalism was a central tenet of the KLA and many in its ranks supported the creation of a Greater Albania, which would encompass all Albanians in the Balkans, stressing Albanian culture, ethnicity and nation.
The Račak massacre or Račak operation was the massacre of 45 Kosovo Albanians that took place in the village of Račak in central Kosovo in January 1999. The massacre was perpetrated by Serbian security forces in response to Albanian separatist activity in the region. The Serbian government refused to let a war crimes prosecutor visit the site, and maintained that the casualties were all members of the rebel Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA) killed in combat with state security forces.
A feud, also known in more extreme cases as a blood feud, vendetta, faida, clan war, gang war, private war, or mob war, is a long-running argument or fight, often between social groups of people, especially families or clans. Feuds begin because one party perceives itself to have been attacked, insulted, injured, or otherwise wronged by another. Intense feelings of resentment trigger an initial retribution, which causes the other party to feel greatly aggrieved and vengeful. The dispute is subsequently fuelled by a long-running cycle of retaliatory violence. This continual cycle of provocation and retaliation usually makes it extremely difficult to end the feud peacefully. Feuds can persist for generations and may result in extreme acts of violence. They can be interpreted as an extreme outgrowth of social relations based in family honor. A mob war is a time when two or more rival families begin open warfare with one another, destroying each other's businesses and assassinating family members. Mob wars are generally disastrous for all concerned, and can lead to the rise or fall of a family.

The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from the breakup of Yugoslavia, which began in mid-1991, into six independent countries matching the six entities known as republics that had previously constituted Yugoslavia: Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, and Macedonia. SFR Yugoslavia's constituent republics declared independence due to unresolved tensions between ethnic minorities in the new countries, which fuelled the wars. While most of the conflicts ended through peace accords that involved full international recognition of new states, they resulted in a massive number of deaths as well as severe economic damage to the region.

Carla Del Ponte is a Swiss former Chief Prosecutor of two United Nations international criminal law tribunals. A former Swiss attorney general, she was appointed prosecutor for the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) and the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ICTR) in August 1999, replacing Louise Arbour.

Agim Çeku, also known by the Croatians as the nickname Commander Scorched Earth, is a Kosovo Albanian politician, the former minister of Security Forces in Kosovo and formerly the prime minister. Of military background, he was a commander of the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA) that fought against Serbian rule in 1998–1999, earlier being a commander in the Croatian War of Independence in the Croatian Army.

Ramush Haradinaj is a Kosovo Albanian politician, leader of the AAK party, and the third prime minister of Kosovo. He is a former officer and leader of the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA), and previously served as Prime Minister of Kosovo between 2004 and 2005.

Hashim Thaçi is a Kosovar Albanian politician who was the president of Kosovo from April 2016 until his resignation on 5 November 2020 to face a war crimes tribunal. He was the first prime minister of Kosovo and the Foreign minister and deputy prime minister in the new cabinet led by Isa Mustafa, which assumed office on 12 December 2014.
Albanian mafia or Albanian organized crime are the general terms used for criminal organizations based in Albania or composed of ethnic Albanians. Albanian organized crime is active in Europe, North America, South America, and various other parts of the world including the Middle East and Asia. The Albanian Mafia participates in a diverse range of criminal enterprises including trafficking in drugs, arms, and humans. Thanks to their close ties with the Serbian mafia and 'Ndrangheta of Calabria, they control a large part of the billion dollar wholesale cocaine market in Europe and appear to be the primary distributors of cocaine in various European drug hubs including London. Albanian organized crime is characterized by diversified criminal enterprises which, in their complexity, demonstrate a very high criminal capacity. In Albania, there are over 15 mafia families that control organized crime.

The flag of the Republic of Kosovo was adopted by the Assembly of the Republic of Kosovo immediately following the unilateral declaration of independence of Kosovo on 17 February 2008. The flag design emerged from an international competition, organized by an informal group from the Provisional Institutions of Self-Government known as the Kosovo Unity Team, which attracted almost one thousand entries. The winning design was proposed by Muhamer Ibrahimi. It shows six white stars in an arc above a golden map of Kosovo, all on a blue field. The stars symbolize Kosovo's six major ethnic groups: Albanians, Serbs, Bosniaks, Turks, Romani, and Gorani.

Balkan sworn virgins are people who are assigned female at birth and who take a vow of chastity and live as men in patriarchal northern Albanian society, Kosovo and Montenegro. To a lesser extent, the practice exists, or has existed, in other parts of the western Balkans, including Bosnia, Dalmatia (Croatia), Serbia and North Macedonia.
The 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, which proclaimed the Republic of Kosovo to be a state independent from Serbia, was adopted at a meeting held on 17 February 2008 by 109 out of the 120 members of the Assembly of Kosovo, including the Prime Minister of Kosovo, Hashim Thaçi, and by the President of Kosovo, Fatmir Sejdiu. It was the second declaration of independence by Kosovo's Albanian-majority political institutions; the first was proclaimed on 7 September 1990.
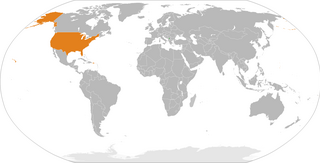
Kosovo was officially recognized as a country by the United States on February 18, 2008, one day after Kosovo declared its independence from Serbia.

Finland–Kosovo relations are foreign relations between Finland and Kosovo. Kosovo declared its independence from Serbia on 17 February 2008 and Finland recognised it on 7 March 2008. Finland maintains an embassy in Pristina.

Behgjet Isa Pacolli is a Kosovar Albanian politician and businessman who served as the first deputy prime minister of Kosovo and minister of foreign affairs from 2017 to 2019 under the Ramush Haradinaj government. Pacolli is a former president of Kosovo, and served as the first deputy prime minister of Kosovo between 2011 and 2014. Pacolli was one of the signatories of the 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence.

Slobodan Milošević was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the President of Serbia between 1989–1997 and President of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1997 until his оverthrow in 2000. Milošević played a major role in the Yugoslav Wars and became the first sitting head of state charged with war crimes.

The Staro Gracko massacre was the mass killing of 14 Kosovo Serb farmers in the village of Staro Gracko in the Kosovo municipality of Lipjan on 23 July 1999. The killings occurred after Yugoslav troops withdrew from the region in the aftermath of the Kosovo War. The massacre is the worst single crime in Kosovo since the conflict ended in June 1999. As of 2019 the perpetrators of the killings have never been found and held accountable.

Kosovo Independence Day is a national independence day celebrated in Kosovo every 17 February.















