
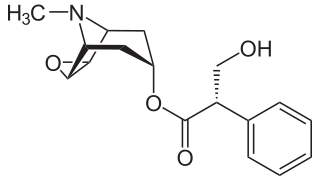
Duloxetine, sold under the brand name Cymbalta among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain and central sensitization. It is taken by mouth.

Desipramine, sold under the brand name Norpramin among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used in the treatment of depression. It acts as a relatively selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, though it does also have other activities such as weak serotonin reuptake inhibitory, α1-blocking, antihistamine, and anticholinergic effects. The drug is not considered a first-line treatment for depression since the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants, which have fewer side effects and are safer in overdose.
Fluoxetine, sold under the brand name Prozac, among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. It is also approved for treatment of major depressive disorder in adolescents and children 8 years of age and over. It has also been used to treat premature ejaculation. Fluoxetine is taken by mouth.
A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor is a protein involved in the transmission of signals through certain parts of the nervous system, and muscarinic receptor antagonists work to prevent this transmission from occurring. Notably, muscarinic antagonists reduce the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system. The normal function of the parasympathetic system is often summarised as "rest-and-digest", and includes slowing of the heart, an increased rate of digestion, narrowing of the airways, promotion of urination, and sexual arousal. Muscarinic antagonists counter this parasympathetic "rest-and-digest" response, and also work elsewhere in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.

A serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking the action of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic neurotransmission. It is a type of monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI); other types of MRIs include dopamine reuptake inhibitors and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.

Etazolate (SQ-20,009, EHT-0202) is an anxiolytic drug which is a pyrazolopyridine derivative and has unique pharmacological properties. It acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor at the barbiturate binding site, as an adenosine antagonist of the A1 and A2 subtypes, and as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor selective for the PDE4 isoform. It is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

Nisoxetine, originally synthesized in the Lilly research laboratories during the early 1970s, is a potent and selective inhibitor for the reuptake of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) into synapses. It currently has no clinical applications in humans, although it was originally researched as an antidepressant. Nisoxetine is now widely used in scientific research as a standard selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It has been used to research obesity and energy balance, and exerts some local analgesia effects.
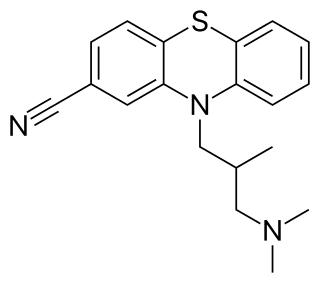
Cyamemazine (Tercian), also known as cyamepromazine, is a typical antipsychotic drug of the phenothiazine class which was introduced by Theraplix in France in 1972 and later in Portugal as well.

LR-5182 is a stimulant drug which acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, structurally related to the better known drug fencamfamine. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly in the 1970s, and researched for potential use as an antidepressant, although never marketed. LR-5182 has two stereoisomers, both of which are active, although one isomer blocks reuptake of only dopamine and noradrenaline, while the other blocks reuptake of serotonin as well.
Klaus Schmiegel, is most famous for his work in organic chemistry, which led to the invention of Prozac, a widely used antidepressant. Born in Chemitz, Germany, he moved to the U.S. in 1951 to continue his education. After he finished his schooling, Schmiegel joined Eli Lilly as a senior organic chemist; he worked there from 1968 until his retirement in 1993. There, he collaborated with Bryan Molloy to create a new group of compounds. One of them, fluoxetine hydrochloride, became the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used in the antidepressant medication, Prozac. The drug, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1988, has revolutionized treatment for depression. In 1999, Schmiegel and Molloy were inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame and given the American Innovator Award. Throughout his career, Schmiegel garnered eighteen patents related to the synthesis of compounds.

Amfonelic acid is a research chemical and dopaminergic stimulant with antibiotic properties.

Tandamine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor with a tricyclic structure. It was developed in the 1970s as an antidepressant but was never commercialized. Tandamine is analogous to pirandamine, which, instead, acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).

Desmethylsertraline (DMS), also known as norsertraline, is an active metabolite of the antidepressant drug sertraline. Like sertraline, desmethylsertraline acts as a monoamine reuptake inhibitor, and may be responsible for some of its parent's therapeutic benefits; however, the effects of DMS's main activity of increasing serotonin levels via binding to the serotonin transporter appears to be negligible as in vivo testing showed no measurable change in brain activity despite a nearly 20-fold increase in DMS blood levels compared to the EC50 (i.e. the amount required to achieve the desired effect in 50% of the population) of its parent drug sertraline. DMS is significantly less potent relative to sertraline as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (Ki = 76 nM vs. 3 nM, respectively), but conversely, is more balanced as a monoamine reuptake inhibitor (5-HT (Ki) = 76 nM; NE (Ki) = 420 nM; DA (Ki) = 440 nM), which has the effective result of DMS contrarily behaving as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), with about 5.5-fold preference for inhibiting serotonin reuptake relative to catecholamine reuptake.

6-Chloro-2-aminotetralin (6-CAT) is a drug which acts as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) and is a putative entactogen in humans. It is a rigid analogue of para-chloroamphetamine (PCA).
EXP-561 is an investigational drug that acts as an inhibitor of the reuptake of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. It was developed in the 1960s by Du Pont and was suggested as a potential antidepressant but failed in trials and was never marketed.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.

LY-367,265 is a drug developed by Eli Lilly, which acts as both a potent and selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, and also a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It has antidepressant effects in animal studies, reduces glutamate signalling in the brain and increases the analgesic effects of morphine.
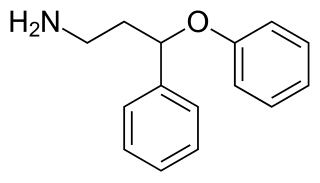
PPPA, or 3-phenoxy-3-phenylpropan-1-amine, is a drug which is described as an antidepressant. It was derived by Eli Lilly from the antihistamine diphenhydramine, a 2-diphenylmethoxyethanamine derivative with additional properties as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), and has been the basis for the subsequent discovery of a number of other antidepressant drugs.
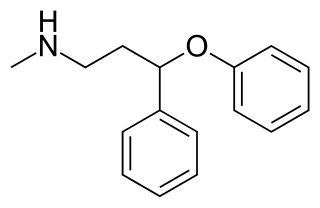
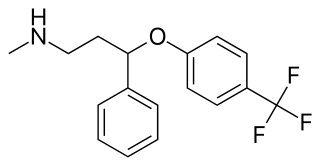
N-Methyl-PPPA, or N-methyl-3-phenoxy-3-phenylpropan-1-amine, is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) which was developed by Eli Lilly from diphenhydramine in the early 1970s while in search of new antidepressants, but was never marketed. It is closely related structurally to fluoxetine, atomoxetine, and nisoxetine.

Toludesvenlafaxine, also formerly known as ansofaxine and sold under the brand name Ruoxinlin, is an antidepressant which is approved for the treatment of major depressive disorder in China. It is also under development for use in other countries like the United States. It is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) and was developed by Luye Pharma Group.


















