
Genetically modified maize (corn) is a genetically modified crop. Specific maize strains have been genetically engineered to express agriculturally-desirable traits, including resistance to pests and to herbicides. Maize strains with both traits are now in use in multiple countries. GM maize has also caused controversy with respect to possible health effects, impact on other insects and impact on other plants via gene flow. One strain, called Starlink, was approved only for animal feed in the US but was found in food, leading to a series of recalls starting in 2000.
DeKalb or De Kalb may refer to:
The Monsanto Company was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed in the 1970s. Later, the company became a major producer of genetically engineered crops. In 2018, the company ranked 199th on the Fortune 500 of the largest United States corporations by revenue.

DeKalb is a city in DeKalb County, Illinois, United States. The population was 40,290 at the 2020 census, down from 43,862 at the 2010 census. The city is named after decorated Franconian-French war hero Johann de Kalb, who died during the American Revolutionary War.
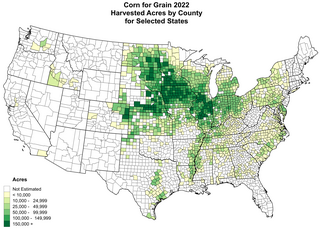
The Corn Belt is a region of the Midwestern United States and part of the Southern United States that, since the 1850s, has dominated corn production in the United States. In North America, corn is the common word for maize. More generally, the concept of the Corn Belt connotes the area of the Midwest dominated by farming and agriculture.
G.D. Searle, LLC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Pfizer. It is currently a trademark company and subsidiary of Pfizer, operating in more than 43 countries. It also operates as a distribution trademark for various pharmaceuticals that were developed by G. D. Searle & Company. Searle is most notable for having developed the first female birth control pill, and the artificial sweetener NutraSweet. Searle also developed the drug Lomotil, an antidiarrheal medication. One of the notable Alumni of Searle is Donald Rumsfeld, the Secretary of Defense for George W. Bush in the 2000s. Prior to its 1985 merger with Monsanto, Searle was a company mainly focusing on life sciences, specifically pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and animal health.

Genetically modified crops are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. In most cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. Examples in food crops include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, reduction of spoilage, resistance to chemical treatments, or improving the nutrient profile of the crop. Examples in non-food crops include production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation.

Syngenta AG is a provider of agricultural science and technology, in particular seeds and pesticides with its management headquarters in Basel, Switzerland. It is owned by ChemChina, a Chinese state-owned enterprise.

Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. is a U.S.-based producer of seeds for agriculture. They are a major producer of genetically modified crops with insect and herbicide resistance.

The Frederick B. Townsend House is located in the DeKalb County, Illinois county seat of Sycamore. The home is within the boundaries of the Sycamore Historic District. The district was designated and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in May 1978. The Queen Anne style home was designed and constructed in 1890 or 1892 by the same architect and general contractor responsible for Altgeld Hall at Northern Illinois University and the nearby DeKalb County Courthouse, as well as the courthouse in Lee County.

Intensive crop farming is a modern industrialized form of crop farming. Intensive crop farming's methods include innovation in agricultural machinery, farming methods, genetic engineering technology, techniques for achieving economies of scale in production, the creation of new markets for consumption, patent protection of genetic information, and global trade. These methods are widespread in developed nations.
Holden Foundation Seeds is an American company that specializes in the research, development, and production of patented foundation seed corn for agriculture. Foundation corn is the parent seed from which hybrids are made.
Robert B. Shapiro is an American businessman and attorney who has worked extensively with the biochemical corporations G. D. Searle & Company and Monsanto. Before working in this sector he was Vice-President and legal counsel at General Instrument from 1972 to 1979. His father, Moses, was Chairman of this company from 1969 to 1975.

Maize, also known as corn in North American and Australian English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears which yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors.

The Bayer AG is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include: pharmaceuticals, consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the EURO STOXX 50 stock market index.

Asgrow is a seed company owned and operated by Bayer Crop Science.

KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA is a European independent and family-owned company based in Germany that focuses on plant breeding, with activities in about 70 countries. KWS is the fourth largest seed producer worldwide based on sales in agricultural crops. The product range includes seed varieties for sugar beet, corn, cereals, oil and protein plants, sorghum, catch crops ans vegetables. The capital letters "K," "W" and "S" in the name KWS stand for Klein Wanzlebener Saatzucht, which means seed breeding from Klein Wanzleben. The company's original headquarters were in Klein Wanzleben, an East German town located near the city of Magdeburg. Its main markets are in Europe, North and South America as well as Asia. KWS has breeding and distribution activities in more than 70 countries. In 1954, the company went public on the Hamburg-Hannover Stock Exchange and has been on the SDAX list of the Frankfurt Stock Exchange since June 2006. In addition, the shares are listed in the Nisax20 index of shares in Lower Saxony.
J. E. M. Ag Supply, Inc. v. Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc., 534 U.S. 124 (2001), was a decision of the United States Supreme Court holding for the first time that utility patents may be issued for crops and other flowering plants under 35 U.S.C. § 101. The Supreme Court rejected the argument that the exclusive ways to protect these plants are under the Plant Variety Protection Act (PVPA), 7 U.S.C. § 2321, and the Plant Patent Act of 1930 (PPA), 35 U.S.C. §§ 161-164.
Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Co. (Mahyco) is an agricultural company based in India. It is one of the country's major producers of seed. As of 2015, the company is also active in Vietnam, Indonesia, Philippines and Bangladesh, and planned expansion to Africa. The company produces seeds for cotton, wheat, rice, sorghum, pearl millet, maize oilseeds and vegetables crops. Through a joint venture with Monsanto named Mahyco Monsanto Biotech, Mahyco sublicenses Bt cotton technology in India. The Indian government has maintained price controls on Bt cotton seeds since at least 2011.

Surinder Mohan (Suri) Sehgal is an Indian-American philanthropist with a long career as a crop scientist, seedsman, entrepreneur, and leading global hybrid seed industry expert. His research and professional successes in the areas of plant breeding and genetics, ag biotechnology, intellectual property, business management, and seed industry development were carried out in executive capacities in several companies in the United States, Belgium, and Germany. After the divestment of a group of four seed companies that Sehgal founded and ran with his wife, Edda Sehgal, the couple created two nonprofit organizations to promote rural development in Suri's country of origin: Sehgal (Family) Foundation in 1998 in the US, and S M Sehgal Foundation in India. The foundation focuses on water security, food security, and social justice, particularly empowerment. A proponent of corporate social responsibility and environmental sustainability, Sehgal has also provided support individually and through the foundations for projects related to agriculture research, the preservation of biodiversity and the conservation of natural resources.













