Related Research Articles
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending. This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale anthropogenic or natural disaster.
An economic depression is a period of carried long-term economic downturn that is the result of lowered economic activity in one major or more national economies. Economic depression maybe related to one specific country where there is some economic crisis that has worsened but most often reflexes historically the American Great Depression and similar economic status that may be recognized as existing at some country, several countries or even in many countries. It is often understood in economics that economic crisis and the following recession that maybe named economic depression are part of economic cycles where the slowdown of the economy follows the economic growth and vice versa. It is a result of more severe economic problems or a downturn than the recession itself, which is a slowdown in economic activity over the course of the normal business cycle of growing economy.

The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.
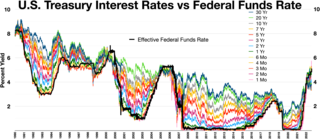
The early 2000s recession was a major decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The recession affected the European Union during 2000 and 2001 and the United States from March to November 2001. The UK, Canada and Australia avoided the recession, while Russia, a nation that did not experience prosperity during the 1990s, began to recover from it. Japan's 1990s recession continued.

The Japanese asset price bubble was an economic bubble in Japan from 1986 to 1991 in which real estate and stock market prices were greatly inflated. In early 1992, this price bubble burst and Japan's economy stagnated. The bubble was characterized by rapid acceleration of asset prices and overheated economic activity, as well as an uncontrolled money supply and credit expansion. More specifically, over-confidence and speculation regarding asset and stock prices were closely associated with excessive monetary easing policy at the time. Through the creation of economic policies that cultivated the marketability of assets, eased the access to credit, and encouraged speculation, the Japanese government started a prolonged and exacerbated Japanese asset price bubble.

The early 1980s recession was a severe economic recession that affected much of the world between approximately the start of 1980 and 1982. It is widely considered to have been the most severe recession since World War II until the 2007–2008 financial crisis.
At the micro-economic level, deleveraging refers to the reduction of the leverage ratio, or the percentage of debt in the balance sheet of a single economic entity, such as a household or a firm. It is the opposite of leveraging, which is the practice of borrowing money to acquire assets and multiply gains and losses.

The Great Depression (1929–1939) was a severe global economic downturn that affected many countries across the world. It became evident after a sharp decline in stock prices in the United States, leading to a period of economic depression. The economic contagion began around September 1929 and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of 24 October. This crisis marked the start of a prolonged period of economic hardship characterized by high unemployment rates and widespread business failures.

The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline observed in national economies globally, i.e. a recession, that occurred in the late 2000s. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country. At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations.

A global recession is recession that affects many countries around the world—that is, a period of global economic slowdown or declining economic output.
While beginning in the United States, the Great Recession spread to Asia rapidly and has affected much of the region.
North America was one of the focal points of the global Great Recession. While Canada has managed to return its economy nearly to the levels it enjoyed prior to the recession, the United States and Mexico are still under the influence of the worldwide economic slowdown. The cost of staple items dropped dramatically in the United States as a result of the recession.

The Lost Decades is a lengthy period of economic stagnation in Japan precipitated by the asset price bubble's collapse beginning in 1990. The singular term Lost Decade originally referred to the 1990s, but the 2000s and the 2010s have been included by commentators as the phenomenon continued.
A global saving glut is a situation in which desired saving exceeds desired investment. By 2005 Ben Bernanke, chairman of the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, expressed concern about the "significant increase in the global supply of saving" and its implications for monetary policies, particularly in the United States. Although Bernanke's analyses focused on events in 2003 to 2007 that led to the 2007–2009 financial crisis, regarding GSG countries and the United States, excessive saving by the non-financial corporate sector (NFCS) is an ongoing phenomenon, affecting many countries. Bernanke's global saving glut (GSG) hypothesis argued that increased capital inflows to the United States from GSG countries were an important reason that U.S. longer-term interest rates from 2003 to 2007 were lower than expected.
The 1990s economic boom in the United States was an economic expansion that began after the end of the early 1990s recession in March 1991, and ended in March 2001 with the start of the early 2000s recession during the Dot-com bubble crash (2000–2002). It was the longest recorded economic expansion in the history of the United States until July 2019.
This information is related to the effects of the Great Recession that happened worldwide from 2007 to 2012.

An economic recovery is the phase of the business cycle following a recession. The overall business outlook for an industry looks optimistic during the economic recovery phase.
The Great Regression refers to worsening economic conditions affecting lower earning sections of the population in the United States, Western Europe and other advanced economies starting around 1981. These deteriorating conditions include rising inequality; and falling or stagnating wages, pensions, unemployment insurance, and welfare benefits. The decline in these conditions has been by no means uniform. Specific trends vary depending on the metric being tracked, the country, and which specific demographic is being examined. For most advanced economies, the worsening economic conditions affecting the less well off accelerated sharply after the late-2000s recession.

The financial crisis in Russia in 2014–2016 was the result of the sharp devaluation of the Russian rouble beginning in the second half of 2014. A decline in confidence in the Russian economy caused investors to sell off their Russian assets, which led to a decline in the value of the Russian rouble and sparked fears of a financial crisis. The lack of confidence in the Russian economy stemmed from at least two major sources. The first is the fall in the price of oil in 2014. Crude oil, a major export of Russia, declined in price by nearly 50% between its yearly high in June 2014 and 16 December 2014. The second is the result of international economic sanctions imposed on Russia following Russia's annexation of Crimea, the war in Donbas and the broader Russo-Ukrainian War.
The COVID-19 recession, also known as the Great Lockdown, was a global economic recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. The recession began in most countries in February 2020. After a year of global economic slowdown that saw stagnation of economic growth and consumer activity, the COVID-19 lockdowns and other precautions taken in early 2020 drove the global economy into crisis. Within seven months, every advanced economy had fallen to recession.
References
- ↑ "Decoupling: Theory vs. reality." International Herald Tribune. January 27, 2008.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul (2010-11-09). "We Are Not The World". The New York Times.
- ↑ Korinek, Anton; Agustin Roitman; Carlos Vegh (2010), "Decoupling and Recoupling" (PDF), American Economic Review 100(2), pp. 393-397