Related Research Articles
Frame rate is typically the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images (frames) are captured or displayed. This definition applies to film and video cameras, computer animation, and motion capture systems. In these contexts, frame rate may be used interchangeably with frame frequency and refresh rate, which are expressed in hertz. Additionally, in the context of computer graphics performance, FPS is the rate at which a system, particularly a GPU, is able to generate frames, and refresh rate is the frequency at which a display shows completed frames. In electronic camera specifications frame rate refers to the maximum possible rate frames could be captured, but in practice, other settings may reduce the actual frequency to a lower number than the frame rate.
In digital signal processing, spatial anti-aliasing is a technique for minimizing the distortion artifacts (aliasing) when representing a high-resolution image at a lower resolution. Anti-aliasing is used in digital photography, computer graphics, digital audio, and many other applications.
In computer graphics, mipmaps or pyramids are pre-calculated, optimized sequences of images, each of which is a progressively lower resolution representation of the previous. The height and width of each image, or level, in the mipmap is a factor of two smaller than the previous level. Mipmaps do not have to be square. They are intended to increase rendering speed and reduce aliasing artifacts. A high-resolution mipmap image is used for high-density samples, such as for objects close to the camera; lower-resolution images are used as the object appears farther away. This is a more efficient way of downfiltering (minifying) a texture than sampling all texels in the original texture that would contribute to a screen pixel; it is faster to take a constant number of samples from the appropriately downfiltered textures. Mipmaps are widely used in 3D computer games, flight simulators, other 3D imaging systems for texture filtering, and 2D and 3D GIS software. Their use is known as mipmapping. The letters MIP in the name are an acronym of the Latin phrase multum in parvo, meaning "much in little".

The RIVA 128, or "NV3", was a consumer graphics processing unit created in 1997 by Nvidia. It was the first to integrate 3D acceleration in addition to traditional 2D and video acceleration. Its name is an acronym for Real-time Interactive Video and Animation accelerator.
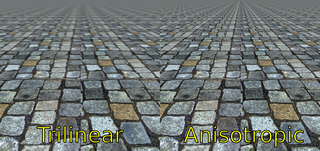
In 3D computer graphics, anisotropic filtering is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces of computer graphics that are at oblique viewing angles with respect to the camera where the projection of the texture appears to be non-orthogonal.
In computer graphics, texture filtering or texture smoothing is the method used to determine the texture color for a texture mapped pixel, using the colors of nearby texels.

720p is a progressive HD signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HD (1.78:1). All major HD broadcasting standards include a 720p format, which has a resolution of 1280×720p.

Pixel art scaling algorithms are graphical filters that attempt to enhance the appearance of hand-drawn 2D pixel art graphics. These algorithms are a form of automatic image enhancement. Pixel art scaling algorithms employ methods significantly different than the common methods of image rescaling, which have the goal of preserving the appearance of images.
A video scaler is a system which converts video signals from one display resolution to another; typically, scalers are used to convert a signal from a lower resolution to a higher resolution, a process known as "upconversion" or "upscaling".

In computer graphics and digital imaging, imagescaling refers to the resizing of a digital image. In video technology, the magnification of digital material is known as upscaling or resolution enhancement.
Multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA) is a type of spatial anti-aliasing, a technique used in computer graphics to remove jaggies.

The Rockstar Advanced Game Engine (RAGE) is a proprietary game engine of Rockstar Games, developed by the RAGE Technology Group division of Rockstar San Diego. Since its first game, Rockstar Games Presents Table Tennis in 2006, released for the Xbox 360 and Wii, the engine has been used by Rockstar Games' internal studios to develop advanced open world games for consoles and computers.
Temporal anti-aliasing (TAA) is a spatial anti-aliasing technique for computer-generated video that combines information from past frames and the current frame to remove jaggies in the current frame. In TAA, each pixel is sampled once per frame but in each frame the sample is at a different location within the pixel. Pixels sampled in past frames are blended with pixels sampled in the current frame to produce an anti-aliased image. Although this method makes TAA achieve a result comparable to supersampling, the technique inevitably causes ghosting and blurriness to the image.
Anti-aliasing may refer to any of a number of techniques to combat the problems of aliasing in a sampled signal such as a digital image or digital audio recording
Fast approximate anti-aliasing (FXAA) is a screen-space anti-aliasing algorithm created by Timothy Lottes at Nvidia.

GPUOpen is a middleware software suite originally developed by AMD's Radeon Technologies Group that offers advanced visual effects for computer games. It was released in 2016. GPUOpen serves as an alternative to, and a direct competitor of Nvidia GameWorks. GPUOpen is similar to GameWorks in that it encompasses several different graphics technologies as its main components that were previously independent and separate from one another. However, GPUOpen is partially open source software, unlike GameWorks which is proprietary and closed.

The GeForce 20 series is a family of graphics processing units developed by Nvidia. Serving as the successor to the GeForce 10 series, the line started shipping on September 20, 2018, and after several editions, on July 2, 2019, the GeForce RTX Super line of cards was announced.
Deep learning super sampling (DLSS) is a family of real-time deep learning image enhancement and upscaling technologies developed by Nvidia that are exclusive to its RTX line of graphics cards, and available in a number of video games. The goal of these technologies is to allow the majority of the graphics pipeline to run at a lower resolution for increased performance, and then infer a higher resolution image from this that approximates the same level of detail as if the image had been rendered at this higher resolution. This allows for higher graphical settings and/or frame rates for a given output resolution, depending on user preference.

Video super-resolution (VSR) is the process of generating high-resolution video frames from the given low-resolution video frames. Unlike single-image super-resolution (SISR), the main goal is not only to restore more fine details while saving coarse ones, but also to preserve motion consistency.

Intel Arc is a brand of graphics processing units designed by Intel. These are discrete GPUs mostly marketed for the high-margin PC gaming market. The brand also covers Intel's consumer graphics software and services.
References
- 1 2 Kostovic, Aleksandar (2021-09-20). "Nvidia Readies Deep Learning Anti-Aliasing Debut with The Elder Scrolls Online Update". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved 2022-02-20.
- ↑ Hruska, Joel (2021-09-21). "Nvidia's DLAA Could Be a Huge Step Forward for Anti-Aliasing". ExtremeTech.
- 1 2 Liu, Edward (2020-03-23). "DLSS 2.0 – Image Reconstruction for Real-Time Rendering With Deep Learning" (PDF). Behind the Pixels.
- ↑ "Nvidia's DLAA makes PC games look better with little performance hit". PCWorld. Retrieved 2024-04-20.
- ↑ Yang, Lei; Liu, Shiqiu; Salvi, Marco. "A Survey of Temporal Antialiasing Techniques" (PDF). Computer Graphics Forum. 39 (2): 607–621. doi:10.1111/cgf.14018 – via Behind the Pixels.
- ↑ De Meo, Francesco (2021-09-23). "The Elder Scrolls Online DLAA vs DLSS vs TAA Comparison Video Highlights DLAA Superior Image Quality". Wccftech. Retrieved 2022-02-20.
- ↑ Karis, Brian. "High Quality Temporal Supersamplin" (PDF).
- ↑ "GTC 2020: DLSS 2.0 - Image Reconstruction for Real-time Rendering with Deep Learning". NVIDIA Developer. 2020-06-09. Retrieved 2022-06-26.
- ↑ "NVIDIA DLSS 2.0: A Big Leap In AI Rendering". www.nvidia.com. Retrieved 2022-06-26.
- ↑ maxus24; on; Studios, in Game Testing Manufacturer: Zenimax Online (2021-09-22). "NVIDIA DLAA Anti-Aliasing Review - DLSS at Native Resolution". TechPowerUp. Retrieved 2024-03-22.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ Archer, James (2022-06-27). "Nvidia DLAA: How it works, supported games and performance vs DLSS". Rock, Paper, Shotgun. Retrieved 2022-07-09.