Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol 2
H
or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among every 6,420 atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans (i.e., 4.85×1013 tonnes of deuterium – mainly in form of HOD and only rarely in form of D2O – in 1.4×1018 tonnes of water), while protium accounts for 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water)

Heavy water is a form of water whose hydrogen atoms are all deuterium rather than the common hydrogen-1 isotope that makes up most of the hydrogen in normal water. The presence of the heavier hydrogen isotope gives the water different nuclear properties, and the increase in mass gives it slightly different physical and chemical properties when compared to normal water.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

A solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell.
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with the formula CHCl3 and a common solvent. It is a very volatile, colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and in turn PTFE. Chloroform is a trihalomethane that serves as a powerful anesthetic, euphoriant, anxiolytic, and sedative when inhaled or ingested. Chloroform was used as an anesthetic between the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. It is miscible with many solvents but it is only very slightly soluble in water.
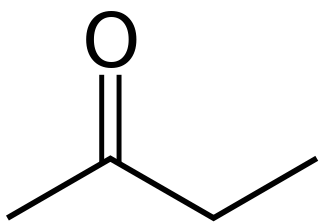
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) or ethyl methyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colorless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

3-Pentanone is a simple, symmetrical dialkyl ketone. It is a colorless liquid ketone with an odor like that of acetone. It is soluble in about 25 parts water, but miscible with organic solvents.

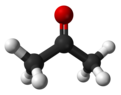
Acetone is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO. It is the simplest and smallest ketone. It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor.

Proton nuclear magnetic resonance is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen (H) is used, practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1H.
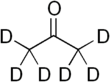
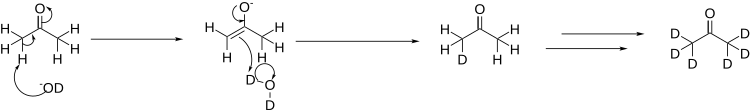
Hydrogen–deuterium exchange is a chemical reaction in which a covalently bonded hydrogen atom is replaced by a deuterium atom, or vice versa. It can be applied most easily to exchangeable protons and deuterons, where such a transformation occurs in the presence of a suitable deuterium source, without any catalyst. The use of acid, base or metal catalysts, coupled with conditions of increased temperature and pressure, can facilitate the exchange of non-exchangeable hydrogen atoms, so long as the substrate is robust to the conditions and reagents employed. This often results in perdeuteration: hydrogen-deuterium exchange of all non-exchangeable hydrogen atoms in a molecule.
Deuterated chloroform, also known as chloroform-d, is the organic compound with the formula CDCl3 or C2HCl3. Deuterated chloroform is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy. The properties of CDCl3 and ordinary CHCl3 (chloroform) are virtually identical.

Deuterated benzene (C6D6) is an isotopologue of benzene (C6H6) in which the hydrogen atom ("H") is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D").

Deuterated methanol (CD3OD), is a form (called an isotopologue) of methanol (CH3OH) in which the hydrogen atoms ("H") are replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D"). Deuterated methanol is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.

Deuterated DMSO, also known as dimethyl sulfoxide-d6, is an isotopologue of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, (CH3)2S=O)) with chemical formula ((CD3)2S=O) in which the hydrogen atoms ("H") are replaced with their isotope deuterium ("D"). Deuterated DMSO is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group it is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of propan-1-ol and ethyl methyl ether. They all have the formula C3H8O.

Deuterated solvents are a group of compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms are substituted by deuterium atoms.
Deuterated dichloromethane (CD2Cl2) is a form (called an isotopologue) of dichloromethane (DCM, CH2Cl2) in which the hydrogen atoms ("H") are replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D"). Deuterated DCM is not a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy as it is expensive compared to deuterated chloroform.

Acetone azine is the simplest ketazine. It is an intermediate in some hydrazine manufacturing processes.

Methoxyamine is the organic compound with the formula CH3ONH2. Also called O-methylhydroxylamine, it is a colourless volatile liquid that is soluble in polar organic solvent and in water. It is a derivative of hydroxylamine with the hydroxyl hydrogen replaced by a methyl group. Alternatively, it can be viewed as a derivative of methanol with the hydroxyl hydrogen replaced by an amino group. It is an isomer of N-methylhydroxylamine and aminomethanol. It decomposes in an exothermic reaction (-56 kJ/mol) to methane and azanone unless stored as a hydrochloride salt.