A general election is an electoral process to choose most or all members of an elected body, typically a legislature. They are distinct from by-elections, which fill a seat that has become vacant between general elections. In most systems, a general election is a regularly scheduled election, typically including members of a legislature, and sometimes other officers such as a directly elected president. General elections may also take place at the same time as local, state/autonomous region, European Parliament, and other elections, where applicable. For example, on 25 May 2014, Belgian voters elected their national parliament, 21 members of the European Parliament, and regional parliaments.

The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 members known as members of Parliament (MPs). MPs are elected to represent constituencies by the first-past-the-post system and hold their seats until Parliament is dissolved.

The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster in London. Parliament possesses legislative supremacy and thereby holds ultimate power over all other political bodies in the United Kingdom and the Overseas Territories. While Parliament is bicameral, it has three parts: the sovereign, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The three parts acting together to legislate may be described as the King-in-Parliament. The Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is de facto vested in the House of Commons.

The 1832 United Kingdom general election, the first after the Reform Act, saw the Whigs win an overall majority of 224 seats, with the Tories winning less than 30% of the vote.

The governor-general of Belize is the representative of the Belizean monarch, currently King Charles III, in Belize. The governor-general is appointed by the monarch on the recommendation of the prime minister of Belize. The functions of the governor-general include appointing ministers, judges, and ambassadors; giving royal assent to legislation passed by the National Assembly; and issuing writs for election.
Dissolution of a legislative assembly is the simultaneous termination of service of all of its members, in anticipation that a successive legislative assembly will reconvene later with possibly different members. In a democracy, the new assembly is chosen by a general election. Dissolution is distinct on the one hand from abolition of the assembly, and on the other hand from its adjournment or prorogation, or the ending of a legislative session, any of which begins a period of inactivity after which it is anticipated that the same members will reassemble. For example, the "second session of the fifth parliament" could be followed by the "third session of the fifth parliament" after a prorogation, but would be followed by the "first session of the sixth parliament" after a dissolution.

A writ of election is a writ issued ordering the holding of an election. In Commonwealth countries writs are the usual mechanism by which general elections are called and are issued by the head of state or their representative. In the United States, writs are more commonly used to call special elections for political offices.
Elections in Australia take place periodically to elect the legislature of the Commonwealth of Australia, as well as for each Australian state and territory and for local government councils. Elections in all jurisdictions follow similar principles, although there are minor variations between them. The elections for the Australian Parliament are held under the federal electoral system, which is uniform throughout the country, and the elections for state and territory Parliaments are held under the electoral system of each state and territory.
A fixed-term election is an election that occurs on a set date, and cannot be changed by incumbent politicians other than through exceptional mechanisms if at all. The office holder generally takes office for a set amount of time, and their term of office or mandate ends automatically.
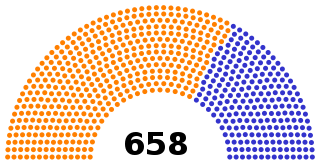
The 1806 United Kingdom general election was the election of members to the 3rd Parliament of the United Kingdom. This was the second general election to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland.
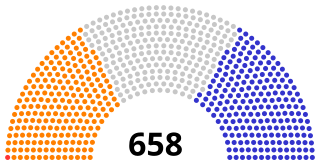
The 1807 United Kingdom general election was the third general election to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland.
In Canada, the federal government and all provinces and territories have enacted legislation setting election dates, usually every four years, one year sooner than the constitutionally set five year maximum life of a parliament. However, the governor general, lieutenant governors, and commissioners still have the legal power to call a general election on the advice of the relevant first minister at any point before the fixed date. By-elections, used to fill vacancies in a legislature, are also not affected by fixed election dates.

There are five types of elections in the United Kingdom: elections to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, elections to devolved parliaments and assemblies, local elections, mayoral elections, and police and crime commissioner elections. Within each of those categories, there may also be by-elections. Elections are held on Election Day, which is conventionally a Thursday, and under the provisions of the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022 the timing of general elections can be held at the discretion of the prime minister during any five-year period. All other types of elections are held after fixed periods, though early elections to the devolved assemblies and parliaments can occur in certain situations. The five electoral systems used are: the single member plurality system (first-past-the-post), the multi-member plurality, the single transferable vote, the additional member system, and the supplementary vote.

There are five types of elections in England: elections to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, elections to the devolved London Assembly, local council elections, metro mayor elections, and the Police and crime commissioner elections, in addition to by-elections for each aforementioned election. Elections are held on Election Day, which is conventionally a Thursday.

The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 (FTPA) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which, for the first time, set in legislation a default fixed election date for general elections in the United Kingdom. It remained in force until 2022, when it was repealed. Since then, as before its passage, elections are required by law to be held at least once every five years, but can be called earlier if the prime minister advises the monarch to exercise the royal prerogative to do so. Prime ministers have often employed this mechanism to call an election before the end of their five-year term, sometimes fairly early in it. Critics have said this gives an unfair advantage to the incumbent prime minister, allowing them to call a general election at a time that suits them electorally. While it was in force, the FTPA removed this longstanding power of the prime minister.

Dáil Éireann is the lower house, and principal chamber, of the Oireachtas, which also includes the president of Ireland and a senate called Seanad Éireann. It consists of 160 members, each known as a Teachta Dála. TDs represent 39 constituencies and are directly elected for terms not exceeding five years, on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). Its powers are similar to those of lower houses under many other bicameral parliamentary systems and it is by far the dominant branch of the Oireachtas. Subject to the limits imposed by the Constitution of Ireland, it has power to pass any law it wishes, and to nominate and remove the Taoiseach. Since 1922, it has met in Leinster House in Dublin.
The 2024 United Kingdom general election is scheduled to be held on Thursday, 4 July 2024. It will determine the composition of the House of Commons, which determines the Government of the United Kingdom. Significant constituency boundary changes will be in effect, the first such changes since before the 2010 general election. It will be the first UK general election where voter identification is required to vote in person in Great Britain. The general election will be the first since the UK's departure from the European Union on 31 January 2020, which was a major issue in the previous election; it will also be the first to take place under the Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022.

The Early Parliamentary General Election Act 2019, also known as the Election Bill, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that made legal provision for the holding of the 2019 United Kingdom general election on 12 December 2019.

The Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Act 2022 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that repealed the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 and reinstated the prior constitutional situation, by reviving the power of the monarch to dissolve and summon parliament. As the monarch exercises this power at the request of the prime minister, this restored the power of the prime minister to have a general election called at a time chosen by the Prime Minister.

The next Australian federal election will be held on or before 27 September 2025 to elect members of the 48th Parliament of Australia. All 150 seats in the House of Representatives and likely 40 of the 76 seats in the Senate will be contested. It is expected that at this election, the Labor government of Prime Minister Anthony Albanese will be seeking re-election to a second term in office, opposed by the Liberal/National Coalition under Leader of the Opposition Peter Dutton.













