In distributed computing, a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space, which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction, typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPCs are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures are largely the same whether they are local or remote, but usually they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orders of magnitude slower and less reliable than local calls, so distinguishing them is important.
Jakarta Enterprise Beans is one of several Java APIs for modular construction of enterprise software. EJB is a server-side software component that encapsulates business logic of an application. An EJB web container provides a runtime environment for web related software components, including computer security, Java servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and other web services. The EJB specification is a subset of the Java EE specification.
Java Platform, Standard Edition is a computing platform for development and deployment of portable code for desktop and server environments. Java SE was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition (J2SE).
In computing, the Java Remote Method Invocation is a Java API that performs remote method invocation, the object-oriented equivalent of remote procedure calls (RPC), with support for direct transfer of serialized Java classes and distributed garbage-collection.
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) is a standard defined by the Object Management Group (OMG) designed to facilitate the communication of systems that are deployed on diverse platforms. CORBA enables collaboration between systems on different operating systems, programming languages, and computing hardware. CORBA uses an object-oriented model although the systems that use the CORBA do not have to be object-oriented. CORBA is an example of the distributed object paradigm.
Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) is a proprietary Microsoft technology for communication between software components on networked computers. DCOM, which originally was called "Network OLE", extends Microsoft's COM, and provides the communication substrate under Microsoft's COM+ application server infrastructure.

In computer science, inter-process communication or interprocess communication (IPC) refers specifically to the mechanisms an operating system provides to allow the processes to manage shared data. Typically, applications can use IPC, categorized as clients and servers, where the client requests data and the server responds to client requests. Many applications are both clients and servers, as commonly seen in distributed computing.
In distributed computing, an object request broker (ORB) is a middleware which allows program calls to be made from one computer to another via a computer network, providing location transparency through remote procedure calls. ORBs promote interoperability of distributed object systems, enabling such systems to be built by piecing together objects from different vendors, while different parts communicate with each other via the ORB.
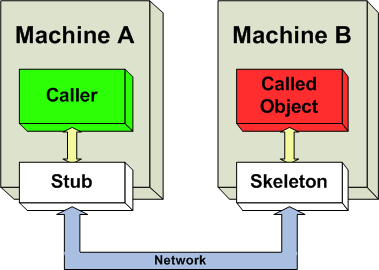
A method stub or simply stub in software development is a piece of code used to stand in for some other programming functionality. A stub may simulate the behavior of existing code or be a temporary substitute for yet-to-be-developed code. Stubs are therefore most useful in porting, distributed computing as well as general software development and testing.
In computer science, message passing is a technique for invoking behavior on a computer. The invoking program sends a message to a process and relies on that process and its supporting infrastructure to then select and run some appropriate code. Message passing differs from conventional programming where a process, subroutine, or function is directly invoked by name. Message passing is key to some models of concurrency and object-oriented programming.

In distributed computing, distributed objects are objects that are distributed across different address spaces, either in different processes on the same computer, or even in multiple computers connected via a network, but which work together by sharing data and invoking methods. This often involves location transparency, where remote objects appear the same as local objects. The main method of distributed object communication is with remote method invocation, generally by message-passing: one object sends a message to another object in a remote machine or process to perform some task. The results are sent back to the calling object.
Jakarta XML RPC allows a Jakarta EE application to invoke a Java-based web service with a known description while still being consistent with its WSDL description. JAX-RPC is one of the Java XML programming APIs. It can be seen as Java RMIs over web services. JAX-RPC 2.0 was renamed JAX-WS 2.0. JAX-RPC 1 is deprecated with Java EE 6. The JAX-RPC service utilizes W3C standards like WSDL or Web Service Description Language. The core API classes are located in the Java package javax.xml.rpc.
RMI-IIOP denotes the Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) interface over the Internet Inter-Orb Protocol (IIOP), which delivers Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) distributed computing capabilities to the Java platform. It was initially based on two specifications: the Java Language Mapping to OMG IDL, and CORBA/IIOP 2.3.1.
In distributed programming, a portable object is an object which can be accessed through a normal method call while possibly residing in memory on another computer. It is portable in the sense that it moves from machine to machine, irrespective of operating system or computer architecture. This mobility is the end goal of many remote procedure call systems.

RPyC, or Remote Python Call, is a Python library for remote procedure calls (RPC), as well as distributed computing. Unlike regular RPC mechanisms, such as ONC RPC, CORBA or Java RMI, RPyC is transparent, symmetric, and requires no special decoration or definition languages. Moreover, it provides programmatic access to any pythonic element, be it functions, classes, instances or modules.
.NET Remoting is a Microsoft application programming interface (API) for interprocess communication released in 2002 with the 1.0 version of .NET Framework. It is one in a series of Microsoft technologies that began in 1990 with the first version of Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) for 16-bit Windows. Intermediate steps in the development of these technologies were Component Object Model (COM) released in 1993 and updated in 1995 as COM-95, Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM), released in 1997, and COM+ with its Microsoft Transaction Server (MTS), released in 2000. It is now superseded by Windows Communication Foundation (WCF), which is part of the .NET Framework 3.0.
A stub in distributed computing is a piece of code that converts parameters passed between client and server during a remote procedure call (RPC).
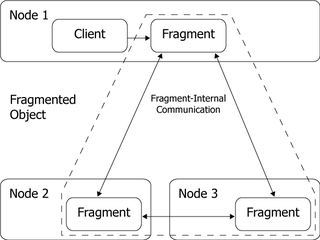
In computing, fragmented objects are truly distributed objects. It is a novel design principle extending the traditional concept of stub based distribution.
In computer science, marshalling or marshaling is the process of transforming the memory representation of an object into a data format suitable for storage or transmission. It is typically used when data must be moved between different parts of a computer program or from one program to another.
Component Object Model (COM) is a binary-interface standard for software components introduced by Microsoft in 1993. It is used to enable inter-process communication object creation in a large range of programming languages. COM is the basis for several other Microsoft technologies and frameworks, including OLE, OLE Automation, Browser Helper Object, ActiveX, COM+, DCOM, the Windows shell, DirectX, UMDF and Windows Runtime. The essence of COM is a language-neutral way of implementing objects that can be used in environments different from the one in which they were created, even across machine boundaries. For well-authored components, COM allows reuse of objects with no knowledge of their internal implementation, as it forces component implementers to provide well-defined interfaces that are separated from the implementation. The different allocation semantics of languages are accommodated by making objects responsible for their own creation and destruction through reference-counting. Type conversion casting between different interfaces of an object is achieved through the QueryInterface method. The preferred method of "inheritance" within COM is the creation of sub-objects to which method "calls" are delegated.