
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula CnH2n−2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated as MeCHO. It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body.
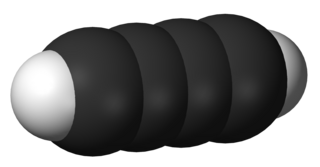
Diacetylene (also known as butadiyne) is the organic compound with the formula C4H2. It is the simplest compound containing two triple bonds. It is first in the series of polyynes, which are of theoretical but not of practical interest.

In organic chemistry, a sulfide or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity R−S−R' as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A sulfide is similar to an ether except that it contains a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen. The grouping of oxygen and sulfur in the periodic table suggests that the chemical properties of ethers and sulfides are somewhat similar, though the extent to which this is true in practice varies depending on the application.

In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group. The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.

In organic chemistry, a sulfoxide, also called a sulphoxide, is an organosulfur compound containing a sulfinyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent.

Vinylacetylene is the organic compound with the formula C4H4. The colourless gas was once used in the polymer industry. It is composed of both alkyne and alkene groups and is the simplest enyne.

In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include the reagent 3,4-dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols. An exception is the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.

A dithiane is a heterocyclic compound composed of a cyclohexane core structure wherein two methylene bridges are replaced by sulfur. The three isomeric parent heterocycles are 1,2-dithiane, 1,3-dithiane and 1,4-dithiane. They are all colorless solids.
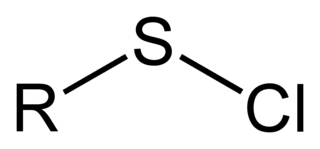
In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfenyl chloride is a functional group with the connectivity R−S−Cl, where R is alkyl or aryl. Sulfenyl chlorides are reactive compounds that behave as sources of RS+. They are used in the formation of RS−N and RS−O bonds. According to IUPAC nomenclature they are named as alkyl thiohypochlorites, i.e. esters of thiohypochlorous acid.
Methyl vinyl ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3OCH=CH2. A colorless gas, it is the simplest enol ether. It is used as a synthetic building block, as is the related compound ethyl vinyl ether (a liquid at room temperature).
In organic chemistry, vinylation is the process of attaching a vinyl group to a substrate. Many organic compounds contain vinyl groups, so the process has attracted significant interest, especially since the reaction scope includes substituted vinyl groups. The reactions can be classified according to the source of the vinyl group.

Cyanoethylation is a process for the attachment of CH2CH2CN group to another organic substrate. The method is used in the synthesis of organic compounds.
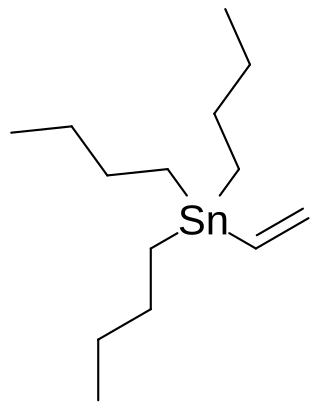
Vinyl tributyltin is an organotin compound with the formula Bu3SnCH=CH2 (Bu = butyl). It is a white, air-stable solid. It is used as a source of vinyl anion equivalent in Stille coupling reactions. As a source of vinyltin reagents, early work used vinyl trimethyltin, but trimethyltin compounds are avoided nowadays owing to their toxicity.
In organic chemistry, methylenation is a chemical reaction that inserts a methylene group into a chemical compound:

Sodium acetylacetonate is an organic compound with the nominal formula Na[CH(C(O)CH3)2]. This white, water-soluble solid is the conjugate base of acetylacetone.

Bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula (ClCH2CH2)2S. It is a prominent member of a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. Sometimes referred to as mustard gas, the term is technically incorrect: bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide is a liquid at room temperature. In warfare it was dispersed in the form of a fine mist of liquid droplets.

Diphenyl sulfide is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula (C6H5)2S, often abbreviated as Ph2S, where Ph stands for phenyl. It is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Diphenyl sulfide is an aromatic sulfide. The molecule consists of two phenyl groups attached to a sulfur atom.
















