Related Research Articles

Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Infection can occur through four methods: contact with the skin, inhalation by the lungs, intestinal absorption, and via injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The skin form presents with a small blister with surrounding swelling that often turns into a painless ulcer with a black center. The inhalation form presents with fever, chest pain and shortness of breath. The intestinal form presents with diarrhea, abdominal pains, nausea and vomiting. The injection form presents with fever and an abscess at the site of drug injection.
Incapacitating agent is a chemical or biological agent which renders a person unable to harm themselves or others, regardless of consciousness.

Porton Down is a science and defence technology campus in Wiltshire, England, just north-east of the village of Porton, near Salisbury. It is home to two British government facilities: a site of the Ministry of Defence's Defence Science and Technology Laboratory – known for over 100 years as one of the UK's most secretive and controversial military research facilities, occupying 7,000 acres (2,800 ha) – and a site of the UK Health Security Agency. Since 2018, part of the campus has housed Porton Science Park, which is owned and operated by Wiltshire Council and has private sector companies in the health, life science and defence and security sectors.

Serratia marcescens is a species of rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe and an opportunistic pathogen in humans. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy. S. marcescens is commonly involved in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), also called nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections, and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of HAI cases in the United States. It is commonly found in the respiratory and urinary tracts of hospitalized adults and in the gastrointestinal systems of children.
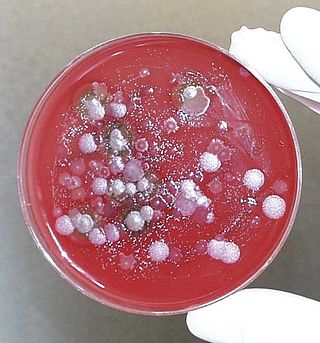
A biological agent is a bacterium, virus, protozoan, parasite, fungus, or toxin that can be used purposefully as a weapon in bioterrorism or biological warfare (BW). In addition to these living or replicating pathogens, toxins and biotoxins are also included among the bio-agents. More than 1,200 different kinds of potentially weaponizable bio-agents have been described and studied to date.

Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. B. subtilis has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. B. subtilis is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies.
Operation Cauldron was a series of secret biological warfare trials undertaken by the British government in 1952. Scientists from Porton Down and the Royal Navy were involved in releasing biological agents, including pneumonic and bubonic plague, brucellosis and tularaemia and testing the effects of the agents on caged monkeys and guinea pigs.
Unit Ei 1644 — also known as Unit 1644, Detachment Ei 1644, Detachment Ei, Detachment Tama, The Nanking Detachment, or simply Unit Ei, was a Japanese laboratory and biological warfare facility under control of the Epidemic Prevention and Water Purification Department. It was established in 1939 in Japanese-occupied Nanking as a satellite unit of Unit 731. It had 12 branches and employed about 1,500 men.
The United States biological weapons program officially began in spring 1943 on orders from U.S. President Franklin Roosevelt. Research continued following World War II as the U.S. built up a large stockpile of biological agents and weapons. Over the course of its 27-year history, the program weaponized and stockpiled the following seven bio-agents :

Project 112 was a biological and chemical weapon experimentation project conducted by the United States Department of Defense from 1962 to 1973.

Operation LAC was a United States Army Chemical Corps operation which dispersed microscopic zinc cadmium sulfide (ZnCdS) particles over much of the United States and Canada in order to test dispersal patterns and the geographic range of chemical or biological weapons.
The M143 bomblet was a biological cluster bomb sub-munition developed by the United States during the 1960s. The spherical bomblet was the biological version of the Sarin-filled M139 chemical bomblet.

The Deseret Test Center was a U.S. Army operated command in charge for testing chemical and biological weapons during the 1960s. The Deseret was headquartered at Fort Douglas, Utah, a former U.S. Army base.
Zinc cadmium sulfide is a mixture of zinc sulfide (ZnS) and cadmium sulfide (CdS). It is used for its fluorescent properties. Bioaccumulation of this chemical may occur along the food chain, for example in plants and in seafood. Long-term or repeated exposures are expected to have harmful effects on the kidneys, bones, and respiratory tract, resulting in kidney impairment, osteoporosis, and chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract.
The E48 particulate bomb was a U.S. biological sub-munition designed during the 1950s for use with the E96 cluster bomb.
Operation Dew refers to two separate field trials conducted by the United States in the 1950s. The tests were designed to study the behavior of aerosol-released biological agents.
Operation Polka Dot was a U.S. Army test of a biological cluster bomb during the early 1950s.
Operation Night Train was part of a series of chemical and biological warfare tests overseen by the Deseret Test Center as part of Project 112. The test was conducted near Fort Greely, Alaska from November 1963 to January 1964. The primary purpose of Night Train was to study the penetration of an arctic inversion by a biological aerosol cloud. The test's first purpose was to study the downwind travel and diffusion of this cloud when disseminated into different arctic meteorological regimes. All documents about Night Train were considered classified by the US military until 2002, when the Department of Defense (DOD) released medically relevant information of all the chemical and biological warfare agent tests conducted under Project 112.
Operation Sea-Spray was a 1950 U.S. Navy secret biological warfare experiment in which Serratia marcescens and Bacillus globigii bacteria were sprayed over the San Francisco Bay Area in California, in order to determine how vulnerable a city like San Francisco may be to a bioweapon attack.
Biological warfare (BW)—also known as bacteriological warfare, or germ warfare—has had a presence in popular culture for over 100 years. Public interest in it became intense during the Cold War, especially the 1960s and '70s, and continues unabated. This article comprises a list of popular culture works referencing BW or bioterrorism, but not those pertaining to natural, or unintentional, epidemics.
References
- ↑ Barnett, Antony (April 21, 2002). "Millions were in germ war tests:Much of Britain was exposed to bacteria sprayed in secret trials". guardian.com. The Observer. Retrieved March 8, 2015.
- ↑ The Dorset Biological Warfare Experiments 1963-75
- ↑ Jim Carlton,Of Microbes and Mock Attacks: Years Ago, The Military Sprayed Germs on U.S. Cities, The Wall Street Journal , (October 22, 2001).