Related Research Articles

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that provides a location for shared disk access, i.e. storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are able to reach the computer that shares the access through a computer network. The term server highlights the role of the machine in the traditional client–server scheme, where the clients are the workstations using the storage. A file server does not normally perform computational tasks or run programs on behalf of its client workstations.
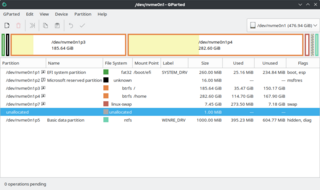
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.

In computer data storage, drive letter assignment is the process of assigning alphabetical identifiers to volumes. Unlike the concept of UNIX mount points, where volumes are named and located arbitrarily in a single hierarchical namespace, drive letter assignment allows multiple highest-level namespaces. Drive letter assignment is thus a process of using letters to name the roots of the "forest" representing the file system; each volume holds an independent "tree".
Linux has several filesystem drivers for the File Allocation Table (FAT) filesystem format. These are commonly known by the names used in the mount command to invoke particular drivers in the kernel: msdos, vfat, and umsdos.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.

NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol.
A path is a string of characters used to uniquely identify a location in a directory structure. It is composed by following the directory tree hierarchy in which components, separated by a delimiting character, represent each directory. The delimiting character is most commonly the slash ("/"), the backslash character ("\"), or colon (":"), though some operating systems may use a different delimiter. Paths are used extensively in computer science to represent the directory/file relationships common in modern operating systems and are essential in the construction of Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). Resources can be represented by either absolute or relative paths.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.

In computing, a file system or filesystem is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one large body of data with no way to tell where one piece of data stopped and the next began, or where any piece of data was located when it was time to retrieve it. By separating the data into pieces and giving each piece a name, the data are easily isolated and identified. Taking its name from the way a paper-based data management system is named, each group of data is called a "file". The structure and logic rules used to manage the groups of data and their names is called a "file system."

The USB mass storage device class is a set of computing communications protocols, specifically a USB Device Class, defined by the USB Implementers Forum that makes a USB device accessible to a host computing device and enables file transfers between the host and the USB device. To a host, the USB device acts as an external hard drive; the protocol set interfaces with a number of storage devices.
In computing, a temporary folder or temporary directory is a directory used to hold temporary files. Many operating systems and some software automatically delete the contents of this directory at bootup or at regular intervals, leaving the directory itself intact.
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition.
In computing, SUBST is a command on the DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems used for substituting paths on physical and logical drives as virtual drives.
DriveSpace is a disk compression utility supplied with MS-DOS starting from version 6.0 in 1993 and ending in 2000 with the release of Windows Me. The purpose of DriveSpace is to increase the amount of data the user could store on disks by transparently compressing and decompressing data on-the-fly. It is primarily intended for use with hard drives, but use for floppy disks is also supported. This feature was removed in Windows XP and later.
In computing, a shared resource, or network share, is a computer resource made available from one host to other hosts on a computer network. It is a device or piece of information on a computer that can be remotely accessed from another computer transparently as if it were a resource in the local machine. Network sharing is made possible by inter-process communication over the network.
In Unix-like operating systems, a device file or special file is an interface to a device driver that appears in a file system as if it were an ordinary file. There are also special files in DOS, OS/2, and Windows. These special files allow an application program to interact with a device by using its device driver via standard input/output system calls. Using standard system calls simplifies many programming tasks, and leads to consistent user-space I/O mechanisms regardless of device features and functions.

DOS is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of Microsoft's MS-DOS and a rebranded version, IBM PC DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.
In computing, a directory structure is the way an operating system arranges files that are accessible to the user. Files are typically displayed in a hierarchical tree structure.
References
- ↑ Clarke, Glen E.; Tetz, Edward (January 30, 2007). CompTIA A+ Certification All-In-One Desk Reference For Dummies. John Wiley & Sons. p. 967. ISBN 978-0471748113.
- ↑ Harris, Jeffrey (2003). Novell NetWare 6.5 Administrator's Handbook. p. 599. ISBN 0789741547.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)