
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word "alcoholism", it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predominant diagnostic classifications are alcohol use disorder (DSM-5) or alcohol dependence (ICD-11); these are defined in their respective sources.

Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behaviour of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behaviour.

Alcohol abuse encompasses a spectrum of unhealthy alcohol drinking behaviors, ranging from binge drinking to alcohol dependence, in extreme cases resulting in health problems for individuals and large scale social problems such as alcohol-related crimes.
Medical anthropology studies "human health and disease, health care systems, and biocultural adaptation". It views humans from multidimensional and ecological perspectives. It is one of the most highly developed areas of anthropology and applied anthropology, and is a subfield of social and cultural anthropology that examines the ways in which culture and society are organized around or influenced by issues of health, health care and related issues.

A tavern is a place of business where people gather to drink alcoholic beverages and be served food such as different types of roast meats and cheese, and where travelers would receive lodging. An inn is a tavern that has a license to put up guests as lodgers. The word derives from the Latin taberna whose original meaning was a shed, workshop, stall, or pub.
A date rape drug is any drug that incapacitates another person and renders that person vulnerable to sexual assault, including rape. The substances are associated with date rape because of reported incidents of their use in the context of two people dating, during which the victim is sexually assaulted or raped or suffers other harm. The substances are not exclusively used to perpetrate sexual assault or rape, but are the properties or side-effects of substances normally used for legitimate medical purposes. One of the most common incapacitating agents for date rape is alcohol, administered either surreptitiously or consumed voluntarily, rendering the victim unable to make informed decisions or give consent.
Neo-prohibitionism is a current movement to attempt to stop consumption of alcohol in society through legislation and policies which further restrict the sale, possession, and marketing of alcohol in order to reduce average per capita consumption and change social norms to reduce its acceptability.
Merrill Singer is a medical anthropologist and professor in Anthropology at The University of Connecticut and in Community Medicine at The University of Connecticut Health Center. He is best known for his research on substance abuse, HIV/AIDS, syndemics, health disparities, and minority health.
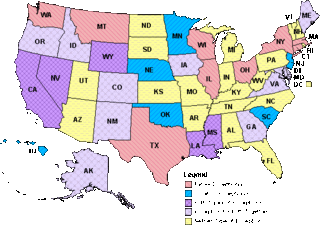
Alcohol consumption by youth in the United States of America is an umbrella term for alcohol consumption by individuals under the age of 18 in the country.
William Richard Miller is an American clinical psychologist, an emeritus distinguished professor of psychology and psychiatry at the University of New Mexico in Albuquerque. Miller and Stephen Rollnick are the co-founders of motivational interviewing.
Elvin Morton "Bunky" Jellinek, E. Morton Jellinek, or most often, E. M. Jellinek, was a biostatistician, physiologist, and an alcoholism researcher, fluent in nine languages and able to communicate in four others.
The modern disease theory of alcoholism states that problem drinking is sometimes caused by a disease of the brain, characterized by altered brain structure and function.
Robert A. Rubinstein is a cultural anthropologist whose work bridges the areas of political and medical anthropology, and the history and theory of the discipline. He is a Distinguished Professor of Anthropology and Professor of International Relations at the Maxwell School of Syracuse University.

John M. Janzen is a Professor Emeritus in the Department of Anthropology at the University of Kansas. He has been a leading figure on issues of health, illness, and healing in Southern and Central Africa since the 1960s and has dedicated much of his career to providing a better understanding of African society. Janzen’s knowledge of the Kikongo language and his intermittent visits to the lower Congo region between 1964 and 2013 have paved the way for a contextual understanding of the roots of Western Equatorial African approaches to sickness and healing, combining African and Western derived biomedical therapies. Janzen’s research has expanded to include other African countries such as Rwanda, Burundi, Senegal, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, and Sudan. He is the former director of the Kansas African Studies Center at the University of Kansas..
Louise Lamphere is an American anthropologist who has been distinguished professor of anthropology at the University of New Mexico since 2001. She was a faculty member at UNM from 1976–1979 and again from 1986–2009, when she became a professor emerita.

Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably.

R. S. Khare is a socio-cultural anthropologist and a Professor of Anthropology at the University of Virginia, U.S. He is known for studying “from within/without” India's changing society, religions, food systems, and political cultures, and for following the trajectories of contemporary Indian traditional and modern cultural discourses. His anthropology has endeavored to widen reasoned bridges across the India-West cultural, religious-philosophical, and literary distinctions and differences.

Brian Vincent Street was a professor of language education at King's College London and visiting professor at the Graduate School of Education in University of Pennsylvania. During his career, he mainly worked on literacy in both theoretical and applied perspectives, and is perhaps best known for his book Literacy in Theory and Practice (1984).

Charles P. O'Brien is a research scientist, medical educator and a leading expert in the science and treatment of addiction. He is board certified in neurology, psychiatry and addiction psychiatry. He is currently the Kenneth E. Appel Professor of Psychiatry, and vice chair of psychiatry, in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
Alcohol abuse among college students refers to unhealthy alcohol drinking behaviors by college and university students. While the legal drinking age varies by country, the high amount of underage students that consume alcohol has presented many problems and consequences for universities. The causes of alcohol abuse tend to be peer pressure, fraternity/sorority involvement, and stress. College students who abuse alcohol can suffer from health concerns, poor academic performance or legal consequences. Prevention and treatment include campus counseling, stronger enforcement of underage drinking or changing the campus culture.









