Related Research Articles
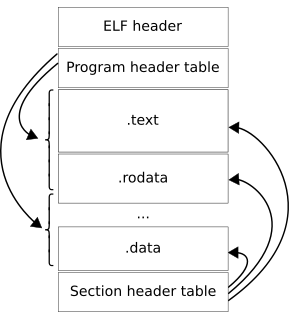
In computing, the Executable and Linkable Format, is a common standard file format for executable files, object code, shared libraries, and core dumps. First published in the specification for the application binary interface (ABI) of the Unix operating system version named System V Release 4 (SVR4), and later in the Tool Interface Standard, it was quickly accepted among different vendors of Unix systems. In 1999, it was chosen as the standard binary file format for Unix and Unix-like systems on x86 processors by the 86open project.
MIPS is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States.
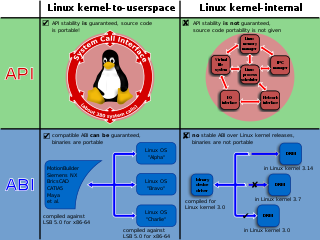
In computer software, an application binary interface (ABI) is an interface between two binary program modules. Often, one of these modules is a library or operating system facility, and the other is a program that is being run by a user.
The Portable Executable (PE) format is a file format for executables, object code, DLLs and others used in 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows operating systems. The PE format is a data structure that encapsulates the information necessary for the Windows OS loader to manage the wrapped executable code. This includes dynamic library references for linking, API export and import tables, resource management data and thread-local storage (TLS) data. On NT operating systems, the PE format is used for EXE, DLL, SYS, MUI and other file types. The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specification states that PE is the standard executable format in EFI environments.
Bytecode, also termed p-code, is a form of instruction set designed for efficient execution by a software interpreter. Unlike human-readable source code, bytecodes are compact numeric codes, constants, and references that encode the result of compiler parsing and performing semantic analysis of things like type, scope, and nesting depths of program objects.

In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often for software development. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets.

In computing, executable code, an executable file, or an executable program, sometimes simply referred to as an executable or binary, causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions", as opposed to a data file that must be interpreted (parsed) by a program to be meaningful.
The Common Object File Format (COFF) is a format for executable, object code, and shared library computer files used on Unix systems. It was introduced in Unix System V, replaced the previously used a.out format, and formed the basis for extended specifications such as XCOFF and ECOFF, before being largely replaced by ELF, introduced with SVR4. COFF and its variants continue to be used on some Unix-like systems, on Microsoft Windows, in UEFI environments and in some embedded development systems.
An object file is a computer file containing object code, that is, machine code output of an assembler or compiler. The object code is usually relocatable, and not usually directly executable. There are various formats for object files, and the same machine code can be packaged in different object file formats. An object file may also work like a shared library.
The archiver, also known simply as ar, is a Unix utility that maintains groups of files as a single archive file. Today, ar is generally used only to create and update static library files that the link editor or linker uses and for generating .deb packages for the Debian family; it can be used to create archives for any purpose, but has been largely replaced by tar for purposes other than static libraries. An implementation of ar is included as one of the GNU Binutils.
.exe is a common filename extension denoting an executable file for Microsoft Windows.
Not Another Completely Heuristic Operating System, or Nachos, is instructional software for teaching undergraduate, and potentially graduate level operating systems courses. It was developed at the University of California, Berkeley, designed by Thomas Anderson, and is used by numerous schools around the world.
Mach-O, short for Mach object file format, is a file format for executables, object code, shared libraries, dynamically-loaded code, and core dumps. It was developed to replace the a.out format.
The Interactive Disassembler (IDA) is a disassembler for computer software which generates assembly language source code from machine-executable code. It supports a variety of executable formats for different processors and operating systems. It also can be used as a debugger for Windows PE, Mac OS X Mach-O, and Linux ELF executables. A decompiler plug-in for programs compiled with a C/C++ compiler is available at extra cost. The latest full version of IDA Pro is commercial, while an earlier and less capable version is available for download free of charge.

UPX is an open source executable packer supporting a number of file formats from different operating systems.
Relocation is the process of assigning load addresses for position-dependent code and data of a program and adjusting the code and data to reflect the assigned addresses. Prior to the advent of multiprocess systems, and still in many embedded systems, the addresses for objects were absolute starting at a known location, often zero. Since multiprocessing systems dynamically link and switch between programs it became necessary to be able to relocate objects using position-independent code. A linker usually performs relocation in conjunction with symbol resolution, the process of searching files and libraries to replace symbolic references or names of libraries with actual usable addresses in memory before running a program.
Azure RTOS ThreadX is a highly deterministic, embedded real-time operating system (RTOS) programmed mostly in the language C.
Tektronix hex format and Extended Tektronix hex format / Extended Tektronix Object Format are ASCII-based hexadecimal file formats, created by Tektronix, for conveying binary information for applications like programming microcontrollers, EPROMs, and other kinds of chips.
Android Package (APK) is the Android application package file format used by the Android operating system, and a number of other Android-based operating systems for distribution and installation of mobile apps, mobile games and middleware. It can be written in either Java or Kotlin.
Dalvik Turbo is a proprietary alternative to Google's implementation of the Dalvik virtual machine that runs on the Android operating system and other platforms. It is developed by French/Swiss firm Myriad Group.
References
- ↑ Marshall, Chris (2021-05-27), ChrisRx/psxsdk , retrieved 2021-05-31