An ectopia is a displacement or malposition of an organ or other body part, which is then referred to as ectopic. Most ectopias are congenital, but some may happen later in life.

Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes parathyroid hormone in response to a low blood calcium, which plays a key role in regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones.

Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
Disorders of calcium metabolism occur when the body has too little or too much calcium. The serum level of calcium is closely regulated within a fairly limited range in the human body. In a healthy physiology, extracellular calcium levels are maintained within a tight range through the actions of parathyroid hormone, vitamin D and the calcium sensing receptor. Disorders in calcium metabolism can lead to hypocalcemia, decreased plasma levels of calcium or hypercalcemia, elevated plasma calcium levels.

Parathyroid chief cells are one of the two cell types of the parathyroid glands, along with oxyphil cells. The chief cells are much more prevalent in the parathyroid gland than the oxyphil cells. It is perceived that oxyphil cells may be derived from chief cells at puberty, as they are not present at birth like chief cells.
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone. This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany, and several other symptoms. It is a very rare disease. The condition can be inherited, but it is also encountered after thyroid or parathyroid gland surgery, and it can be caused by immune system-related damage as well as a number of rarer causes. The diagnosis is made with blood tests, and other investigations such as genetic testing depending on the results. The primary treatment of hypoparathyroidism is calcium and vitamin D supplementation. Calcium replacement or vitamin D can ameliorate the symptoms but can increase the risk of kidney stones and chronic kidney disease. However teriparatide, brand name Forteo, a biosimilar peptide to parathyroid hormone, may be given by injection.

Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands or outside the parathyroid glands. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium leaving the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis.

Hyperphosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is an elevated level of phosphate in the blood. Most people have no symptoms while others develop calcium deposits in the soft tissue. Often there is also low calcium levels which can result in muscle spasms.

Dystrophic calcification (DC) is the calcification occurring in degenerated or necrotic tissue, as in hyalinized scars, degenerated foci in leiomyomas, and caseous nodules. This occurs as a reaction to tissue damage, including as a consequence of medical device implantation. Dystrophic calcification can occur even if the amount of calcium in the blood is not elevated and cause metastatic calcification. Basophilic calcium salt deposits aggregate, first in the mitochondria, then progressively throughout the cell. These calcifications are an indication of previous microscopic cell injury, occurring in areas of cell necrosis when activated phosphatases bind calcium ions to phospholipids in the membrane.

Parathyroidectomy is the surgical removal of one or more of the (usually) four parathyroid glands. This procedure is used to remove an adenoma or hyperplasia of these glands when they are producing excessive parathyroid hormone (PTH): hyperparathyroidism. The glands are usually four in number and located adjacent to the posterior surface of the thyroid gland, but their exact location is variable. When an elevated PTH level is found, a sestamibi scan or an ultrasound may be performed in order to confirm the presence and location of abnormal parathyroid tissue.
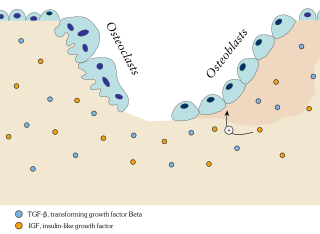
Ossification in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor.

Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue, causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells.

Myositis ossificans comprises two syndromes characterized by heterotopic ossification (calcification) of muscle.
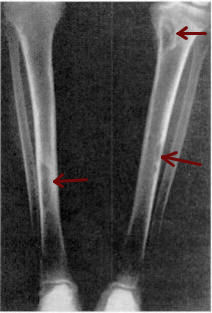
Osteitis fibrosa cystica, is a skeletal disorder resulting in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue, and the formation of cyst-like brown tumors in and around the bone. Osteitis fibrosis cystica, abbreviated OFC, also known as osteitis fibrosa, osteodystrophia fibrosa, and von Recklinghausen's disease of bone, is caused by hyperparathyroidism, which is a surplus of parathyroid hormone from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy. Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium, from the bone into the bloodstream, causing both elevated blood calcium levels, and the structural changes which weaken the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss.

Metastatic calcification is deposition of calcium salts in otherwise normal tissue, because of elevated serum levels of calcium, which can occur because of deranged metabolism as well as increased absorption or decreased excretion of calcium and related minerals, as seen in hyperparathyroidism.

Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism is a condition involving the overproduction of the hormone, parathyroid hormone, produced by the parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are involved in monitoring and regulating blood calcium levels and respond by either producing or ceasing to produce parathyroid hormone. Anatomically, these glands are located in the neck, Para-lateral to the thyroid gland, which does not have any influence in the production of parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone is released by the parathyroid glands in response to low blood calcium circulation. Persistent low levels of circulating calcium are thought to be the catalyst in the progressive development of adenoma in the parathyroid glands resulting in primary hyperparathyroidism. While primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common form of this condition, secondary and tertiary are thought to result due to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Estimates of CKD prevalence in the global community range from 11-13% which translate to a large portion of the global population at risk of developing tertiary hyperparathyroidism. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism was first described in the late 1960s and had been misdiagnosed as primary prior to this. Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, the tertiary form presents as a progressive stage of resolved secondary hyperparathyroidism with biochemical hallmarks that include elevated calcium ion levels in the blood, hypercalcemia, along with autonomous production of parathyroid hormone and adenoma in all four parathyroid glands. Upon diagnosis treatment of tertiary hyperparathyroidism usually leads to a surgical intervention.

A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It generally causes hyperparathyroidism; there are very few reports of parathyroid adenomas that were not associated with hyperparathyroidism.

Paricalcitol (chemically it is 19-nor-1,25-(OH)2-vitamin D2. Marketed by Abbott Laboratories under the trade name Zemplar) is a drug used for the prevention and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism (excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone) associated with chronic kidney failure. It is an analog of 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol, the active form of vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).
Many conditions are associated with disorders of the function of the parathyroid gland. Some disorders may be purely anatomical resulting in an enlarged gland which will raise concern. Such benign disorders, such as parathyroid cyst, are not discussed here. Parathyroid diseases can be divided into those causing hyperparathyroidism, and those causing hypoparathyroidism.

Bone mineral is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed predominantly from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower crystallinity.














