Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by decreasing glucose levels in the blood. With the exception of insulin, most GLP-1 receptor agonists, and pramlintide, all diabetes medications are administered orally and are thus called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of hypoglycemic drugs, and selection of the appropriate agent depends on the nature of diabetes, age, and situation of the person, as well as other patient factors.

Bromocriptine, originally marketed as Parlodel and subsequently under many brand names, is an ergoline derivative and dopamine agonist that is used in the treatment of pituitary tumors, Parkinson's disease, hyperprolactinaemia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and, as an adjunct, type 2 diabetes.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

Fenofibrate, is an oral medication of the fibrate class used to treat abnormal blood lipid levels. It is less commonly used compared than statins because it treats a different type of cholesterol abnormality to statins. While statins have strong evidence for reducing heart disease and death, there is evidence to suggest that fenofibrate also reduces the risk of heart disease and death. However, this seems only to apply to specific populations of people with elevated triglyceride levels and reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Its use is recommended together with dietary changes.
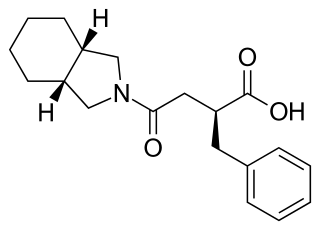
Mitiglinide is a drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
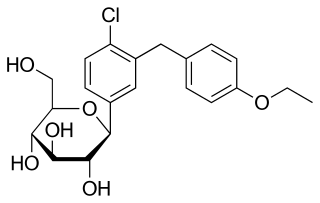
Dapagliflozin, sold under the brand names Farxiga (US) and Forxiga (EU) among others, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is also used to treat adults with heart failure and chronic kidney disease. It reversibly inhibits sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) in the renal proximal convoluted tubule to reduce glucose reabsorption and increase urinary glucose excretion.

GW501516 is a PPARδ receptor agonist that was invented in a collaboration between Ligand Pharmaceuticals and GlaxoSmithKline in the 1990s. It entered into clinical development as a drug candidate for metabolic and cardiovascular diseases, but was abandoned in 2007 because animal testing showed that the drug caused cancer to develop rapidly in several organs.

PPAR agonists are drugs which act upon the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. They are used for the treatment of symptoms of the metabolic syndrome, mainly for lowering triglycerides and blood sugar.

Vedaclidine (INN, codenamed LY-297,802, NNC 11-1053) is an experimental analgesic drug which acts as a mixed agonist–antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, being a potent and selective agonist for the M1 and M4 subtypes, yet an antagonist at the M2, M3 and M5 subtypes. It is orally active and an effective analgesic over 3× the potency of morphine, with side effects such as salivation and tremor only occurring at many times the effective analgesic dose. Human trials showed little potential for development of dependence or abuse, and research is continuing into possible clinical application in the treatment of neuropathic pain and cancer pain relief.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, also known as GLP-1 analogs, GLP-1DAs or incretin mimetics, are a class of drugs that reduce blood sugar and energy intake by activating the GLP-1 receptor. They mimic the actions of the endogenous incretin hormone GLP-1 that is released by the gut after eating.
Lixisenatide is a once-daily injectable GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
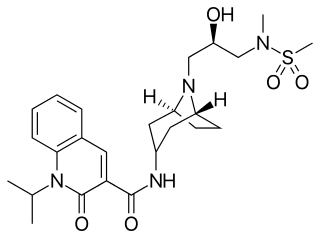
Velusetrag (INN, USAN; previously known as TD-5108) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of gastric neuromuscular disorders including gastroparesis, and lower gastrointestinal motility disorders including chronic idiopathic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome. It is a potent, selective, high efficacy 5-HT4 receptor serotonin agonist being developed by Theravance Biopharma and Alfa Wassermann. Velusetrag demonstrates less selectivity for other serotonin receptors, such as 5-HT2 and 5-HT3, to earlier generation 5-HT agonists like cisapride and tegaserod.

Abediterol is a once-daily experimental drug candidate for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but it has never been marketed.

Tofogliflozin is an experimental drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and is being developed by Chugai Pharma in collaboration with Kowa and Sanofi. It is an inhibitor of subtype 2 sodium-glucose transport protein (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. As of September 2012, the drug is in Phase III clinical trials.

Seladelpar is a PPARδ receptor agonist that is being investigated for drug use by Metabolex. According to a press release they are examining its potential use for the treatment of dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The compound was licensed from Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. The drug completed a phase II trial for primary biliary cholangitis. "Seladelpar demonstrated robust, dose-dependent, clinically significant, and durable improvements in biochemical markers of cholestasis and inflammation in patients with PBC at risk of disease progression. Seladelpar appeared safe and well tolerated and was not associated with any increase in pruritus." A phase III trial in patients with PBC also found reduced pruritus and improved liver biochemistry, despite being terminated early.

Saroglitazar is a drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, NASH and NAFLD It is approved for use in India by the Drug Controller General of India. Saroglitazar is indicated for the treatment of diabetic dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia with type 2 diabetes mellitus not controlled by statin therapy. In clinical studies, saroglitazar has demonstrated reduction of triglycerides (TG), LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol and an increase in HDL cholesterol a characteristic hallmark of atherogenic diabetic dyslipidemia (ADD). It has also shown anti-diabetic medication properties by reducing the fasting plasma glucose and HBA1c in diabetes patients.
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications that inhibit sodium-glucose transport proteins in the nephron, unlike SGLT1 inhibitors that perform a similar function in the intestinal mucosa. The foremost metabolic effect of this is to inhibit reabsorption of glucose in the kidney and therefore lower blood sugar. They act by inhibiting sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2). SGLT2 inhibitors are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Apart from blood sugar control, gliflozins have been shown to provide significant cardiovascular benefit in people with type 2 diabetes. As of 2014, several medications of this class had been approved or were under development. In studies on canagliflozin, a member of this class, the medication was found to enhance blood sugar control as well as reduce body weight and systolic and diastolic blood pressure.

Ipragliflozin is a pharmaceutical drug for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Ipragliflozin, jointly developed by Astellas Pharma and Kotobuki Pharmaceutical, was approved in Japan on January 17, 2014, and in Russia on May 22, 2019.
Sotagliflozin, sold under the brand name Inpefa among others, is a medication used to reduce the risk of death due to heart failure.

Tirzepatide, sold under the brand names Mounjaro and Zepbound, is an antidiabetic medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and for weight loss. Tirzepatide is administered via subcutaneous injections.















