
Brixton is a district in South London, part of the London Borough of Lambeth, England. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London. Brixton experienced a rapid rise in population during the 19th century as communications with central London improved.

Piccadilly Circus is a road junction and public space of London's West End in the City of Westminster. It was built in 1819 to connect Regent Street with Piccadilly. In this context, a circus, from the Latin word meaning "circle", is a round open space at a street junction.
The 1999 London nail bombings were a series of bomb explosions in London, England. Over three successive weekends between 17 and 30 April 1999, homemade nail bombs were detonated in Brixton in South London; at Brick Lane, Spitalfields, in the East End; and at the Admiral Duncan pub in Soho in the West End. Each bomb contained up to 1,500 4-inch (100 mm) nails, in holdalls that were left in public spaces. The bombs killed three people and injured 140 people, four of whom lost limbs.

Brixton Hill is the name given to a two-thirds of a mile (1 km) section of road between Brixton and Streatham Hill in south London, England.

Brixton Market comprises a street market in the centre of Brixton, south London, and the adjacent covered market areas in nearby arcades Reliance Arcade, Market Row and Granville Arcade.

A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution became ubiquitous in developed countries in the 20th century, lights for urban streets followed, or sometimes led.

The 1981 Brixton riot, or Brixton uprising, was a series of clashes between mainly black youths and the Metropolitan Police in Brixton, London, between 10 and 12 April 1981. It resulted from racist discrimination against the black community by the mainly white police, especially the police's increased use of stop-and-search in the area, and ongoing tensions resulting from the deaths of 13 black teenagers and young adults in the suspicious New Cross house fire that January. The main riot on 11 April, dubbed "Bloody Saturday" by Time magazine, resulted in 279 injuries to police and 45 injuries to members of the public; over a hundred vehicles were burned, including 56 police vehicles; almost 150 buildings were damaged, thirty of which were burnt out, and many shops were looted. There were 82 arrests. Reports suggested that up to 5,000 people were involved. The Brixton riot was followed by similar riots in July in many other English cities and towns. The Thatcher government commissioned an inquiry, which resulted in the Scarman Report.

The history of street lighting in the United States is closely linked to the urbanization of America. Artificial illumination has stimulated commercial activity at night, and has been tied to the country's economic development, including major innovations in transportation, particularly the growth in automobile use. In the two and a half centuries before LED lighting emerged as the new "gold standard", cities and towns across America relied on oil, coal gas, carbon arc, incandescent, and high-intensity gas discharge lamps for street lighting.

Edmond Montague Grant is a Guyanese-British singer, songwriter and multi-instrumentalist, known for his genre-blending sound and socially-conscious lyrics; his music has blended elements of pop, British rock, soul, funk, reggae, electronic music, African polyrhythms, and Latin music genres such as samba, among many others. In addition to this, he also helped to pioneer the genre of "Ringbang". He was a founding member of the Equals, one of the United Kingdom's first racially mixed pop groups who are best remembered for their million-selling UK chart-topper, the Grant-penned "Baby, Come Back".
Electric Avenue is a market street in Brixton, London, England.

The Euclid Avenue station is an express station on the IND Fulton Street Line of the New York City Subway, located at the intersection of Euclid and Pitkin Avenues in East New York, Brooklyn. It is served by the A train at all times and is the southern terminal for the C train at all times except nights. During nights, this is the northern terminal for the Lefferts Boulevard shuttle train from Ozone Park, Queens.

The Equals are an English rock band. They are best remembered for their million-selling chart-topper "Baby, Come Back", though they had several other chart hits in the UK and Europe. Drummer John Hall founded the group with Eddy Grant, Pat Lloyd and brothers Derv and Lincoln Gordon, and they were noted as being "the first major interracial rock group in the UK" and "one of the few racially mixed bands of the era".
General Electric has a long history, involving numerous mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures.

Brixton Road is a road in the London Borough of Lambeth, leading from the Oval at Kennington to Brixton, where it forms the high street and then forks into Effra Road and Brixton Hill at St Matthew's church at the junction with Acre Lane and Coldharbour Lane. Brixton Market is located in Electric Avenue near Brixton Underground station and in a network of covered arcades adjacent to the two railway viaducts. The market arcades were declared listed buildings in 2009 following controversial proposals by Lambeth Council to replace them with a large US-style mall. The former "Brixton Oval" is at the southern end with Lambeth Town Hall, the Ritzy Cinema, the Brixton Tate Library and St Matthew's church. The space was renamed Windrush Square in 2010, in honour of the area's early Caribbean migrants and the HMT Empire Windrush, which in 1948 brought 492 passengers from Jamaica to London.

The Grant Avenue station is a station on the IND Fulton Street Line of the New York City Subway. Located at Grant Avenue just north of Pitkin Avenue in City Line, Brooklyn, near the border between the boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens, it is served by the A train at all times. The station is the line's easternmost stop in Brooklyn; the Fulton Street Line continues east into Queens via the Fulton Street Elevated.

Killer on the Rampage is the sixth studio album by Eddy Grant. It remains his most successful album, hitting the top 10 in the US and the UK. It features the hits "Electric Avenue", "I Don't Wanna Dance" and "War Party".

"Electric Avenue" is a song by Guyanese-British musician Eddy Grant. Written and produced by Grant, it was released on his 1982 studio album Killer on the Rampage. In the United States, with the help of the MTV music video he made, it was one of the biggest hits of 1983. The song refers to Electric Avenue in London the 1981 Brixton riot.

"Gimme Hope Jo'anna" is a British anti-apartheid song written and originally released by Guyanese-British singer, songwriter and multi-instrumentalist Eddy Grant in 1988, during the apartheid era in South Africa. The song was banned by the South African government when it was released, but was widely played there nonetheless. It reached number seven on the UK Singles Chart, becoming Grant's first British top 10 hit for five years.
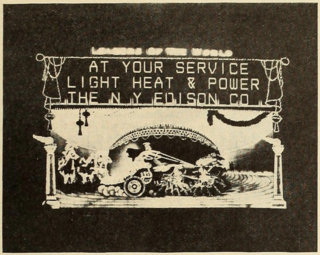
Leaders of the World was an electric advertising sign in New York City from 1910 to 1912 and one of the largest in New York City when it was built. It displayed an animated scene of a Roman chariot race along with a text message for the advertiser. The sign began operation on July 19, 1910, and was destroyed in a storm on February 22, 1912.
The Dark and Light Theatre (DLT) was a British theatre company, founded in 1969 by Jamaican actor Frank Cousins and based in south London at Longfield Hall until 1975. It was the first black-led theatre company to be funded by the UK's Arts Council. According to the DLT's mission statement, "The aim of the Company is to promote understanding between people of different races through the media of the performing arts. By examining the nature of prejudice it is hoped to identify its sources and thereby decrease its manifestations.” In 1975, the company under a change of management was renamed as The Black Theatre of Brixton.

















