
CD-R is a digital optical disc storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be only written once and can only be read designated/limited times.

An optical disc is a flat, usually disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid of a beam of light. Optical discs can be reflective, where the light source and detector are on the same side of the disc, or transmissive, where light shines through the disc to be detected on the other side.

MiniDisc (MD) is an erasable magneto-optical disc-based data storage format offering a capacity of 60, 74, and later, 80 minutes of digitized audio.
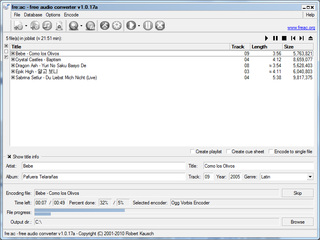
A CD ripper, CD grabber, or CD extractor is software that rips raw digital audio in Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD-DA) format tracks on a compact disc to standard computer sound files, such as WAV or MP3.

A CD player is an electronic device that plays audio compact discs, which are a digital optical disc data storage format. CD players were first sold to consumers in 1982. CDs typically contain recordings of audio material such as music or audiobooks. CD players may be part of home stereo systems, car audio systems, personal computers, or portable CD players such as CD boomboxes. Most CD players produce an output signal via a headphone jack or RCA jacks. To use a CD player in a home stereo system, the user connects an RCA cable from the RCA jacks to a hi-fi and loudspeakers for listening to music. To listen to music using a CD player with a headphone output jack, the user plugs headphones or earphones into the headphone jack.

The LaserDisc (LD) is a home video format and the first commercial optical disc storage medium, initially licensed, sold and marketed as MCA DiscoVision in the United States in 1978. Its diameter typically spans 30 cm (12 in). Unlike most optical-disc standards, LaserDisc is not fully digital, and instead requires the use of analog video signals.

The Digital Compact Cassette (DCC) is a magnetic tape sound recording format introduced by Philips and Matsushita Electric in late 1992 and marketed as the successor to the standard analog Compact Cassette. It was also a direct competitor to Sony's MiniDisc (MD), but neither format toppled the then-ubiquitous analog cassette despite their technical superiority, and DCC was discontinued in October 1996.

In computing, an optical disc drive is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives.
A DVD recorder is an optical disc recorder that uses optical disc recording technologies to digitally record analog or digital signals onto blank writable DVD media. Such devices are available as either installable drives for computers or as standalone components for use in television studios or home theater systems.
Gapless playback is the uninterrupted playback of consecutive audio tracks, such that relative time distances in the original audio source are preserved over track boundaries on playback. For this to be useful, other artifacts at track boundaries should not be severed either. Gapless playback is common with compact discs, gramophone records, or tapes, but is not always available with other formats that employ compressed digital audio. The absence of gapless playback is a source of annoyance to listeners of music where tracks are meant to segue into each other, such as some classical music, progressive rock, concept albums, electronic music, and live recordings with audience noise between tracks.

Mini CDs, or pocket CDs, are CDs with a smaller diameter and one-third the storage capacity of a standard 120 mm disc.
In computing, buffer underrun or buffer underflow is a state occurring when a buffer used for communicating between two devices or processes is fed with data at a lower speed than the data is being read from it. The term is distinct from buffer overflow, a condition where a portion of memory forms a buffer of a fixed size yet is filled with more than that amount of data. This requires the program or device reading from the buffer to pause its processing while the buffer refills. This can cause undesired and sometimes serious side effects because the data being buffered is generally not suited to stop-start access of this kind.
A skip occurs when a phonograph (gramophone), cassette tape or compact disc player malfunctions or is disturbed so as to play incorrectly, causing a break in sound or a jump to another part of the recording.

DVD recordable and DVD rewritable are optical disc recording technologies. Both terms describe DVD optical discs that can be written to by a DVD recorder, whereas only 'rewritable' discs are able to erase and rewrite data. Data is written ('burned') to the disc by a laser, rather than the data being 'pressed' onto the disc during manufacture, like a DVD-ROM. Pressing is used in mass production, primarily for the distribution of home video.

Optical disc authoring requires a number of different optical disc recorder technologies working in tandem, from the optical disc media to the firmware to the control electronics of the optical disc drive.

A compressed audio optical disc, MP3 CD, or MP3 CD-ROM or MP3 DVD is an optical disc that contains digital audio in the MP3 file format. Discs are written in the "Yellow Book" standard data format, as opposed to the Red Book standard audio format.

The DVD is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 1995 and first released on November 1, 1996, in Japan. The medium can store any kind of digital data and has been widely used to store video programs, software and other computer files. DVDs offer significantly higher storage capacity than compact discs (CD) while having the same dimensions. A standard single-layer DVD can store up to 4.7 GB of data, a dual-layer DVD up to 8.5 GB. Variants can store up to a maximum of 17.08 GB.

A portable CD player is a portable audio player used to play compact discs. The first audio player released was the Discman D-50 by Sony.
In the history of optical storage media there have been and there are different optical disc formats with different data writing/reading speeds.

A CD-ROM is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data. Computers can read—but not write or erase—CD-ROMs. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data is only usable on a computer.











