
Eritrea is an ancient name, associated in the past with its Greek form Erythraia, Ἐρυθραία, and its derived Latin form Erythræa. This name relates to that of the Red Sea, then called the Erythræan Sea, from the Greek for "red", ἐρυθρός, erythros. But earlier Eritrea was called Mdre Bahri. The Italians created the colony of Eritrea in the 19th century around Asmara and named it with its current name. After World War II, Eritrea annexed to Ethiopia. Following the communist Ethiopian government's defeat in 1991 by the coalition created by various armed groups notably the EPLF and the TPLF among others, Eritrea declared its independence. Eritrea officially celebrated its 1st anniversary of independence on May 24,1994.

Italian East Africa was an Italian colony in the Horn of Africa. It was formed in 1936 after the Second Italo-Ethiopian War through the merger of Italian Somalia, Italian Eritrea, and the newly occupied Ethiopian Empire.

The coat of arms of Western Australia is the official coat of arms of the Australian state of Western Australia. It was granted by a royal warrant of Elizabeth II, Queen of Australia dated 17 March 1969.

The flag of Eritrea is the national flag of Eritrea. It was adopted on 5th December, 1995. The flag combines the basic layout and colors from the flag of the Eritrean People's Liberation Front with an emblem of a wreath and an upright olive-branch derived from the Eritrean flag from 1952 to 1962.

The coat of arms of Ukraine is a blue shield with a golden trident. Officially referred to as the Emblem of the Royal State of Volodymyr the Great, or, colloquially, the tryzub, the insignia derives from the seal-trident of Volodymyr the Great, the first Grand Prince of Kyiv.

The current coat of arms of Zimbabwe was adopted on 21 September 1981, one year and five months after the national flag was adopted. Previously the coat of arms of Zimbabwe was identical to the former coat of arms of Rhodesia.

The coat of arms of Malta is the national coat of arms of the country of Malta.

The coat of arms of Somalia was adopted on October 10, 1956 and features a golden framed shield of the Somali flag supported by two Leopards standing on spears. The Leopard is a common animal seen in Somalia. Leopards are a common motif in Somali culture.

The coat of arms of Nigeria consists of a black shield with a wavy white pall, symbolizing the meeting of the Niger and Benue Rivers at Lokoja. The black shield represents Nigeria's fertile soil, while the two supporting horses or chargers on each side represent dignity. The eagle represents strength, while the green and white twists of the torse on the top of the shield represent the rich soil.

The emblem of the Italian Republic was formally adopted by the newly formed Italian Republic on 5 May 1948. Although often referred to as a coat of arms, it is an emblem as it was designed not to conform to traditional heraldic rules. The emblem is used extensively by the Italian government.

The Eritrean War of Independence was a war for independence which Eritrean independence fighters waged against successive Ethiopian governments from 1 September 1961 to 24 May 1991.
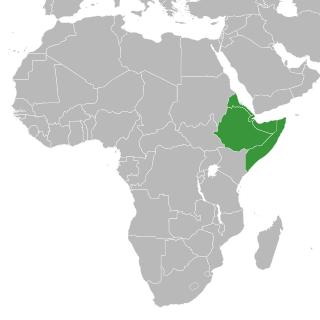
Conflicts in the Horn of Africa have been occurring since the 17th century BCE. The Horn of Africa includes the nations of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia and the de facto independent nation of Somaliland.

The coat of arms of Malawi is based on the earlier heraldic arms of Nyasaland. It is supported by a lion and a leopard, above a scroll reading "Unity and Freedom". A rising sun in a black field, like in the lower field in the shield, is also present in the flag of Malawi.

Socialist-style emblems usually follow a unique style consisting of communist symbolism. Although commonly referred to as coats of arms, most are not actually traditional heraldic achievements. Many communist governments purposely diverged from heraldic tradition in order to distance themselves from the monarchies that they usually replaced, with coats of arms being seen as symbols of the monarchs.

Italian Eritreans are Eritrean-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Eritrea during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Eritrea.

The Royal Corps Of Eritrean Colonial Troops were indigenous soldiers from Eritrea, who were enrolled as askaris in the Royal Corps of Colonial Troops of the Royal Italian Army during the period 1889–1941.

Italian Eritrea was a colony of the Kingdom of Italy in the territory of present-day Eritrea. The first Italian establishment in the area was the purchase of Assab by the Rubattino Shipping Company in 1869, which came under government control in 1882. Occupation of Massawa in 1885 and the subsequent expansion of territory would gradually engulf the region and in 1889 borders with the Ethiopian Empire were defined in the Treaty of Wuchale. In 1890 the Colony of Eritrea was officially founded.
A national coat of arms is a symbol which denotes an independent state in the form of a heraldic achievement. While a national flag is usually used by the population at large and is flown outside and on ships, a national coat of arms is normally considered a symbol of the government or the head of state personally and tends to be used in print, on armorial ware, and as a wall decoration in official buildings. The royal arms of a monarchy, which may be identical to the national arms, are sometimes described as arms of dominion or arms of sovereignty.

The first coat of arms of South Africa was granted to the Union of South Africa by King George V and later amended by the British College of Arms. It contained representation of the four provinces within the Union. The coat of arms was later retained by the Republic of South Africa after independence and for a period until after the end of apartheid, until being retired in 2000. The 1910 coat of arms was replaced in 2000 by the current coat of arms of South Africa.
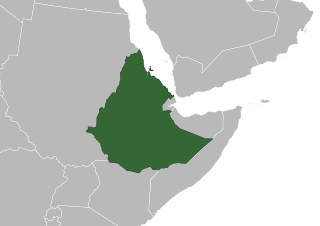
Beginning with the Kingdom of Aksum, Ethiopia's territory evolved significantly through conquest of the lands surrounding it. Strong Aksumite trading partnerships with other world powers gave prominence to its territorial expansion. In 330, Aksum besieged the Nubian city of Meroë, marking the beginning of its great expansion. It finally declined after the rise of Islamic dominion in South Arabia, and it ultimately collapsed in the 10th century.




































