Related Research Articles
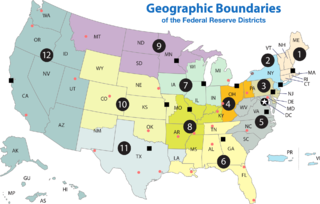
A Federal Reserve Bank is a regional bank of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. There are twelve in total, one for each of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts that were created by the Federal Reserve Act of 1913. The banks are jointly responsible for implementing the monetary policy set forth by the Federal Open Market Committee, and are divided as follows:

The Federal Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund and Federal Disability Insurance Trust Fund are trust funds that provide for payment of Social Security benefits administered by the United States Social Security Administration.

Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit: the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget of a government, private company, or individual. Government deficit spending was first identified as a necessary economic tool by John Maynard Keynes in the wake of the Great Depression. It is a central point of controversy in economics, as discussed below.
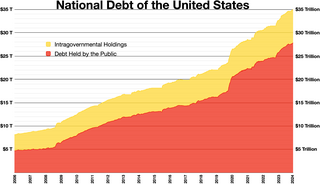
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

The New-York Historical Society is an American history museum and library in New York City, along Central Park West between 76th and 77th Streets, on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. The society was founded in 1804 as New York's first museum. It presents exhibitions, public programs, and research that explore the history of New York and the nation.

Dia Art Foundation is a nonprofit organization that initiates, supports, presents, and preserves art projects. It was established in 1974 by Philippa de Menil, the daughter of Houston arts patron Dominique de Menil and an heiress to the Schlumberger oil exploration fortune; art dealer Heiner Friedrich, Philippa's husband; and Helen Winkler, a Houston art historian. Dia provides support to projects "whose nature or scale would preclude other funding sources."

A country's gross government debt is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit occurs when a government's expenditures exceed revenues. Government debt may be owed to domestic residents, as well as to foreign residents. If owed to foreign residents, that quantity is included in the country's external debt.
A loan shark is a person who offers loans at extremely high or illegal interest rates, has strict terms of collection, and generally operates outside the law, often using the threat of violence or other illegal, aggressive, and extortionate actions when seeking to enforce the satisfaction of the debt. As a consistent or repeated illegal business operation or "racket", loansharking is generally associated with organized crime and certain criminal organizations.
A balanced budget amendment is a constitutional rule requiring that a state cannot spend more than its income. It requires a balance between the projected receipts and expenditures of the government.

A financial endowment is a legal structure for managing, and in many cases indefinitely perpetuating, a pool of financial, real estate, or other investments for a specific purpose according to the will of its founders and donors. Endowments are often structured so that the inflation-adjusted principal or "corpus" value is kept intact, while a portion of the fund can be spent each year, utilizing a prudent spending policy.
The Social Security debate in the United States encompasses benefits, funding, and other issues. xSocial Security is a social insurance program officially called "Old-age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance" (OASDI), in reference to its three components. It is primarily funded through a dedicated payroll tax. During 2015, total benefits of $897 billion were paid out versus $920 billion in income, a $23 billion annual surplus. Excluding interest of $93 billion, the program had a cash deficit of $70 billion. Social Security represents approximately 40% of the income of the elderly, with 53% of married couples and 74% of unmarried persons receiving 50% or more of their income from the program. An estimated 169 million people paid into the program and 60 million received benefits in 2015, roughly 2.82 workers per beneficiary. Reform proposals continue to circulate with some urgency, due to a long-term funding challenge faced by the program as the ratio of workers to beneficiaries falls, driven by the aging of the baby-boom generation, expected continuing low birth rate, and increasing life expectancy. Program payouts began exceeding cash program revenues in 2011; this shortfall is expected to continue indefinitely under current law.

Michael M. Kaiser is an American arts administrator who served as president of the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts (2001–2014) in Washington, D.C.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. CBO estimated in February 2024 that Federal debt held by the public is projected to rise from 99 percent of GDP in 2024 to 116 percent in 2034 and would continue to grow if current laws generally remained unchanged. Over that period, the growth of interest costs and mandatory spending outpaces the growth of revenues and the economy, driving up debt. Those factors persist beyond 2034, pushing federal debt higher still, to 172 percent of GDP in 2054.

Fund accounting is an accounting system for recording resources whose use has been limited by the donor, grant authority, governing agency, or other individuals or organisations or by law. It emphasizes accountability rather than profitability, and is used by Nonprofit organizations and by governments. In this method, a fund consists of a self-balancing set of accounts and each are reported as either unrestricted, temporarily restricted or permanently restricted based on the provider-imposed restrictions.
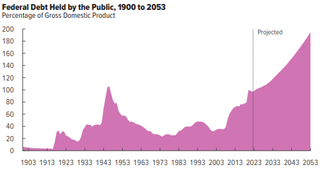
The history of the United States public debt began with federal government debt incurred during the American Revolutionary War by the first U.S treasurer, Michael Hillegas, after the country's formation in 1776. The United States has continuously experienced fluctuating public debt, except for about a year during 1835–1836. To facilitate comparisons over time, public debt is often expressed as a ratio to gross domestic product (GDP). Historically, the United States public debt as a share of GDP has increased during wars and recessions, and subsequently declined.
Great Northern Way Campus Ltd (GNWC) is a private limited company and educational enterprise located in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It is the offspring of a consortium of four local academic institutions that has attracted significant public and private funding. The company is the trustee of the Great Northern Way Campus Trust, whose stated purpose is to create "a centre of convergence for arts and culture, digital media and the environment." At present, it manages a Master's degree in Digital Media, which admitted its first students in the Fall of 2007.

The Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., abbreviated WMF, is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization headquartered in San Francisco, California, and registered there as a charitable foundation. It is best known as the host of Wikipedia, the seventh most visited website in the world. However, the foundation also hosts 14 other related content projects. It also supports the development of MediaWiki, the wiki software that underpins them all.
The Uniform Prudent Management of Institutional Funds Act (UPMIFA) is a uniform act that provides guidance on investment decisions and endowment expenditures for nonprofit and charitable organizations. As of 2012 UPMIFA is the law in 49 states, the District of Columbia and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Neither Pennsylvania nor Puerto Rico has adopted UPMIFA.
The Yale University endowment is the world's third-largest university endowment and has a reputation as one of the best-performing investment portfolios in American higher education. The endowment was established at Yale University, then Yale College, in 1718 from an initial fund of £562 provided by Elihu Yale and has grown to more than $40 billion in value over the ensuing 300 years. It is managed by the Yale Investments Office.

Daniel Veech McLean was a Presbyterian minister and the fifth president of Lafayette College.
References
- ↑ "Prudent Management of Institutional Funds Act". National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved June 5, 2014.
- 1 2 Pogrebin, Robin (June 17, 2009). "City Opera Tries to Hold Off the Ultimate Finale" . The New York Times . Archived from the original on Jul 17, 2014. Retrieved 2009-06-18.
During Ms. Baker's tenure, City Opera has raided its endowment — which now stands at $16 million, down from $57 million when she was appointed in December 2003 — to pay off debts and cover operating expenses. The practice, known as endowment invasion, requires approval from the state attorney general's office and the State Supreme Court, and is widely considered a last resort for any arts institution.
- ↑ McGill, Douglas C. (November 30, 1988). "Historical Society Reshaping Itself for Survival" . The New York Times . Archived from the original on Mar 9, 2014. Retrieved 2009-06-18.
Last January, after many years of using money from the society's endowment to pay for yearly operating deficits, the trustees determined that the endowment had dwindled to the point where the institution would be bankrupt in 18 months.
- ↑ McGill, Douglas C. (August 28, 1988). "Troubled Museums Try to Master the Fine Art of Survival" . The New York Times . Archived from the original on Mar 9, 2014. Retrieved 2009-06-24.
In recent weeks, the New York Historical Society, which for years had used money from its endowment and from a few wealthy trustees and patrons to compensate for growing annual deficits, finally reached ...