Related Research Articles
Luteinizing hormone is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. In females, an acute rise of LH known as an LH surge, triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum. In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell–stimulating hormone (ICSH), it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone. It acts synergistically with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).

Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo, which eventually forms the placenta after implantation. The presence of hCG is detected in some pregnancy tests. Some cancerous tumors produce this hormone; therefore, elevated levels measured when the patient is not pregnant may lead to a cancer diagnosis and, if high enough, paraneoplastic syndromes, however, it is not known whether this production is a contributing cause, or an effect of carcinogenesis. The pituitary analog of hCG, known as luteinizing hormone (LH), is produced in the pituitary gland of males and females of all ages.

Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) work together in the reproductive system.
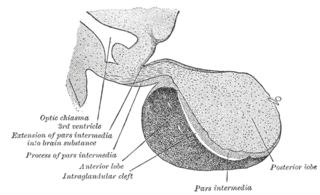
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released from GnRH neurons within the hypothalamus. The peptide belongs to gonadotropin-releasing hormone family. It constitutes the initial step in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis.
Gonadotropins are glycoprotein hormones secreted by gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary of vertebrates. This family includes the mammalian hormones follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), the placental/chorionic gonadotropins, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG), as well as at least two forms of fish gonadotropins. These hormones are central to the complex endocrine system that regulates normal growth, sexual development, and reproductive function. LH and FSH are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, while hCG and eCG are secreted by the placenta in pregnant humans and mares, respectively. The gonadotropins act on the gonads, controlling gamete and sex hormone production.

The hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis refers to the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonadal glands as if these individual endocrine glands were a single entity. Because these glands often act in concert, physiologists and endocrinologists find it convenient and descriptive to speak of them as a single system.

The luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor (LHCGR), also lutropin/choriogonadotropin receptor (LCGR) or luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR), is a transmembrane receptor found predominantly in the ovary and testis, but also many extragonadal organs such as the uterus and breasts. The receptor interacts with both luteinizing hormone (LH) and chorionic gonadotropins and represents a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Its activation is necessary for the hormonal functioning during reproduction.

Glycoprotein hormones, alpha polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGA gene.

Follitropin subunit beta also known as follicle-stimulating hormone beta subunit (FSH-B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSHB gene. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein.

Luteinizing hormone subunit beta also known as lutropin subunit beta or LHβ is a polypeptide that in association with an alpha subunit common to all gonadotropin hormones forms the reproductive signaling molecule luteinizing hormone. In humans it is encoded by the LHB gene.

Deslorelin, sold under the brand names Ovuplant, SucroMate, and Suprelorin among others, is an injectable gonadotropin releasing hormone superagonist which is used in veterinary medicine for various indications.
Gonadotropin preparations are drugs that mimic the physiological effects of gonadotropins, used therapeutically mainly as fertility medication for ovarian hyperstimulation and ovulation induction. For example, the so-called menotropins consist of LH and FSH extracted from human urine from menopausal women. There are also recombinant variants.

Choriogonadotropin subunit beta (CG-beta) also known as chorionic gonadotrophin chain beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CGB gene.

Leydig cell hypoplasia (LCH), also known as Leydig cell agenesis, is a rare autosomal recessive genetic and endocrine syndrome affecting an estimated 1 in 1,000,000 genetic males. It is characterized by an inability of the body to respond to luteinizing hormone (LH), a gonadotropin which is normally responsible for signaling Leydig cells of the testicles to produce testosterone and other androgen sex hormones. The condition manifests itself as pseudohermaphroditism, hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, reduced or absent puberty, and infertility.
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH), is due to problems with either the hypothalamus or pituitary gland affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Hypothalamic disorders result from a deficiency in the release of gonadotropic releasing hormone (GnRH), while pituitary gland disorders are due to a deficiency in the release of gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is the central regulator in reproductive function and sexual development via the HPG axis. GnRH is released by GnRH neurons, which are hypothalamic neuroendocrine cells, into the hypophyseal portal system acting on gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary. The release of gonadotropins, LH and FSH, act on the gonads for the development and maintenance of proper adult reproductive physiology. LH acts on Leydig cells in the male testes and theca cells in the female. FSH acts on Sertoli cells in the male and follicular cells in the female. Combined this causes the secretion of gonadal sex steroids and the initiation of folliculogenesis and spermatogenesis. The production of sex steroids forms a negative feedback loop acting on both the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus causing a pulsatile secretion of GnRH. GnRH neurons lack sex steroid receptors and mediators such as kisspeptin stimulate GnRH neurons for pulsatile secretion of GnRH.
The gonadotropin receptors are a group of receptors that bind a group of pituitary hormones called gonadotropins. They include the:

The fertile eunuch syndrome or Pasqualini syndrome is a cause of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism caused by a luteinizing hormone deficiency. It is characterized by hypogonadism with spermatogenesis. Pasqualini and Bur published the first case of eunuchoidism with preserved spermatogenesis in 1950 in la Revista de la Asociación Médica Argentina. The hypoandrogenism with spermatogenesis syndrome included:
Pulsatile secretion is a biochemical phenomenon observed in a wide variety of cell and tissue types, in which chemical products are secreted in a regular temporal pattern. The most common cellular products observed to be released in this manner are intercellular signaling molecules such as hormones or neurotransmitters. Examples of hormones that are secreted pulsatilely include insulin, thyrotropin, TRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and growth hormone (GH). In the nervous system, pulsatility is observed in oscillatory activity from central pattern generators. In the heart, pacemakers are able to work and secrete in a pulsatile manner. A pulsatile secretion pattern is critical to the function of many hormones in order to maintain the delicate homeostatic balance necessary for essential life processes, such as development and reproduction. Variations of the concentration in a certain frequency can be critical to hormone function, as evidenced by the case of GnRH agonists, which cause functional inhibition of the receptor for GnRH due to profound downregulation in response to constant (tonic) stimulation. Pulsatility may function to sensitize target tissues to the hormone of interest and upregulate receptors, leading to improved responses. This heightened response may have served to improve the animal's fitness in its environment and promote its evolutionary retention.
Gonadotropin surge-attenuating factor (GnSAF) is a nonsteroidal ovarian hormone produced by the granulosa cells of small antral ovarian follicles in females. GnSAF is involved in regulating the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary and the ovarian cycle. During the early to mid-follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, GnSAF acts on the anterior pituitary to attenuate LH release, limiting the secretion of LH to only basal levels. At the transition between follicular and luteal phase, GnSAF bioactivity declines sufficiently to permit LH secretion above basal levels, resulting in the mid-cycle LH surge that initiates ovulation. In normally ovulating women, the LH surge only occurs when the oocyte is mature and ready for extrusion. GnSAF bioactivity is responsible for the synchronised, biphasic nature of LH secretion.
References
- Gordon, Ian R. (2004). Reproductive technologies in farm animals. CABI. ISBN 978-0-85199-862-6.
- Adams, H. Richard (2001). Veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8138-1743-9.