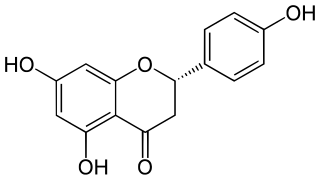
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs.

Diospyros melanoxylon, the Coromandel ebony or East Indian ebony, is a species of flowering tree in the family Ebenaceae native to India and Sri Lanka; it has a hard, dry bark. Its common name derives from Coromandel, the coast of southeastern India. Locally it is known as temburini or by its Hindi name tendu. In Odisha, Jharkhand, and Assam, it is known as kendu. The leaves can be wrapped around tobacco to create the Indian beedi, which has outsold conventional cigarettes in India.
Grapefruit seed extract (GSE), also known as citrus seed extract, is a liquid extract derived from the seeds, pulp, and white membranes of grapefruit. GSE is prepared by grinding the grapefruit seed and juiceless pulp, then mixing with glycerin. Commercially available GSEs sold to consumers are made from the seed, pulp, glycerin blended together. GSE is sold as a dietary supplement and is used in cosmetics. Laboratory tests have found that GSE has no antimicrobial or other anti-disease attributes.
Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds. While flavonoids have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, neoflavonoids have the 4-phenylchromen backbone with no hydroxyl group substitution at position 2.

Erythravine is a tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid found in the plant Erythrina mulungu and other species of the genus Erythrina.

Conessine is a steroid alkaloid found in a number of plant species from the family Apocynaceae, including Holarrhena floribunda, Holarrhena antidysenterica and Funtumia elastica. It acts as a histamine antagonist, selective for the H3 subtype (with an affinity of pKi = 8.27; Ki = ~5 nM). It was also found to have long CNS clearance times, high blood-brain barrier penetration and high affinity for the adrenergic receptors.

Galangin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid.
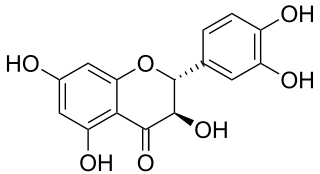
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols.

Prenylated flavonoids or prenylflavonoids are a sub-class of flavonoids. They are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. Some are known to have phytoestrogenic or antioxidant properties. They are given in the list of adaptogens in herbalism. Chemically they have a prenyl group attached to their flavonoid backbone. It is usually assumed that the addition of hydrophobic prenyl groups facilitate attachment to cell membranes. Prenylation may increase the potential activity of its original flavonoid.

Xanthohumol is a natural product found in the female inflorescences of Humulus lupulus, also known as hops. This compound is also found in beer and belongs to a class of compounds that contribute to the bitterness and flavor of hops. Xanthohumol is a prenylated chalconoid, biosynthesized by a type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and subsequent modifying enzymes.

Millettia pachycarpa is a perennial climbing shrub belonging to the genus Millettia. It is one of the most well known among ~150 species of Millettia, as it is widely used in traditional practices, such as for poisoning fish, agricultural pesticide, blood tonic, and treatments of cancer and infertility. The bark fiber is used for making strong ropes.

Barbigerone is one of a few pyranoisoflavones among several groups of isoflavones. It was first isolated from the seed of a leguminous plant Tephrosia barbigera; hence the name "barbigerone". Members of the genus Millettia are now known to be rich in barbigerone, including M. dielsiena, M. ferruginea, M. usaramensis, and M. pachycarpa. It has also been isolated from the medicinal plant Sarcolobus globosus. Barbigerone from S. globosus is validated to have significant antioxidant property. Barbigerone exhibits profound antiplasmodial activity against the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. It is also demonstrated that it has anti-cancer potential as it causes apoptosis of murine lung-cancer cells.

Sarcolobus globosus is a twining shrub native to tropical regions of Asia including India, China, Thailand, Malaysia, Myanmar-Burma, the Philippines and Indonesia.

Bobgunnia madagascariensis, also called the snake bean plant, is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae.
Biflavonoids are a type of flavonoids with the general formula scheme (C6-C3-C6)2.

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.
Tergallic acids are trimers of gallic acid, often found naturally in the form of glycosides. Tergallic acid O- or C-glucosides that can be found in acorns of several Quercus (oak) species. The dehydrated tergallic acid C-glucoside and tergallic acid O-glucoside can be characterised in the acorns of Quercus macrocarpa. Dehydrated tergallic-C-glucoside can be found in the cork from Quercus suber.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the fruit, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of pomegranates.

7-O-Methylluteone is a prenylated isoflavone. It can be found in the bark of Erythrina burttii.

Furoquinoline alkaloids are a group of alkaloids with simple structure. Distribution of this group of alkaloids is essentially limited to plant family Rutaceae. The simplest member of this group is dictamnine and most widespread member is skimmianine.
















