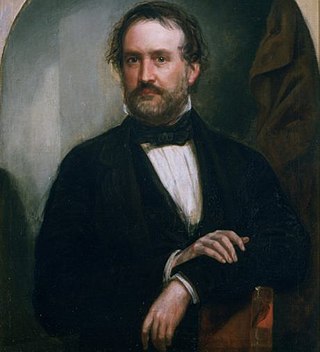Gateway Arch National Park is an American national park located in St. Louis, Missouri, near the starting point of the Lewis and Clark Expedition.
Dred Scott v. Sandford, 60 U.S. 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, and therefore they could not enjoy the rights and privileges the Constitution conferred upon American citizens. The decision is widely considered the worst in the Supreme Court's history, being widely denounced for its overt racism, judicial activism, poor legal reasoning, and crucial role in the start of the American Civil War four years later. Legal scholar Bernard Schwartz said that it "stands first in any list of the worst Supreme Court decisions". A future chief justice, Charles Evans Hughes, called it the Court's "greatest self-inflicted wound".

Dred Scott was an enslaved African American man who, along with his wife, Harriet, unsuccessfully sued for the freedom of themselves and their two daughters, Eliza and Lizzie, in the Dred Scott v. Sandford case of 1857, popularly known as the "Dred Scott decision". The Scotts claimed that they should be granted freedom because Dred had lived in Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory for four years, where slavery was illegal, and laws in those jurisdictions said that slave holders gave up their rights to slaves if they stayed for an extended period.

Hannibal is a city along the Mississippi River in Marion and Ralls counties in the U.S. state of Missouri. According to the 2020 U.S. Census, the population was 17,312, making it the largest city in Marion County. The bulk of the city is in Marion County, with a tiny sliver in the south extending into Ralls County.

Eugene Field Sr. was an American writer, best known for his children's poetry and humorous essays. He was known as the "poet of childhood".

Edward Bates was an American lawyer, politician and judge. He represented Missouri in the US House of Representatives and served as the U.S. Attorney General under President Abraham Lincoln. A member of the influential Bates family, he was the first US Cabinet appointee from a state west of the Mississippi River.

The Old St. Louis County Courthouse was built as a combination federal and state courthouse in St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Missouri's tallest habitable building from 1864 to 1894, it is now part of Gateway Arch National Park and operated by the National Park Service for historical exhibits and events.

The Scott Joplin House State Historic Site is located at 2658 Delmar Boulevard in St. Louis, Missouri. It preserves the Scott Joplin Residence, the home of composer Scott Joplin from 1901 to 1903. The house and its surroundings are maintained by the Missouri Department of Natural Resources as a state historic site. The house was added to the National Register of Historic Places and designated a U.S. National Historic Landmark in 1976.
This is a list of properties and historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places within the city limits of St. Louis, Missouri, north of Interstate 64 and west of Downtown St. Louis. For listings in Downtown St. Louis, see National Register of Historic Places listings in Downtown and Downtown West St. Louis. For those south of I-64 and west of downtown, see National Register of Historic Places listings in St. Louis south and west of downtown. For listings in St. Louis County and outside the city limits of St. Louis, see National Register of Historic Places listings in St. Louis County, Missouri.

The Gateway Mall in St. Louis, Missouri is an open green space running linearly, one block wide, from the Gateway Arch at Memorial Drive to Union Station at 20th Street. Located in the city's downtown, it runs between Market Street and Chestnut Street.

Barnett, Haynes & Barnett was a prominent architectural firm based in St. Louis, Missouri. Their credits include many familiar St. Louis landmarks, especially a number related to the local Catholic church. Their best-known building is probably the Cathedral Basilica of St. Louis. A number of the firm's works are listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

Harriet Robinson Scott was an African American woman who fought for her freedom alongside her husband, Dred Scott, for eleven years. Their legal battle culminated in the infamous United States Supreme Court decision Dred Scott v. Sandford in 1857. On April 6, 1846, attorney Francis B. Murdoch had initiated Harriet v. Irene Emerson in the Circuit Court of St. Louis County, making the Scotts the first and only married couple to file separate freedom suits in tandem.

The Griot Museum of Black History is a wax museum in St. Louis, Missouri, founded in 1997. Originally named The Black World History Wax Museum, the organization changed its name to The Griot Museum of Black History in 2009. In some west African countries, the griot, is a historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet and/or musician. The griot is a repository of oral tradition and is often seen as a societal leader who preserves and shares cultural traditions of a community. Likewise, the museum collects, preserves, and shares the stories, culture, and history of Black people with a focus on those with a regional connection to St. Louis.

Francis Butter Murdoch was an American attorney and newspaper publisher. As a lawyer, he practiced law in Pennsylvania, Michigan, Illinois and Missouri, and initiated freedom suits for Dred Scott and Harriet Robinson Scott in 1846. Between 1840 and 1847, Murdoch filed nearly one-third of all freedom suits in St. Louis, and secured freedom for many of his clients who had been enslaved, including Polly Berry and her daughter, Lucy A. Delaney. Before that, Murdoch was the city attorney in Alton, Illinois, where he unsuccessfully prosecuted rioters who killed Elijah Parish Lovejoy, an anti-slavery newspaper publisher, in 1837.

Diana Cephas was the plaintiff in a freedom suit filed in St. Louis, Missouri in 1840. She won her case after it went to trial in the Circuit Court of St. Louis County in 1843. Born into slavery in Maryland, she and her young son Josiah had been taken to the free state of Illinois in 1839, where she was hired out by her slaveholder over several months. She was then taken to Missouri, a slave state, but won her freedom with the help of freedom suit attorney Francis B. Murdoch, despite the efforts of lawyers Myron Leslie and Roswell M. Field to discredit her.

John R. Anderson, also known as J. Richard Anderson, was an American minister from St. Louis, Missouri, who fought against slavery and for education for African Americans. As a boy, he was an indentured servant, who attained his freedom at the age of 12. Anderson worked as a typesetter for the Missouri Republican and for Elijah Parish Lovejoy's anti-slavery newspaper, the Alton Observer. He founded the Antioch Baptist Church in Brooklyn, Illinois and then returned to St. Louis where he was a co-founder and the second pastor of the Central Baptist Church. He served the church until his death in 1863.
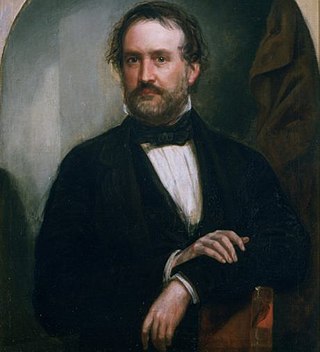
Roswell Martin Field, was an American lawyer and politician. He served on the Vermont House of Representatives. Field was one of the attorneys for the enslaved Dred and Harriet Scott and their daughters in 1853; as related to Dred Scott v. Sandford, where he argued for the rights of African-Americans to earn United States citizenship. He was from the prominent Field family of Vermont.