Circe chess is a chess variant in which captured pieces are reborn on their starting positions as soon as they are captured. The game was invented by French composer Pierre Monréal in 1967 and the rules of Circe chess were first detailed by Monréal and Jean-Pierre Boyer in an article in Problème, 1968.
Capablanca chess is a chess variant invented in the 1920s by World Chess Champion José Raúl Capablanca. It incorporates two new pieces and is played on a 10×8 board. Capablanca believed that chess would be played out in a few decades. This threat of "draw death" for chess was his main motivation for creating a more complex version of the game.
Grand Chess is a large-board chess variant invented by Dutch games designer Christian Freeling in 1984. It is played on a 10×10 board, with each side having two additional pawns and two new pieces: the marshal and the cardinal.

Vernon Rylands Parton was an English chess enthusiast and prolific chess variant inventor, his most renowned variants being Alice chess and Racing Kings. Many of Parton's variants were inspired by the fictional characters and stories in the works of Lewis Carroll. Parton's formal education background, like Lewis Carroll's, was in mathematics. Parton's interests were wide and he was a great believer in Esperanto.

Hexagonal chess is a group of chess variants played on boards composed of hexagon cells. The best known is Gliński's variant, played on a symmetric 91-cell hexagonal board.
Legan chess is a chess variant invented by L. Legan in 1913. It differs from standard chess by the starting position as well as by pawn movements.
Chess with different armies is a chess variant invented by Ralph Betza in 1979. Two sides use different sets of fairy pieces. There are several armies of equal strength to choose from, including the standard FIDE army. In all armies, kings and pawns are the same as in FIDE chess, but the four other pieces are different.

Minichess is a family of chess variants played with regular chess pieces and standard rules, but on a smaller board. The motivation for these variants is to make the game simpler and shorter than standard chess. The first chess-like game implemented on a computer was the 6×6 chess variant Los Alamos chess. The low memory capacity of early computers meant that a reduced board size and a smaller number of pieces were required for the game to be implementable on a computer.
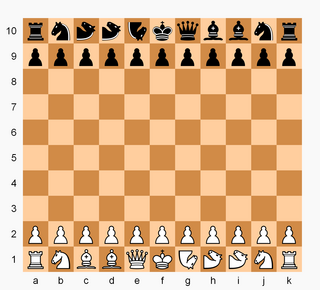
Wildebeest chess is a chess variant created by R. Wayne Schmittberger in 1987. The Wildebeest board is 11×10 squares. Besides the standard chess pieces, each side has two camels and one "wildebeest" - a piece which may move as either a camel or a knight.

Chad is a chess variant for two players created by Christian Freeling in 1979. It is played on an uncheckered 12×12 gameboard with one king and eight rooks per side, where rooks are able to promote to queens.

Dragonfly is a chess variant invented by Christian Freeling in 1983. There are no queens, and a captured bishop, knight, or rook becomes the property of the capturer, who may play it as their own on a turn to any open square. The board is 7×7 squares, or alternatively a 61-cell hexagon with two additional pawns per side.

Rhombic chess is a chess variant for two players created by Tony Paletta in 1980. The gameboard has an overall hexagonal shape and comprises 72 rhombi in three alternating colors. Each player commands a full set of standard chess pieces.

Wolf chess is a chess variant invented by Dr. Arno von Wilpert in 1943. It is played on an 8×10 chessboard and employs several fairy pieces including wolf and fox – compound pieces popular in chess variants and known by different names.

Triangular chess is a chess variant for two players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a hexagon-shaped gameboard comprising 96 triangular cells. Each player commands a full set of chess pieces in addition to three extra pawns and a unicorn.

Tri-chess is the name of a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board comprising 150 triangular cells. The standard chess pieces are present, minus the queens, and plus the chancellor and cardinal compound fairy pieces per side.

Parallel worlds chess is a three-dimensional chess variant invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger in the 1980s. The gamespace comprises three 8×8 chessboards at different levels. Each side commands two full chess armies on levels 1 and 3. Level 2 begins empty and obeys its own move rules.

Falcon–hunter chess is a chess variant invented by Karl Schultz in 1943, employing the two fairy chess pieces falcon and hunter. The game takes several forms, including variations hunter chess and decimal falcon–hunter chess added in the 1950s.

Hostage chess is a chess variant invented by John A. Leslie in 1997. Captured pieces are not eliminated from the game but can reenter active play through drops, similar to shogi. Unlike shogi, the piece a player may drop is one of their own pieces previously captured by the opponent. In exchange, the player returns a previously captured enemy piece which the opponent may drop on a future turn. This is the characteristic feature of the game.
Grant Acedrex is a medieval chess variant dating back to the time of King Alfonso X of Castile. It appears in the Libro de los Juegos of 1283.













