Related Research Articles

An armoured fighting vehicle or armored fighting vehicle (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured cars, assault guns, self-propelled guns, infantry fighting vehicles (IFV), and armoured personnel carriers (APC).

Self-propelled artillery is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled mortar, and rocket artillery. They are high mobility vehicles, usually based on continuous tracks carrying either a large field gun, howitzer, mortar, or some form of rocket/missile launcher. They are usually used for long-range indirect bombardment support on the battlefield.

The M198 is a medium-sized, towed 155 mm artillery piece, developed for service with the United States Army and Marine Corps. It was commissioned to be a replacement for the World War II-era M114 155 mm howitzer. It was designed and prototyped at the Rock Island Arsenal in 1969 with firing tests beginning in 1970 and went into full production there in 1978. It entered service in 1979 and since then 1,600 units have been produced.

The M109 is an American 155 mm turreted self-propelled howitzer, first introduced in the early 1960s to replace the M44. It has been upgraded a number of times, most recently to the M109A7. The M109 family is the most common Western indirect-fire support weapon of maneuver brigades of armored and mechanized infantry divisions.

The AS-90, known officially as Gun Equipment 155 mm L131, is an armoured self-propelled artillery used by the British Army.

Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Allies deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first developed anti-tank weapon was a scaled-up bolt-action rifle, the Mauser 1918 T-Gewehr, that fired a 13.2 mm cartridge with a solid bullet that could penetrate the thin armor of tanks of the time and destroy the engine or ricochet inside, killing occupants. Because tanks represent an enemy's strong force projection on land, military strategists have incorporated anti-tank warfare into the doctrine of nearly every combat service since. The most predominant anti-tank weapons at the start of World War II in 1939 included the tank-mounted gun, anti-tank guns and anti-tank grenades used by the infantry, and ground-attack aircraft.

The G6, sometimes denoted as the G6 Rhino, is a South African mine-protected self-propelled howitzer. It was developed as a turreted, self-propelled variant of the G5 howitzer series, mating the gun to a six-wheeled armoured chassis. Design work on the G6 began in the late 1970s to replace the obsolescent Sexton being retired from service with the artillery regiments of the South African Army. Serial production commenced between 1988 and 1999.

A dual-purpose improved conventional munition (DPICM) is an artillery or surface-to-surface missile warhead designed to burst into submunitions at an optimum altitude and distance from the desired target for dense area coverage. The submunitions use both shaped charges for the anti-armor role, and fragmentation for the antipersonnel role, hence the nomenclature "dual-purpose". Some submunitions may be designed for delayed reaction or mobility denial (mines). The air-to-surface variety of this kind of munition is better known as a cluster bomb. They are banned by more than 100 countries under the Convention on Cluster Munitions.

The M136 Volcano Vehicle-Launched Scatterable Mine System is an automated mine delivery system developed by the United States Army in the 1980s. The system uses prepackaged mine canisters which contain multiple anti-personnel (AP) and/or anti-tank (AT) mines which are dispersed over a wide area when ejected from the canister. The system, commonly referred to as Volcano, is also used by other armies around the world.
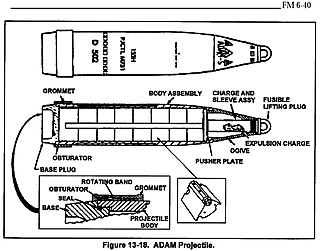
Area denial artillery munition (ADAM) is a family of United States land mines and 155 mm artillery projectiles.

The DANA (Dělo automobilní nabíjené automaticky is a wheeled self-propelled artillery piece. It is also known as the Samohybná Kanónová Húfnica vzor 77. It was designed by Konštrukta Trenčín and built by ZTS Dubnica nad Váhom in the former Czechoslovakia. Introduced in the 1970s, it was the first wheeled 152 mm self-propelled artillery gun to enter service. It is based on a modified eight-wheel drive Tatra 815 chassis with excellent cross-country mobility. Currently it is in service with the Czech Republic, Libya, Poland, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Slovakia, and Ukraine.
The MI AC Disp F1 Minotaur mine is a French scatterable anti-tank mine. The mines can also be scattered from 155 millimetre artillery shells, which can hold six of the mines. The mine is cylindrical with two Misznay Schardin effect warheads, one on each side of the mine, with a 600 gram charge. The warhead is claimed to be able to penetrate 90 mm of armour at a distance of 0.5 m. It uses a magnetic influence fuze combined with an anti-handling device which arms itself 64 seconds after launch. At the end of its active life, which is set to between one and 96 hours the mine self-destructs. The land based scattering system can launch mines to a range of up to 300 m.

The Archer Artillery System, or Archer – FH77BW L52, or Artillerisystem 08, is a Swedish self-propelled howitzer system. The main piece of the system is a fully automated 155 mm L52 (52-calibre-long) gun-howitzer and a M151 Protector remote-controlled weapon station mounted on a modified 6×6 chassis of the Volvo A30D all-terrain articulated hauler. The crew and engine compartment is armoured and the cab is fitted with bullet and fragmentation-resistant windows. The system also includes an ammunition resupply vehicle, a support vehicle, BONUS submunitions and M982 Excalibur guided projectiles.

The PTM-3 is a Soviet scatterable self-liquidating shaped charge anti-tank mine. The mine's case is made up of a stamped steel body with notches in its side. The notches allow the mine to produce a shaped charge effect on five sides - 4 on the sides, and one on the end face. The mine has two arming stages - pyrotechnic and mechanical, and has a magnetic influence battery-powered fuze BT-06. The mine can be delivered using the BM-30 Smerch (9M55K4), BM-27 Uragan (9M59), BM-21 Grad (9M22K) MLRS, helicopter-mounted minelaying system VSM-1, remote mining machine UMZ or portable mining kit PKM. It cannot be placed manually, and must only be placed using remote minelaying systems listed above.

The Nora B-52 is a 155 mm self-propelled howitzer developed by Military Technical Institute and manufactured by Yugoimport SDPR in Velika Plana, Serbia.

The 2K25 Krasnopol is a Soviet 152/155 mm cannon-launched, fin-stabilized, base bleed-assisted, semi-automatic laser-guided artillery weapon system. It automatically 'homes' on a point illuminated by a laser designator, typically operated by a drone or ground-based artillery observer. Krasnopol projectiles are fired mainly from Soviet self-propelled howitzers such as the 2S3 Akatsiya and 2S19 Msta-S and are intended to engage small ground targets such as tanks, other direct fire weapons, strong-points, or other significant point targets visible to the observer. It can be used against both stationary and moving targets.

The PLZ-05 or the Type 05 is a 155 mm self-propelled howitzer developed by the People's Liberation Army of China to replace the Type 59-1 130 mm towed gun and Type 83 152 mm self-propelled gun. The PLZ-05 was officially unveiled at the Military Museum of the Chinese People's Revolution to mark the 80th anniversary of the PLA in July 2007, and first entered service with the PLA in 2008.
The SMArt 155 is a German 155 mm artillery round designed for a long-range, indirect fire top-attack role against armoured vehicles. The projectile was developed in 1989 by Diehl BGT Defence in Überlingen, Germany, with Rheinmetall and started full-rate production for the German Army in 1998. It consists of a 47-kilogram (104 lb) heavy artillery projectile containing two autonomous, sensor-fused, "fire-and-forget" submunitions. Due to the submunitions, it has been considered by some to be a cluster munition. As of 2008, representatives of the German defense ministry have referred to it as not being classified as submunition weapons, which were prohibited by the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions.

The Type 08 is a family of eight-wheeled amphibious, modular armored vehicle developed by Norinco for infantry fire support, battlefield logistics, and quick reaction operations. Developed in the early 2000s, the modern Chinese vehicle family were produced for more than 6000 hulls and widely deployed by the People's Liberation Army Ground Force and People's Liberation Army Marine Corps.

The Remote Anti-Armor Mine System (RAAMS) are two types of 155mm howitzer projectiles containing nine anti-tank mines each: the M718 or M718A1 (RAAM-L) with a self-destruct time over 24 hours and the M741 or M741A1 (RAAM-S) with a self-destruct time under 24 hours. Both projectiles are used with the M577 or M577A1 Mechanical Time and Superquick (MTSQ) fuze, which triggers the ejection mechanism of the mines above enemy territory after a preset time.
References
- ↑ Federation of American Scientists (2000-02-19). "Family of Scatterable Mines - FASCAM" . Retrieved 2014-08-13.